Polestar Abandoned by Volvo Falls Out of Orbit
![]() 07/10 2024
07/10 2024
![]() 610
610
Polestar, abandoned by Volvo, once again faces the risk of being abandoned by capital.
When it received the notification from Nasdaq, Polestar had already sunk to the same level as Faraday Future, Jia Yueting's company, in the capital market.
With the backing of Volvo Cars and Geely Holding Group, Polestar transformed itself from a wealthy second-generation brand into one of the worst-performing new energy vehicle brands on Nasdaq in just two years.
On May 21, Polestar announced the delay in releasing its 2023 annual report and fourth-quarter financial results, causing share price turbulence and marking the first time its share price fell below $1. One month later, on June 26, after receiving a warning from Nasdaq and still failing to release its financial results, Polestar's share price plunged to an all-time low of $0.65.
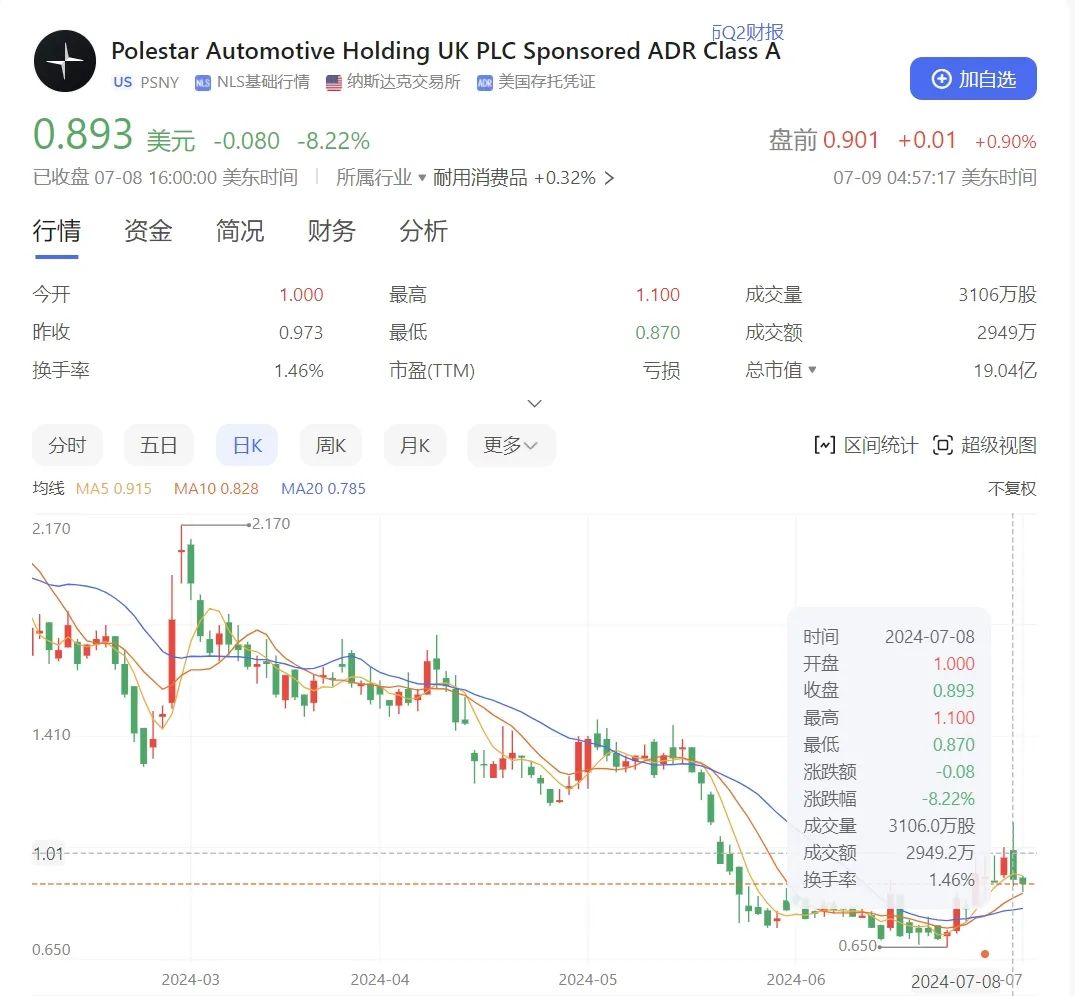
When Polestar went public on June 24, 2022, its share price was $13, with a market value exceeding $20 billion. However, in just two years, its share price has plummeted to a fraction of its former value, and its market value has shrunk to less than $2 billion.
Accompanying the June 28 financial report, Polestar was hit with a series of negative news, including massive layoffs and a decline in sales targets, leaving the company seemingly mired in difficulties.
Polestar's Lavish Spending
In fact, Polestar's decline began to emerge last year amid huge losses. The 2023 financial report revealed that Polestar's revenue was $2.377 billion, a decrease of $67.3 million year-on-year, with operating losses widening by 13% to $542 million.
Meanwhile, Polestar's operating conditions continued to deteriorate, with the first-quarter financial report released on July 2, 2024, showing an additional loss of $274 million, bringing Polestar's cumulative losses close to $2 billion.
Coupled with the decline in market value, Polestar has squandered $20 billion in just two years, losing money at a pace far exceeding the industry average, achieving a certain level of leadership in this regard.
In such a state of operations, Volvo Cars, one of Polestar's shareholders, took the lead in withdrawing, announcing in February this year that it would no longer provide funding to Polestar and would transfer 62.7% of its shares to Geely Group, retaining only 18%.

Apart from its astonishing speed of losing money, Polestar is equally impressive in its spending.
According to the financial report, Polestar's selling, general, and administrative expenses increased by 21% in 2023, from $919 million to $1.113 billion. Looking back at Polestar's promotional activities, each one was a lavish affair.
According to third-party statistics, Polestar spent close to $100 million on advertising in the US market in 2023, with a promotional budget of up to $20 million for the Polestar 3 alone in the second quarter. Of course, these are just routine operations for Polestar.
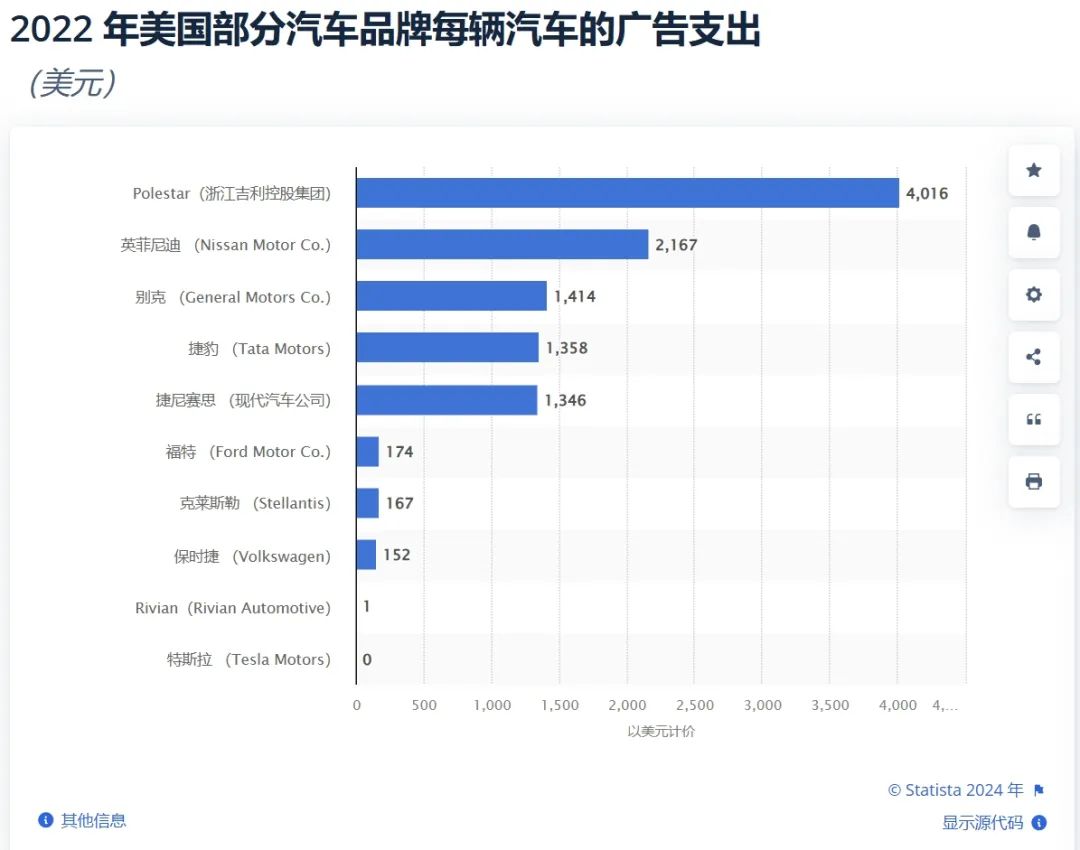
As early as 2022, Polestar sponsored the Super Bowl (equivalent to China's Spring Festival Gala) in the US, spending $6.5 million on advertising, making it the automaker with the highest advertising spending in the US. According to statistics, Polestar's advertising expenditure per vehicle in 2022 averaged $4,016, nearly twice that of the second-place brand and dozens of times that of Ford and Porsche.
In the domestic market, Polestar's promotional approach is similar, with advertisements during prime time on CCTV. On the eve of the 2023 Guangzhou Auto Show, the "Polestar Night" event illuminated the Canton Tower, even though even local automaker GAC Group chose to advertise the night before.

Perhaps born with a golden spoon in its mouth, Polestar has never known the value of money. As Volvo's high-performance sub-brand, Polestar officially announced its independence in 2017.
At the end of 2023, Polestar secured $450 million in financing from Volvo Cars and Geely Sweden, and earlier this year, it obtained an additional $950 million in external financing.
In China, Polestar does not just focus on automobiles but has also ventured into the mobile phone business, leveraging Geely's relationship with Star Technology and Meizu. It attempts to make vehicle-phone integration a brand hallmark. However, in the current market, Huawei-empowered HarmonyOS and Xiaomi's human-vehicle-home ecosystem both have hundreds of millions of mobile phone users. Even NIO, with 200,000 car owners, dared to make phones to expand its ecosystem.
In contrast, Polestar has delivered less than 150,000 vehicles globally, and its sales in China are hardly sufficient to support the balance of its mobile phone business. It can only be said that with a strong backing, Polestar's growth path involves continuous spending.
Lack of Positioning, Uncertain Future
Unlike the North Star, which remains fixed in the northern hemisphere night sky, Polestar's positioning in the automotive industry has always been vague.
On the surface, the main reason for Polestar's losses is insufficient sales. While any brand operating purely electric vehicles globally, apart from Tesla, is not doing well financially, with losses being the norm, Polestar still managed to lose money at an industry-record pace.
According to statistics, Polestar's sales in recent years have been 10,200 in 2020, 29,000 in 2021, 51,500 in 2022, and 54,600 in 2023. It can be seen that Polestar's sales entered a bottleneck in 2023, with a significant slowdown in growth, despite the fact that the global new energy vehicle market grew by 35.4%.

Polestar's growth rate has lagged behind the average, primarily due to a mismatch between its development focus and the global new energy vehicle market.
While the global new energy vehicle market grew by 35.4%, there were significant regional differences. For example, China's new energy vehicle market grew by 37.9% and accounted for 64.8% of global sales, making it the largest market. In contrast, the US market grew by only 18.3%, while Europe, despite a significant growth rate of 48%, the highest in history, had a limited market of only 1.468 million vehicles, accounting for about 10% of the global market.

In Polestar's sales structure, overseas markets dominate. According to Polestar's official data, its first-quarter delivery figure was 7,200 vehicles, of which only 635 were sold in the Chinese market.
The absence from the largest new energy vehicle market in the world has doomed Polestar's sales growth to slow down in 2023.
Apart from the deviation in market positioning, Polestar also has issues with its product positioning. With vehicle pricing ranging from $300,000 to $1.5 million, Polestar is one of the few automakers to offer such a wide price range with only four models.
Moreover, since Polestar's establishment in 2017, its senior management has been in constant flux. Shen Feng, Polestar's Global CTO and CEO of Polestar China, left for NIO after just one year in the role. Since then, Polestar's senior leadership, especially in China, has changed almost annually.

Especially after Polestar's merger with Star Technology and Meizu, Shen Ziyu, who has deep connections within Geely, took over the management of Polestar's development in China. However, within a year, Shen Ziyu stepped down from management, and Su Jing, a co-founder, took over, causing Polestar's China strategy to stagnate.
The most recent departure was that of Chen Siying, Polestar Technology's COO, who left after less than six months in the role. Qin Peiji, appointed by Geely, will take over, and it is rumored that his first move will be to cut costs.
Recently, media reports claimed that Polestar Technology would lay off 30% of its staff, and the Chengdu factory would be shut down, with most operations transferring to Nanjing. On July 9, Polestar officially refuted these rumors, stating that the layoffs were untrue and that the headquarters relocation was part of the plan.
Polestar's turmoil is normal in the automotive industry, where intense competition, especially in the new energy vehicle sector, is driving down gross margins. Larger brands are further enhancing their product competitiveness by leveraging sales-driven cost reductions.
Brands without economies of scale face significant challenges, particularly those like Polestar, whose sales are already in danger. One misstep could be disastrous.

However, Polestar is not without a chance to turn things around. As new energy trade barriers rise, developing overseas markets becomes increasingly difficult, especially in the US market. Polestar is the only Chinese automaker selling in the US and has a factory there. Leveraging the crisis to expand in overseas markets is not impossible.
After all, Polestar still has the support of Geely Group and Volvo Cars. Following the financial report's release, Polestar's share price has rebounded above $1, avoiding the risk of delisting and giving the company time to plan for its future development.
Internally, Polestar expects to achieve breakeven by 2025. However, from the current perspective, making up for the billions of dollars in annual losses remains a significant challenge.
Note: Some images are sourced from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.