Robots Embark on a 'University' Journey for Enhanced Learning
![]() 12/01 2025
12/01 2025
![]() 386
386

Despite years of advancements in robotics, achieving true 'intelligence' remains a significant challenge. Issues such as limited generalization capabilities, restricted application scenarios, and sluggish commercialization continue to impede breakthroughs across the industry. Even the latest generation of robots often encounters basic challenges, including 'tripping,' 'delayed reactions,' and 'incorrect judgments.'
A thorough analysis reveals that the bottleneck in robot development has transitioned from hardware to software, with the greatest challenge lying in breakthroughs in AI models. If we liken robots to humans, hardware represents fully developed limbs, while AI embodies the true 'brain,' and data serves as the learning material. The Data Platform constructed by Tencent Cloud Storage functions as a comprehensive 'university education system,' supporting the holistic growth of robots.
PasiNi Perception Technology, a leading domestic company specializing in high-precision tactile sensing and embodied AI core technologies, has its CTO, Zhang Hengdi, stating in a recent interview: Collecting comprehensive full-modal data of human interactions with the physical world—including visual, joint angles, motion trajectories, speech, and the highly scarce tactile modality—is an enormous and intricate endeavor. After evaluating multiple options, PasiNi has opted to entrust its essential full-modal data for robot training to 'Tencent Cloud University.'
Written by Hanyuan | Edited by Haoran
This article is an original piece by Shangyin Society. For reprints, please contact the background team.
Why Do Robots Appear 'Clumsy?'
During a robot marathon held in April this year, a humanoid robot moved slowly forward, with dozens of engineers trailing behind, adjusting algorithms, replacing batteries, and mitigating interference. Despite these efforts, most robots frequently stumbled, displaying awkward behaviors.
This phenomenon can be attributed to 'Moravec's Paradox,' proposed by Hans Moravec and others in the 1980s. The paradox highlights that tasks difficult for humans, such as complex calculations, are relatively easy for machines, whereas actions humans perform effortlessly, such as perception and movement, are exceptionally challenging for machines.
The reason is that the former involves straightforward subtraction for machines. Technologies like large language models (LLMs) compress millions of years of human knowledge into machines. When you chat with AI, it's akin to conversing with the history of human civilization. When you compete with AI, it's like facing a higher-dimensional intellect.
The latter, however, involves a more complex addition process for robots. For instance, executing a simple instruction like 'pick up a cup' requires a robot to navigate through six steps and thirteen technical domains.

Robot's Breakdown of the 'Pick Up a Cup' Action
PasiNi CTO Zhang Hengdi points out that every human action encompasses multidimensional information, including tactile, visual, joint angles, motion trajectories, and speech. Tasks that humans perform effortlessly are extremely complex for robots.
Zhang further emphasizes, 'Every interaction between a robot and the physical world generates massive data. For example, making pancakes can produce 150TB of data daily, reaching petabyte-scale annually. Traditional local storage cannot handle this.' The data collection, upload, storage, and training processes supported by Tencent Cloud Storage's Data Platform have become crucial for efficiently advancing industrial transformation with massive full-modal embodied data.
Robots Also Need to 'Attend University'
To address the challenges in robot learning, leading industry companies have begun sending robots to 'university' for systematic training. Unlike humans, robots learn through a 'train-data-implant-data' model, with Tencent Cloud Storage's Data Platform serving as the core infrastructure of this 'university.'
Let's first explore why robots struggled to learn in the past:
● Data scarcity. Ken Goldberg, a robotics expert at UC Berkeley, has noted that humanoid robots face a stark contrast to AI chatbots in skill acquisition. The core issue lies in a severe 'data scarcity,' with a gap of 100,000 years between the two.
● Insufficient generalization. Robots rely on data-driven pattern matching rather than understanding and predicting physical laws. This prevents them from handling unknown scenarios, performing common-sense reasoning, or reflecting and adjusting based on understanding after failures.
● Model learning spurious correlations between task-irrelevant features (such as perspective or background) and actions, rather than understanding the true relationship between language instructions and goals.
For example, if you introduce a cat to a child, they will recognize other breeds as 'cats' later. However, if you train a robot, you must input numerous cat photos, types, and features, training it thousands of times before it understands what qualifies as a cat.
During this process, if a cat has spots, the robot might associate 'spots' with 'cats' and mistakenly identify spotted clothing as a cat.
In this context, the volume, quality, and processing methods of data significantly impact robot reactions.
Based on globally leading tactile sensing technology, PasiNi has developed its own 'human-factor' embodied AI data collection system. Using 'multi-dimensional tactile data collection gloves (PMEC)' and 'spatial vision matrices,' it efficiently collects high-quality, full-dimensional data of robot interactions with the physical world, accelerating intelligent generalization across the industry. PasiNi chose Tencent Cloud Storage's Data Platform because, as Zhang Hengdi explains:
First, massive elastic storage. Tencent Cloud Storage provides vast, secure, stable, and low-cost storage, meeting the embodied AI industry's demand for massive unified storage. Automatic tiering of hot and cold data ensures rapid response for hot data and cost-effective storage of cold data in COS object storage.
Second, accelerated model training. A data processing pipeline with TB/s throughput and sub-millisecond access latency eliminates data supply bottlenecks for GPU and other computing resources, ensuring high saturation of computational power and improving efficiency in large-scale model training and inference.
Third, intelligent data governance. It offers global metadata indexing and semantic retrieval capabilities, enabling automatic correlation analysis and lineage tracing of heterogeneous data such as voice, vision, and sensor streams. This enhances file retrieval efficiency, provides highly consistent training samples for simulation decision-making, and unlocks the collaborative value of multi-modal data.
'Tencent Cloud's strengths lie in its ability to quickly load data into the distribution system and retrieve it. It has a complete toolchain, eliminating the need for external tools when accessing models. It provides instant feedback, identifying areas for model revision and helping us iterate rapidly. It offers an excellent simulation environment, allowing extensive cloud-based verification before deployment. Its security capabilities effectively prevent external attacks. The Data Platform excels in computational resource scheduling, enabling the execution of numerous simulation tasks. With just a few simple commands, we can conveniently access various services,' Zhang Hengdi said.
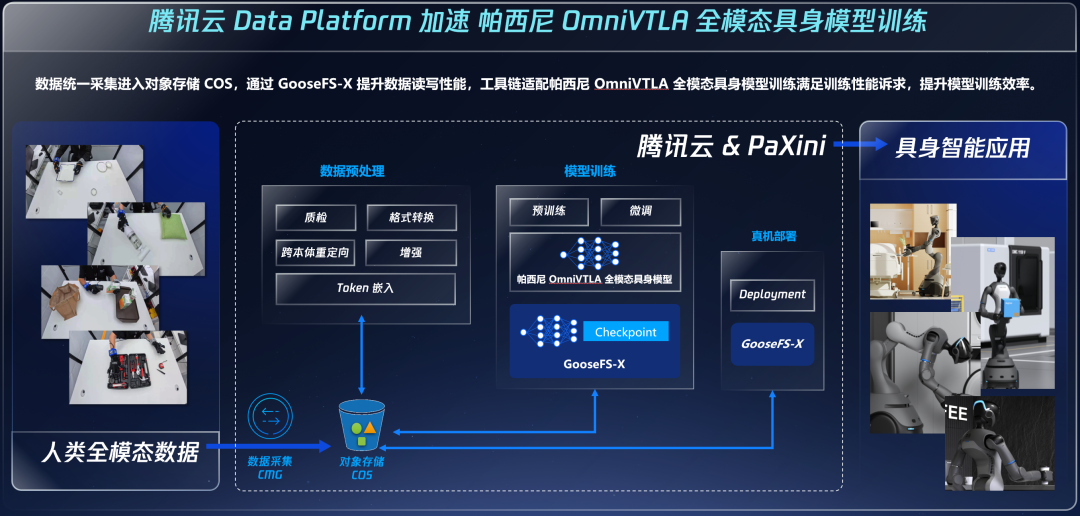
At Tencent Cloud 'University,' data is refined into usable 'textbooks' and uniformly output to robots, enabling them to transcend physical limitations and achieve cloud-based evolution—just as humans transcend physical constraints to upgrade cognition.
From 'Hardware-Driven' to 'Intelligence-Driven': Robots Enter the Era of 'Smart Competition'
In the history of robot evolution, the 'hardware first' approach was once the industry consensus. However, times have changed. Cultivating a 'robot brain' with cognitive and decision-making abilities is no longer just a technological trend but an inevitable choice for industrial development.
From a historical perspective, robots lacking software support are doomed to obsolescence. Take Honda's ASIMO, which could run, kick a ball, and pour coffee. After 22 years, it quietly exited the stage. Its downfall stemmed from relying on 30,000 lines of manually written control code for each action, unable to adapt to the AI-driven new era. In contrast, modern robots master backflips, Tai Chi, and other complex moves in just hours through AI training, showcasing a stark contrast in efficiency and flexibility.
PasiNi CEO Xu Jincheng points out that China leads globally in robot hardware manufacturing. However, 'an adult's body cannot be paired with a child's mind.' Merely stacking hardware performance cannot meet modern industry's demands for flexible production, personalized services, and rapid adaptation.
In this context, 'smart competition' capabilities have become the core competitiveness of robots.
PasiNi CTO Zhang Hengdi emphasizes, 'Our short-term goal is to continuously iterate PasiNi's tactile product matrix, including sensors, dexterous hands, humanoid robots, and data collection systems. Our long-term goal is to drive deep integration between AI and the physical world through full-chain embodied AI core technologies incorporating critical tactile modalities, accelerating the evolution of embodied AI's cognition and operational capabilities in the physical world.' In this journey, Tencent Cloud's storage and computational support serve as critical infrastructure. Its highly available and concurrent data processing capabilities are expected to lower the barriers to embodied AI research and accelerate the arrival of the 'intelligence emergence' moment.
Currently, robot manufacturers are actively building 'data flywheel' loops—continuously optimizing models through data feedback from real-world scenarios to enhance robot intelligence. PasiNi's TORA-ONE robot has been applied in diverse fields, including healthcare, logistics, industrial manufacturing, and even subway security checks. The data characteristics and task requirements across these domains further highlight the importance of cloud-based training and iteration.

Today, within the 'university' environment built by Tencent Cloud Storage, robots are achieving a leap from individual intelligence to collective intelligence. When robots graduate from this 'university,' it will mark the beginning of their true integration into human life and the dawn of a new intelligent era.








