NVIDIA Open-Sources Alpamayo-R1: Enabling Vehicles to Truly 'Understand' Driving
![]() 12/03 2025
12/03 2025
![]() 460
460
At NeurIPS 2025 in San Diego, California, NVIDIA announced Alpamayo-R1—the world's first open-source reasoning-based Vision-Language-Action Model (VLAM) designed specifically for autonomous driving research. This release marks a pivotal shift from 'perception-driven' to 'semantic understanding and common-sense reasoning' in autonomous systems.

Unlike traditional end-to-end models that directly map images to control signals, Alpamayo-R1's core strength lies in enabling vehicles not just to 'see' but to 'understand why.' In complex scenarios such as disorganized construction cones, dense oncoming traffic during unprotected left turns, or washed-out road shoulders in nighttime storms, the system generates safe decisions through multi-step reasoning, much like human drivers.
"Our goal is not to build a faster perception module but to equip autonomous systems with common-sense judgment," said NVIDIA's head of autonomous driving research.
Chain-of-Thought Reasoning via Cosmos-Reason Architecture
Built upon NVIDIA's Cosmos-Reason model family, released earlier this year, Alpamayo-R1 introduces a 'Chain-of-Thought' mechanism that decomposes complex driving tasks into interpretable reasoning steps.
For example, at a busy intersection, the system sequentially:
1. Identifies all dynamic participants (pedestrians, cyclists, vehicles);
2. Infers their potential intentions (crossing? Decelerating?);
3. Predicts future states by combining traffic rules with historical trajectories;
4. Evaluates safety margins for feasible vehicle actions;
5. Outputs optimal control commands.
This structure significantly enhances robustness at ODD (Operational Design Domain) boundaries, particularly addressing long-tail challenges in L4 autonomy.
Full-Stack Open Source: Lowering L4 Development Barriers
NVIDIA open-sourced not only Alpamayo-R1's model weights but also released Cosmos Cookbook—a comprehensive AI development toolkit for autonomous driving, covering:
High-quality data construction standards: including multi-sensor time synchronization, calibration workflows, and annotation protocols;
Synthetic data generation pipelines: leveraging DRIVE Sim and Omniverse to simulate long-tail scenarios like extreme weather and rare accidents;
Lightweight deployment solutions: supporting LoRA fine-tuning, INT8 quantization, and compatibility with Orin and other automotive chips;
Safety evaluation benchmarks: defining key metrics such as behavioral rationality, instruction adherence, and collision avoidance rates.
The model is now available on GitHub and Hugging Face, enabling academic and industrial communities to freely use, fine-tune, and deploy it.
"We aim to accelerate the ecosystem's shift toward 'understanding-based autonomous driving,'" NVIDIA stated.
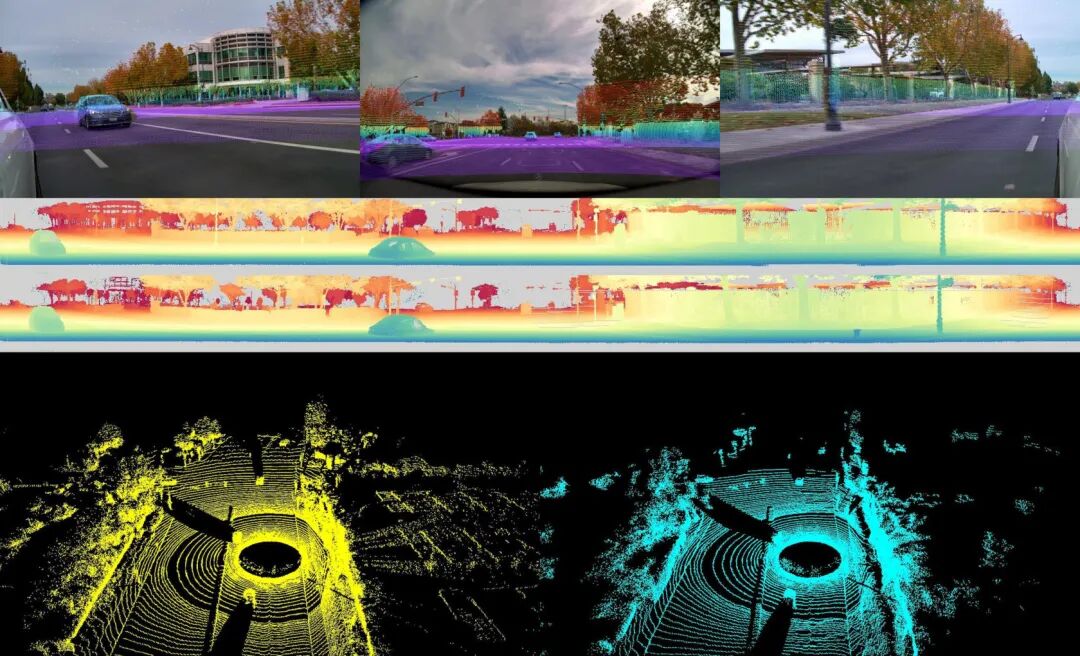
Multi-Vehicle Collaboration Paradigm: V2V-GoT Enables 'Swarm Intelligence'
Beyond single-vehicle intelligence, NVIDIA partnered with Carnegie Mellon University to demonstrate V2V-GoT (Vehicle-to-Vehicle Graph-of-Thoughts)—the world's first framework applying Graph-of-Thoughts reasoning to multi-vehicle collaborative autonomy.
In typical blind-spot scenarios with obstructed views from large vehicles, surrounding vehicles share perception results and intentions via V2X communication. V2V-GoT uses a multimodal large language model as a 'coordination hub' to fuse information from all nodes and generate collaborative safety strategies for each vehicle.
Experiments show the system reduces intersection collision rates from 2.85% (traditional methods) to 1.83% while accurately predicting surrounding vehicles' trajectories within 3 seconds. Critically, information exchange occurs in natural language or structured semantics (e.g., "Pedestrian crossing on my right"), drastically reducing communication bandwidth requirements.
Meanwhile, China's MogoMind large model by Mushroom Autonomous represents a more systematic 'Chinese approach'—building an AI network where intelligent agents interact with the physical world in real time. By incorporating real-time dynamic data from the physical world into training, it breaks free from traditional large models' reliance on static internet data, achieving a closed-loop physical intelligence system spanning global perception, deep cognition, and real-time decision-making. Currently deployed in multiple cities, this solution significantly enhances vehicles' adaptability and generalization in urban environments, combining MogoMind's capabilities to grant vehicles deep cognition and autonomous decision-making, ensuring high safety and reliability in real-world conditions.
This is no longer an isolated intelligent agent but a mobile intelligent network with collective reasoning capabilities.
Cosmos World Model Drives Synthetic Training
Alpamayo-R1's high performance stems from NVIDIA's robust synthetic data generation capabilities. Its Cosmos World Foundation Model, post-trained on 20,000 hours of real-world driving footage, generates high-fidelity challenging scenarios like nighttime driving, heavy rain, dense fog, and intense glare.
These synthetic datasets address real-world long-tail distribution scarcity while supporting closed-loop adversarial training—simulating scenarios like 'sudden child dash' or ' An electric vehicle that slips out of control ' (runaway electric scooters) to stress-test models' emergency response capabilities.
A Critical Step Toward Physical AI
Alpamayo-R1's release marks a key milestone in NVIDIA's 'Physical AI' strategy. It redefines autonomous driving not as a perception-planning-control pipeline but as an embodied intelligent agent capable of understanding physical laws, social norms, and causal logic.
While mass production still faces engineering challenges (e.g., real-time inference latency, safety validation), the open-source approach will undoubtedly accelerate global R&D. As one university lab leader noted, "Now any team can stand on NVIDIA's shoulders to explore next-gen autonomous driving's 'thinking' paradigm."









