Can AI direct by itself? KlingAvatar 2.0 'Joint Reasoning' Black Technology: Enabling Digital Humans Not Just to Act, but Also to Understand Scripts! New SOTA!
![]() 12/29 2025
12/29 2025
![]() 406
406
Interpretation: The AI-Generated Future 

Figure 1. KlingAvatar 2.0 generates vivid, identity-preserving digital humans with precise camera control, rich emotional expression, high-quality movements, and accurate facial-lip and audio synchronization. It achieves coherent alignment between audio, image, and text instructions, extends to various open-domain styles, and supports multi-character synthesis and identity-based audio control. These capabilities stem from our multimodal instruction-following, omnidirectional spatio-temporal cascading framework, enabling high-resolution, long-duration video generation.
Key Highlights
Spatio-Temporal Cascading Framework: Proposes a progressive generation architecture supporting long-duration (up to 5 minutes) and high-resolution video generation, effectively mitigating temporal drifting in long videos.
Collaborative Reasoning Director: Introduces a director module composed of three modality-specific LLM experts, reasoning through multi-round dialogues to resolve multimodal instruction conflicts and incorporates a 'Negative Director' to optimize generation quality.
Multi-Role, Multi-Audio Control: Utilizes deep DiT features for mask prediction, enabling independent audio-driven control of multiple roles in complex dialogue scenarios.
Superior Performance and Generalization: Achieves SOTA (State-of-the-Art) levels in visual quality, lip-sync accuracy, emotional expression, and instruction adherence.
Addressed Challenges
Balancing Generation Efficiency and Quality: Previous virtual human video generation models were inefficient in generating long-duration, high-resolution videos.
Poor Temporal Consistency: Prone to temporal drifting and visual quality degradation as video length increases.
Weak Multimodal Instruction Adherence: Often struggles to maintain coherent responses to text, audio, and image instructions in complex long videos.
Multi-Role Control Challenges: Difficulty in precisely driving specific audio to corresponding roles without interference in multi-role scenarios.
Proposed Solutions
Two-Stage Cascading Generation: First generates low-resolution 'blueprint' keyframes to capture global semantics and motion, then refines and upsamples them into high-resolution, temporally coherent sub-segments through a 'first-last-frame strategy.'
Multi-Expert Collaborative Planning: Transforms ambiguous user inputs into detailed storyboard scripts through collaborative reasoning (Chain-of-Thought) among audio, visual, and text expert models.
ID-Aware Mask Control: Predicts character masks using deep features from the DiT module, enabling precise local audio injection.
Applied Technologies
DiT (Diffusion Transformer): Serves as the foundational video generation backbone network.
MLLM (Multimodal Large Language Model): Used to construct the collaborative reasoning director module for multi-round dialogue reasoning and script planning.
Spatio-Temporal Super-Resolution: Upsamples videos in spatial and temporal dimensions.
Trajectory-Preserving Distillation: Accelerates the video generation process.
Automated Data Annotation Pipeline: Constructs multi-role video datasets by combining YOLO, DWPose, and SAM 2.
Achieved Effects
Enhanced Visual Clarity: Generates results with cinematic-quality visuals.
Realistic Detail Rendering: Achieves accurate lip-sync and lifelike facial expressions.
Strong Identity Preservation: Maintains consistent character identities in long video generation.
Complex Instruction Adherence: Understands and executes complex camera movements and action instructions (e.g., 'cross hands over chest').
Multi-Role Interaction: Successfully implements independent speech and interaction among multiple people in the same scene.
Methodology
KlingAvatar 2.0 extends the pipeline of Kling-Avatar. As shown in Figure 2, given a reference image, input audio, and text instructions, the system efficiently generates high-fidelity, long-duration digital human videos with precise lip-sync and fine-grained control over multiple speakers and roles. Below, we detail the spatio-temporal cascading diffusion framework, collaborative reasoning multimodal story director, multi-role control module, and acceleration techniques.
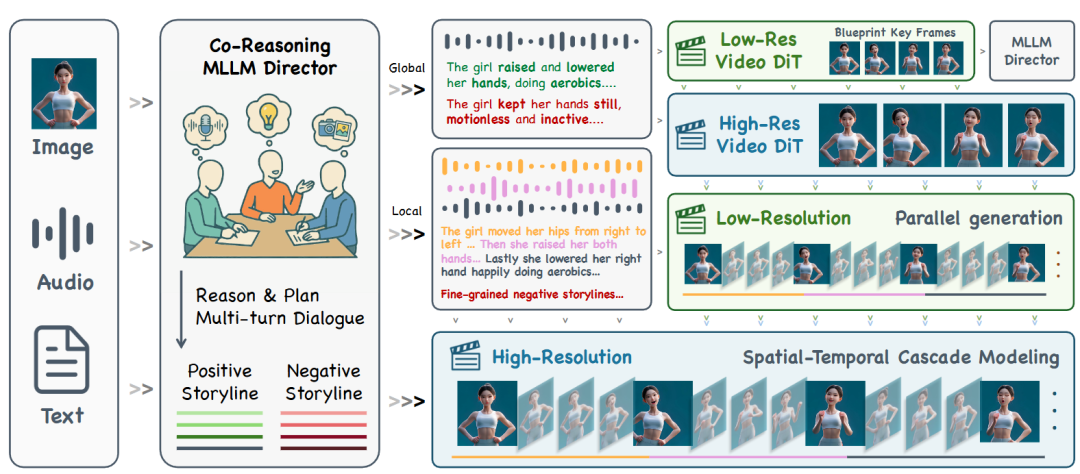 Figure 2. Overview of the KlingAvatar 2.0 framework. Under multimodal instructions, the collaborative director reasons and plans hierarchical, detailed positive and negative storylines through multi-round dialogues, while the spatio-temporal cascading process concurrently generates coherent, long-form, high-resolution avatar videos.
Figure 2. Overview of the KlingAvatar 2.0 framework. Under multimodal instructions, the collaborative director reasons and plans hierarchical, detailed positive and negative storylines through multi-round dialogues, while the spatio-temporal cascading process concurrently generates coherent, long-form, high-resolution avatar videos.
Spatio-Temporal Cascading Modeling
To support long-duration, high-resolution digital human synthesis with computational efficiency, KlingAvatar 2.0 adopts an audio-driven DiT spatio-temporal cascading architecture built upon pre-trained video diffusion models, as shown in Figure 2. The process involves two nested cascades, jointly handling global storyline planning over long spans and local spatio-temporal refinement.
First, a low-resolution diffusion model generates a 'blueprint video' capturing global dynamics, content, and layout; subsequently, representative low-resolution keyframes are upsampled by a high-resolution DiT, enriching details while preserving identity and scene composition under the same collaborative reasoning director's global prompts. Next, the low-resolution video diffusion model expands these high-resolution anchor keyframes into audio-synchronized sub-segments through 'first-last-frame conditioned generation,' where prompts are enhanced by blueprint keyframes to refine subtle movements and expressions. An audio-aware interpolation strategy synthesizes transitional frames to enhance temporal connectivity, lip-sync, and spatial consistency. Finally, the high-resolution video diffusion model super-resolves low-resolution sub-segments, generating high-fidelity, temporally coherent video clips.
Collaborative Reasoning Director
KlingAvatar 2.0 employs a collaborative reasoning director built upon recent MLLM-based virtual human planners, jointly reasoning audio, image, and text through multi-round dialogues. The director is instantiated by three experts: (i) Audio-Centric Expert: Performs transcription and paralinguistic analysis (emotion, prosody, speaking intent); (ii) Visual Expert: Summarizes appearance, layout, and scene context from reference images; (iii) Text Expert: Interprets user instructions, incorporates dialogue history from other experts, and synthesizes logically coherent storyline plans.
These experts engage in multi-round collaborative reasoning through Chain-of-Thought, demonstrating intermediate thought processes to resolve conflicts (e.g., angry tone paired with neutral script) and supplement unspecified details, such as implied actions or camera movements. The director outputs a structured storyline, decomposing the video into a series of shots. Additionally, this work introduces a Negative Director, where positive prompts emphasize desired visual and behavioral attributes, while negative prompts explicitly de-weight untrustworthy poses, artifacts, fine-grained opposing emotions (e.g., sadness vs. happiness), or motion styles (e.g., too fast vs. too slow).
For long videos, the director further refines the global storyline into fragment-level plans aligned with the audio timeline, directly parameterizing the keyframe cascading and fragment-level refinement modules. This high-level multimodal planning transforms loosely specified instructions into coherent scripts that the diffusion backbone network can consistently follow, significantly improving semantic alignment and temporal coherence.
Multi-Role Control
KlingAvatar 2.0 extends the single-speaker virtual human setup to multi-role scenarios and identity-specific audio control. This work's design follows the role-aware audio injection paradigm used in recent multi-person dialogue virtual humans, such as [33, 62, 63]. Empirically, we observe a crucial architectural property: hidden features at different depths of DiT blocks exhibit distinct feature representations. Notably, latent representations in deep DiT layers are organized into semantically coherent and noise-reduced spatial regions, aligning well with individual characters and other salient objects.
Inspired by this observation, we attach a mask-prediction head to selected deep DiT blocks, as shown in Figure 3(a). Specifically, given a specified character in the first frame, the reference identity cropped image is encoded using the same slicing scheme (without adding noise to reference tokens). Cross-attention between video latent tokens and each identity's reference tokens is then computed, and an MLP module regresses character masks for each frame. Ground truth (GT) masks are downsampled to match the spatial and temporal resolution of intermediate latent features. During training, the DiT video backbone network is frozen, and only the mask prediction module is optimized. During denoising, predicted masks inject identity-specific audio streams into corresponding regions.
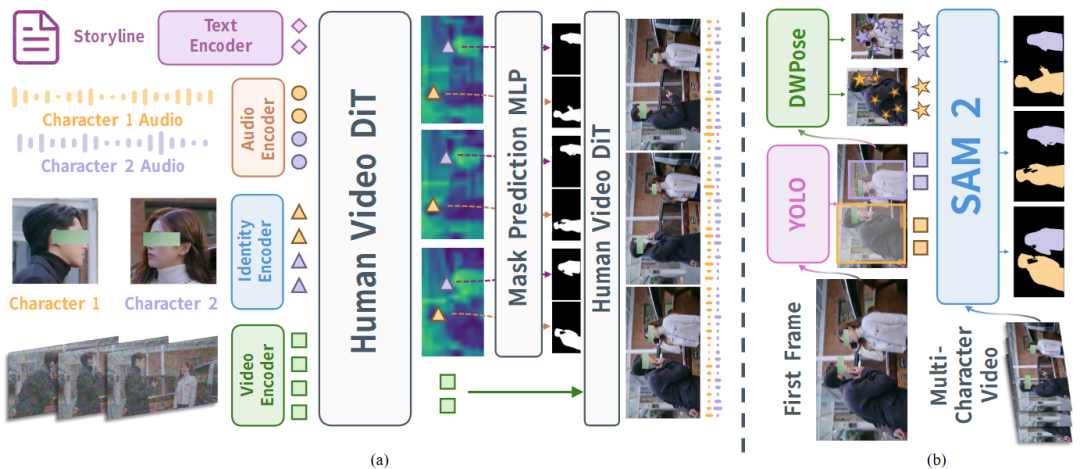 Figure 3(a). Multi-character video generation pipeline with identity-specific audio control. The mask prediction head connects to deep DiT features, predicting masks to inject ID-specific audio into corresponding regions. (b) Automated multi-character video annotation pipeline.
Figure 3(a). Multi-character video generation pipeline with identity-specific audio control. The mask prediction head connects to deep DiT features, predicting masks to inject ID-specific audio into corresponding regions. (b) Automated multi-character video annotation pipeline.
To facilitate the construction of large-scale multi-role training datasets, this work expands data sources to include podcasts, interviews, multi-role TV dramas, etc. To collect GT character masks at scale, we develop an automated annotation pipeline to generate video masks for each character, as shown in Figure 3(b). The pipeline utilizes several expert models: YOLO for person detection, DWPose for keypoint estimation, and SAM 2 for segmentation and temporal tracking. Specifically, YOLO first detects all characters in the first frame, DWPose estimates keypoints for each detection, and the generated bounding boxes and keypoints serve as prompts for SAM 2 to segment and track each person in subsequent frames. Finally, generated video masks are verified against per-frame YOLO and DWPose estimates, and misaligned or low-overlap segments are filtered out to ensure high-quality training annotations.
Accelerated Video Generation
To achieve accelerated inference efficiency, this work explores trajectory-preserving distillation (represented by PCM and DCM) and distribution matching distillation (represented by DMD) schemes. Based on a comprehensive evaluation of experimental costs, training stability, inference flexibility, and final generation performance metrics, the trajectory-preserving distillation method was ultimately selected. To further enhance distillation efficiency, we develop a custom temporal scheduler by analyzing the base model's performance at different time steps, balancing inference speedup ratios with model performance. In the distillation algorithm, we introduce a multi-task distillation paradigm through a series of carefully designed configurations. This paradigm produces a synergistic effect (1+1>2), improving distillation results for each individual task.
Experiments
Experimental Setup
To comprehensively evaluate KlingAvatar 2.0, this work follows a human preference-based subjective evaluation protocol. A test set containing 300 high-quality test cases (100 Chinese speech, 100 English speech, 100 singing samples) was constructed. Evaluators conducted pairwise comparisons between our model and baseline methods under the GSB (Good/Same/Bad) criteria. Evaluation dimensions included: Face-Lip Sync, Visual Quality, Motion Quality, Motion Expressiveness, and Text Relevance.
Experimental Results
This work compares KlingAvatar 2.0 with three strong baselines: HeyGen, Kling-Avatar, and OmniHuman-1.5.
Quantitative Results: As shown in Table 1 and Figure 4, our method achieves leading performance across all dimensions, particularly notable improvements in motion expressiveness and text relevance.
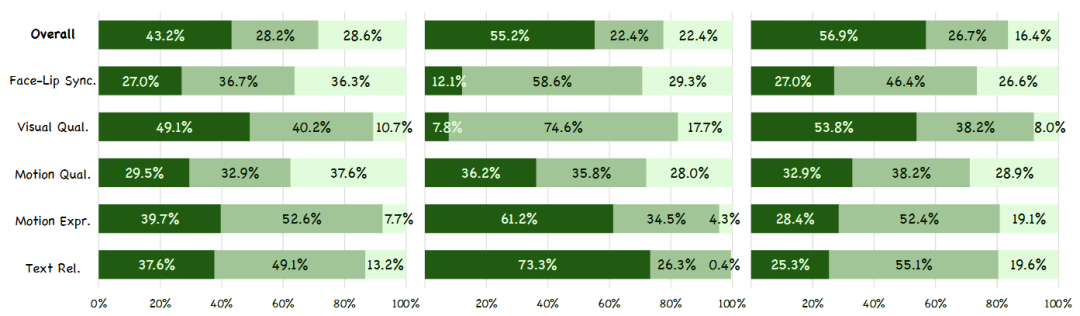 Figure 4. Visualization of GSB benchmark test results comparing KlingAvatar 2.0 with HeyGen, Kling-Avatar, and OmniHuman-1.5 across various evaluation criteria.
Figure 4. Visualization of GSB benchmark test results comparing KlingAvatar 2.0 with HeyGen, Kling-Avatar, and OmniHuman-1.5 across various evaluation criteria.
Qualitative Comparison: As shown in Figure 5, our model generates hair dynamics that are more physically plausible and natural, whereas baseline methods (e.g., Kling-Avatar, OmniHuman-1.5) appear slightly stiff or lack physical realism. In terms of multimodal instruction adherence, our method more accurately executes complex instructions such as 'bottom-to-top camera movement' or 'cross hands over chest,' while baseline methods sometimes ignore action intensity or produce incorrect movements (e.g., placing hands on the waist instead of the chest).
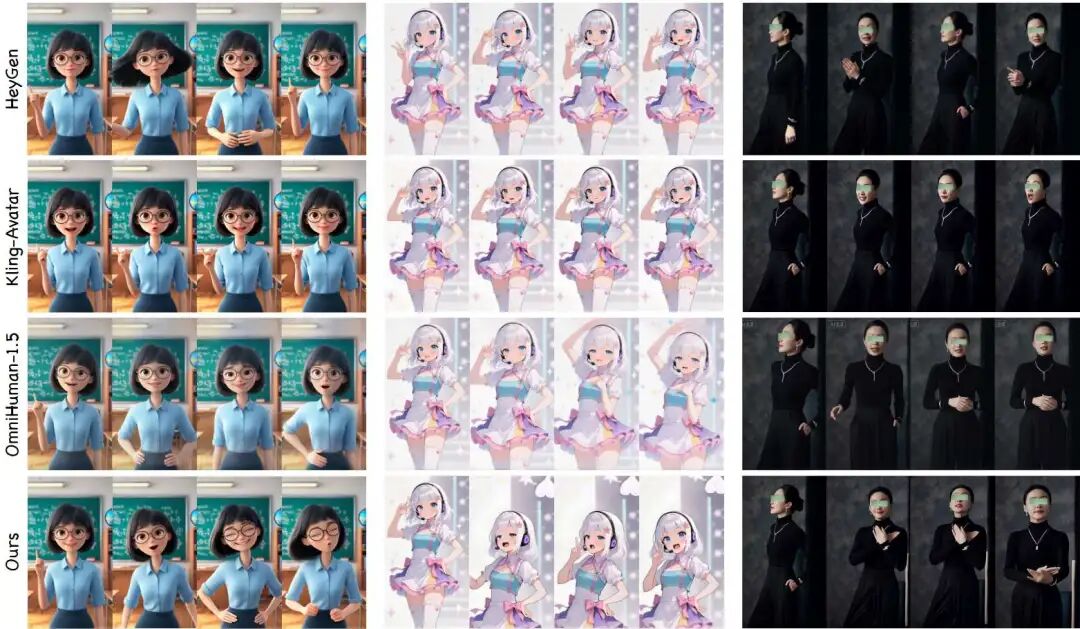 Figure 5. Qualitative comparison between KlingAvatar 2.0 and baseline methods. Left: Our method can generate more natural hair dynamics and vivid facial expressions. Middle: Our results align more closely with the specified bottom-to-top camera motion. Right: Our generated video better matches the prompt "...she turns to the front, crossing her hands over her chest."
Figure 5. Qualitative comparison between KlingAvatar 2.0 and baseline methods. Left: Our method can generate more natural hair dynamics and vivid facial expressions. Middle: Our results align more closely with the specified bottom-to-top camera motion. Right: Our generated video better matches the prompt "...she turns to the front, crossing her hands over her chest."
Multi-Scene and Ablation Studies: Figure 6 demonstrates the model's generalization capability in multi-speaker interaction scenarios. The ablation study in Figure 7 shows that compared to using generic negative prompts, introducing Negative Director for shot-level fine-grained negative prompt control can effectively suppress unreasonable expressions and artifacts, enhancing the accuracy and temporal stability of emotional expression.
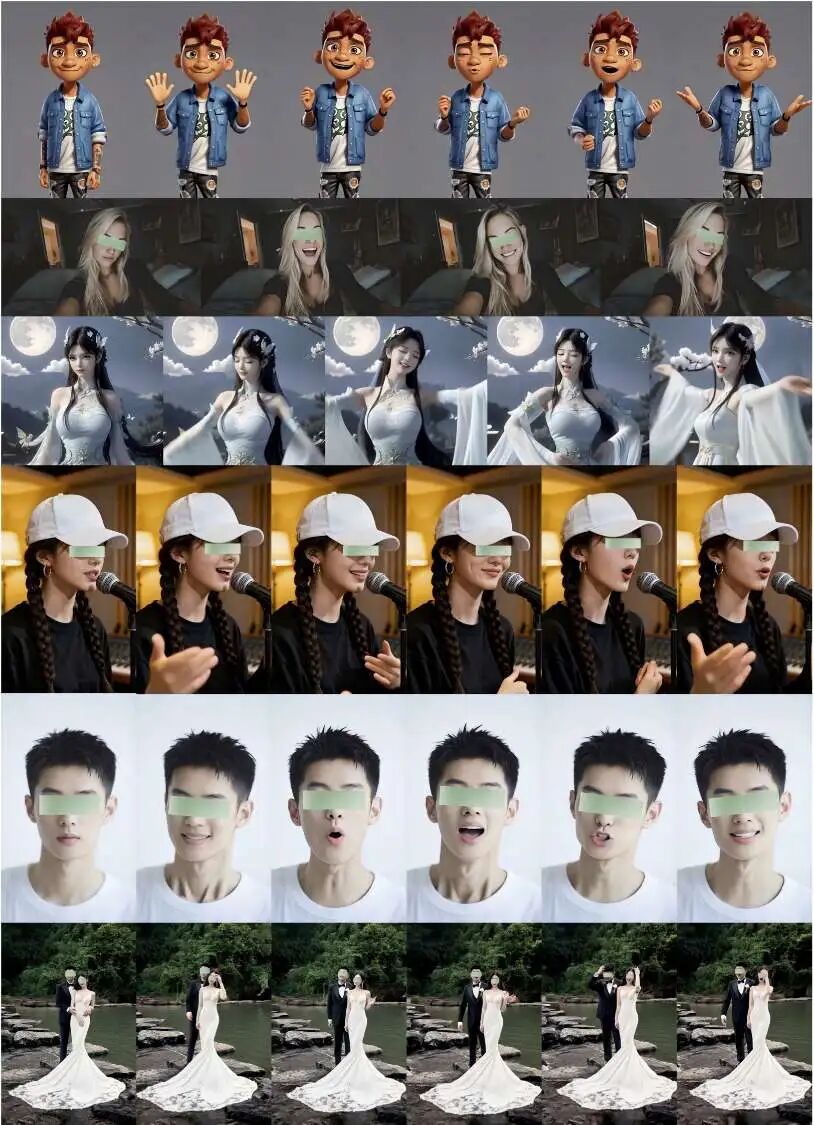 Figure 6. Representative qualitative results generated by our spatiotemporal cascade framework co-directed with multimodal directors.
Figure 6. Representative qualitative results generated by our spatiotemporal cascade framework co-directed with multimodal directors.  Figure 7. Ablation study of negative guidance on blueprint keyframes. Negative Director enhances facial expressions, improves temporal stability and emotional control, and reduces lighting and exposure artifacts.
Figure 7. Ablation study of negative guidance on blueprint keyframes. Negative Director enhances facial expressions, improves temporal stability and emotional control, and reduces lighting and exposure artifacts.
Conclusion
KlingAvatar 2.0 is a unified framework that achieves spatiotemporal cascade generation through omnidirectional collaborative inference directing, synthesizing high-resolution, long-duration, lifelike multi-person virtual human videos. The multimodal, multi-expert collaborative inference directing in this work reasons and plans over audio cues, visual context, and complex instructions through multi-round dialogues to resolve ambiguities and signal conflicts, generating coherent global narratives to guide long video synthesis trajectories and detailed local prompts to refine sub-segment dynamics.
This hierarchical narrative drives the generation of low-resolution blueprint keyframes and spatiotemporally upsampled high-resolution, audio-synchronized sub-segments, which are parallelly and efficiently combined into long videos through first-and-last-frame conditioning. This work further extends application scenarios to multi-role settings with identity-specific audio control and develops an automated annotation pipeline to organize large-scale multi-person video datasets. Experiments show that KlingAvatar 2.0 exhibits leading performance in visual fidelity, identity preservation, lip-audio synchronization, instruction following, long-duration coherence, and multi-role, multi-audio controllability. We believe that our exploration of an omnidirectional, multi-role, multi-audio, long-form, high-resolution virtual human synthesis framework paves the way for future research and applications in digital human generation.
References
[1] KlingAvatar 2.0 Technical Report