The First Sub-Second Launch of a 14B 'Digital Human' Goes Open Source! Efficiency Soars 23x! SoulX-LiveTalk: 32FPS Makes Conversations Smooth as Real Humans
![]() 01/04 2026
01/04 2026
![]() 377
377
Interpretation: The Future of AI Generation
Highlights
SoulX-LiveTalk Framework: A low-latency, real-time, audio-driven virtual avatar framework centered around a 14B-parameter DiT model. It overcomes the challenges of high computational costs and strict latency requirements faced by large-scale diffusion models in real-time, infinite streaming applications.
Improved Model Architecture, Generation Quality, and Training Efficiency: Abandons the strict unidirectional paradigm and adopts a bidirectional teacher-to-bidirectional student distillation strategy.
Built Full-Stack Inference Acceleration Solution: Constructs a full-stack inference acceleration solution to meet the performance requirements of large DiT models under strict real-time streaming conditions.
Achieved Exceptional Performance: Converges to exceptional performance in just 200 distillation steps, approximately 23x more efficient than the 27,500 steps required by LiveAvatar. Achieves a launch latency of 0.87 seconds, approximately 3x faster than the existing baseline of 2.89 seconds.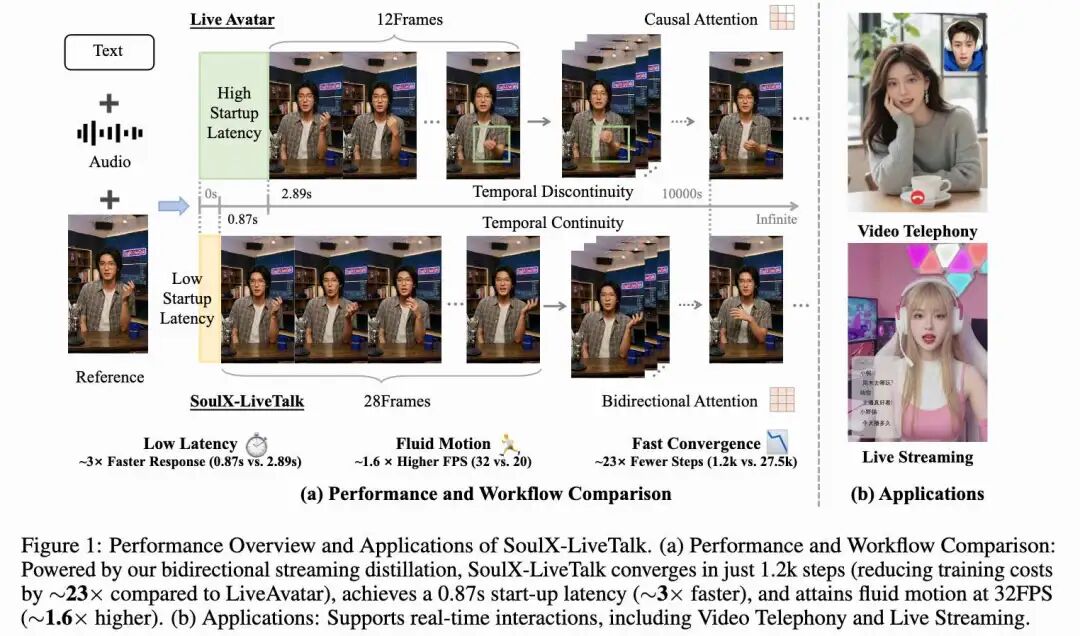
Summary
Problems Addressed
Applying large-scale diffusion models to real-time, infinite-length audio-driven virtual avatar generation presents a conflict between computational load and strict latency constraints. Existing methods often sacrifice visual fidelity by enforcing unidirectional attention mechanisms or reducing model capacity, leading to insufficient motion coherence, loss of visual details, and error accumulation.
Proposed Solution
This paper introduces SoulX-LiveTalk, a 14B-parameter framework that addresses the above issues through several key innovations:
Self-Correcting Bidirectional Distillation Strategy: Unlike traditional unidirectional paradigms, this paper retains bidirectional attention mechanisms within video chunks to maintain critical spatiotemporal associations, significantly enhancing motion coherence and visual details.
Multi-Step Retrospective Self-Correction Mechanism: To ensure stability during infinite generation, this mechanism enables the model to autonomously recover from accumulated errors and prevent generation collapse.
Full-Stack Inference Acceleration Suite: Integrates hybrid sequence parallelism, parallel VAE, and kernel-level optimizations to optimize inference performance.
Applied Technologies
14B-Parameter Diffusion Transformers (DiTs): Serve as a scalable backbone network for high-fidelity generation modeling.
Self-Correcting Bidirectional Distillation: A training strategy that retains bidirectional attention within video chunks and introduces a multi-step retrospective self-correction mechanism to simulate and resolve error propagation in long-period generation.
Hybrid Sequence Parallelism (Ulysses and Ring Attention): Used to accelerate attention operations in DiTs.
Parallel VAE (Slice Parallelism Strategy of LightX2V): Used to accelerate the encoding/decoding process of 3D VAEs.
FlashAttention3: Kernel-level optimization tailored for the NVIDIA Hopper architecture.
torch.compile: Used to unify and optimize the entire inference pipeline.
Latency-Aware Spatiotemporal Adaptation: A training phase that adapts the model to operate effectively at reduced spatial resolutions and shorter frame sequences.
Achieved Results
SoulX-LiveTalk is the first 14B-scale system to achieve sub-second launch latency (0.87 seconds). It reaches a real-time throughput of 32 FPS, setting a new standard for high-fidelity interactive digital human synthesis. The model converges significantly faster, requiring only 1.2k steps to achieve exceptional performance, approximately 23x fewer training steps than LiveAvatar (which requires 27.5k steps). Through bidirectional streaming distillation, it effectively mitigates error accumulation, background texture blurring, and detail loss in long-period generation. It achieves fine-grained lip-sync accuracy, with generated lip geometry strictly aligned with ground truth, minimizing lip drift and stiffness.
Architectural Approach
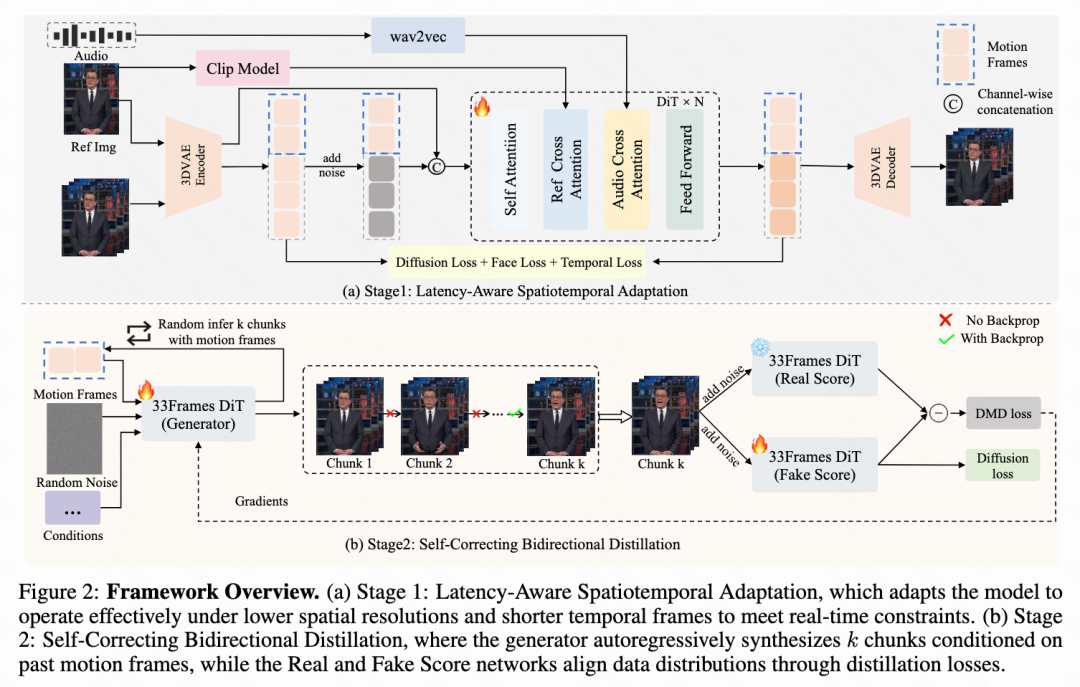
This paper details the core methods of SoulX-LiveTalk. As shown in Figure 2 below, the framework is built upon a 14B-parameter DiT model and integrates a two-stage training pipeline with a full-stack inference acceleration engine. The training process includes a 'latency-aware spatiotemporal adaptation' phase and a 'self-correcting bidirectional distillation' phase, aiming to simultaneously meet the requirements of high-fidelity generation and low-latency streaming.
Model Architecture
The architecture is derived from WAN2.1-I2V-14B and InfiniteTalk, comprising four main components:
3D VAE: This paper utilizes WAN2.1 VAE for latent space compression to enable efficient high-resolution video generation. This module encodes video frames into compact latent representations, achieving a spatiotemporal downsampling factor of 4x8x8 in the time, height, and width dimensions.
DiT-Based Generator: The core generator adopts the DiT architecture. As shown in Figure 2(a), each DiT block contains a 3D attention mechanism for modeling spatiotemporal dependencies. A unified cross-attention layer conditions generation on reference images and text inputs to maintain visual fidelity and provide semantic guidance. Additionally, this paper integrates a dedicated audio cross-attention layer to inject speech-driven signals directly into the generation process.
Conditional Encoders: The model conditions generation on audio, text, and reference images. This paper employs a Wav2Vec model customized for Chinese speech to convert continuous audio signals into sequential embeddings. To ensure identity consistency, this paper uses CLIP and VAE encoders to extract semantic representations and visual features from reference images. For text conditioning, this paper adopts umT5 to support bilingual subtitles. These identity and text conditions are injected through cross-attention layers.
Latent Input Formulation: For a given source video, this paper samples a video clip of length . The initial frames serve as motion frames to capture historical context, while subsequent frames serve as generation targets. Reference frames are randomly sampled from outside the clip boundaries. All inputs are encoded by the 3D VAE and combined to form the DiT input: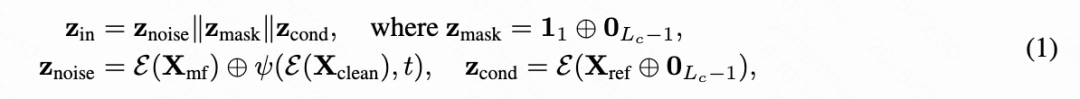
where denotes frame-level concatenation, denotes channel-level concatenation, and represents the 3D VAE encoder. The flow combines historical latent variables with noisy latent variables obtained by applying a forward diffusion process to at time step . The flow injects reference guidance, while uses a binary indicator to identify reference frames. This composite input structure facilitates bidirectional interaction between historical motion context and current generation targets, enabling the model to utilize reference information to correct accumulated errors.
Model Training
To meet real-time inference under strict latency constraints, this paper adopts a two-stage training strategy. The 'latency-aware spatiotemporal adaptation' phase adapts the model to operate at reduced spatial resolutions and shorter frame sequences, while the 'self-correcting bidirectional distillation' phase further reduces sampling steps and eliminates classifier-free guidance. This two-stage process enables rapid model response while maintaining high generation quality.
Phase 1: Latency-Aware Spatiotemporal Adaptation
The high computational cost of the 14B-parameter DiT backbone network poses a significant challenge for real-time applications. Although the original InfiniteTalk model provides high-quality results, its inference latency on standard hardware is too high for interactive streaming. Therefore, this paper adapts the model to operate at reduced spatial resolutions and shorter frame sequences.
Directly deploying a pre-trained model under these constrained settings leads to poor feature alignment and degraded generation quality. This paper addresses this issue by performing a dedicated fine-tuning phase optimized for the target resolution and frame count. During this phase, this paper employs a dynamic aspect ratio bucketing strategy to efficiently organize training samples, reducing data loss due to padding or cropping. This process enables the 14B model to recover fine details and maintain identity consistency even at lower resolutions.
Phase 2: Self-Correcting Bidirectional Distillation
Multi-step sampling and classifier-free guidance incur significant computational overhead. This paper adopts the DMD framework to compress sampling steps and eliminate the need for guidance, enabling real-time streaming.
The framework aims to minimize the distribution difference between the original teacher model and the distilled student model at each time step using Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence as the optimization criterion. The resulting training objective formulation is:
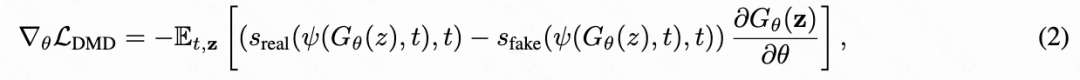
where is frozen to model the teacher distribution, while is trainable and tracks the evolving student distribution. The student generator infers and generates samples in a few steps without classifier guidance. All components are initialized from the Phase 1 SFT model.
Standard DMD fails to address error accumulation or identity drift in long videos. Inspired by Self-Forcing++, this paper introduces self-correcting bidirectional distillation, which includes a multi-step retrospective self-correction mechanism to explicitly simulate error propagation during long-period generation. Specifically, the generator is required to autoregressively synthesize K consecutive chunks, where each chunk is conditioned on previously generated motion frames rather than ground truth.
To balance computational efficiency and training stability, this paper further proposes a random truncation strategy. This paper randomly samples a smaller value than K and generates only the first chunks instead of synthesizing all K chunks. During backpropagation, a denoising step is randomly sampled from T reduced sampling steps, and only the gradient of the th denoising step of the th chunk is retained, while all other steps are detached from the computational graph. This random truncation provides a memory-efficient and unbiased approximation of the full training objective, which can be expressed as:
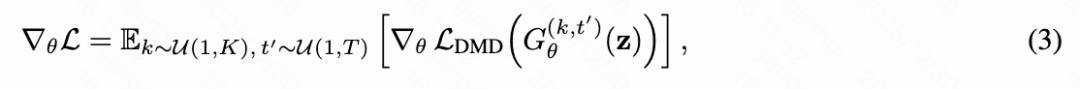
where denotes the model's output at the th denoising step of the th chunk, and during backpropagation, all previous chunks and denoising steps are detached from the computational graph.
Following this two-stage training strategy, SoulX-LiveTalk outperforms existing audio-driven video generation models in terms of both inference speed and generation quality, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Real-Time Inference Acceleration
Optimizing training and inference alone is insufficient to fully meet strict low-latency requirements. To achieve sub-second latency for the 14B-parameter model, this paper implements a full-stack acceleration suite specifically designed for 8 H800 nodes.
The core computational bottleneck lies in the large-scale attention operations of DiTs. To eliminate this obstacle, this paper deploys hybrid sequence parallelism driven by xDiT. By synergizing Ulysses and Ring Attention mechanisms, this paper effectively distributes attention workloads, improving single-step inference speed by approximately 5x compared to standard implementations. Additionally, this paper optimizes DiTs at the kernel level by adopting FlashAttention3, which is specifically designed to leverage the NVIDIA Hopper architecture, including its asynchronous execution pipeline. This improves overlap between data movement and computation, reducing attention latency by an additional 20% compared to FlashAttention2.
With DiT inference fully accelerated, the computational overhead of the high-resolution VAE decoder becomes the primary latency factor. To address this paradigm shift, this paper introduces 3D VAE parallelism to alleviate the decoding burden. By adopting a slice-based strategy to distribute spatial decoding workloads across multiple GPUs, this paper achieves approximately 5x acceleration in VAE processing speed, ensuring it does not become a pipeline bottleneck.
Finally, to eliminate overhead from the Python runtime and fragmented kernel execution, the entire inference pipeline is unified and optimized through torch.compile. This enables aggressive graph-level fusion and memory optimization, maximizing the hardware capabilities of H800 nodes.
Architectural Analysis: Why Bidirectional?
Although autoregressive models dominate streaming video generation, their inherent unidirectional dependency fundamentally limits the modeling of global temporal structures. Under this paradigm, models primarily condition on historical frames and typically avoid strict frame-by-frame synthesis. Instead, generation proceeds in minimal chunks to improve local consistency, where bidirectional attention is applied within each chunk, while unidirectional dependency is enforced between chunks. However, this compromise remains insufficient to prevent temporal inconsistency, error accumulation, and identity drift, particularly in long-period generation.
This paper argues that integrating long histories is not the primary bottleneck for the target task. Instead, effectively suppressing temporal drift and accumulated errors is more crucial. Inspired by this observation, this paper fully retains the bidirectional attention mechanism of the original model, always allowing full-to-full information exchange between frames. This design enables the model to jointly utilize past and implicit future contexts at each step, achieving more accurate and coherent generation while fully aligning with the teacher architecture, thereby significantly accelerating model training.
This bidirectional modeling not only greatly enhances spatiotemporal coherence within individual chunks but also provides streaming generation with more robust and higher-quality basic units, effectively mitigating drift and collapse issues throughout long-sequence video generation.
Experiment Summary
This section introduces the implementation details, datasets, and evaluation metrics of SoulX-LiveTalk, and analyzes its performance, ablation studies on distillation strategies, and inference latency.
Implementation Details: The model is based on the InfiniteTalk architecture and optimized for real-time constraints. Training includes a lightweight SFT phase of 1,000 steps and a distillation phase of 200 steps. The learning rate is set for the generator and Fake Score Network, with an update ratio of 1:5. To simulate error accumulation in long-cycle generation, the generator synthesizes up to consecutive blocks during distillation. The experiment uses 32 NVIDIA H20 GPUs with a batch size of 1 per GPU, employing FSDP, gradient checkpointing, and mixed-precision training for efficiency.
Datasets: Training and evaluation data are sourced from the publicly available SpeakerVid-5M and TalkVid datasets, ensuring no overlap between training and test sets. A dedicated benchmark named TalkBench is constructed, comprising two subsets: TalkBench-Short (100 samples, duration < 10 seconds) and TalkBench-Long (20 samples, duration > 5 minutes).
Evaluation Metrics: Image quality assessment (IQA) and aesthetic score evaluation (ASE) are performed using the Q-Align vision-language model. Lip-sync is measured via Sync-C and Sync-D metrics. Additionally, VBench is employed to assess temporal quality, including subject consistency (Subject-C), background consistency (BG-C), motion smoothness (Motion-S), and temporal flickering (Temporal-F).
Performance of SoulX-LiveTalk
This paper compares SoulX-LiveTalk with state-of-the-art audio-driven generative models, including Ditto, EchoMimic-V3, StableAvatar, OmniAvatar, InfiniteTalk, and LiveAvatar.
Quantitative Analysis
As shown in Table 1 below, SoulX-LiveTalk excels in visual quality and synchronization on both TalkBench-Short and TalkBench-Long datasets. In short video benchmarks, it achieves an ASE of 3.51 and an IQA of 4.79, surpassing Echomimic-V3. For lip-sync, Sync-C scores 1.47, outperforming OmniAvatar. In terms of inference speed, the 14B parameter model achieves a throughput of 32 FPS, exceeding the real-time requirement of 25 FPS and significantly outperforming LiveAvatar's 20.88 FPS.
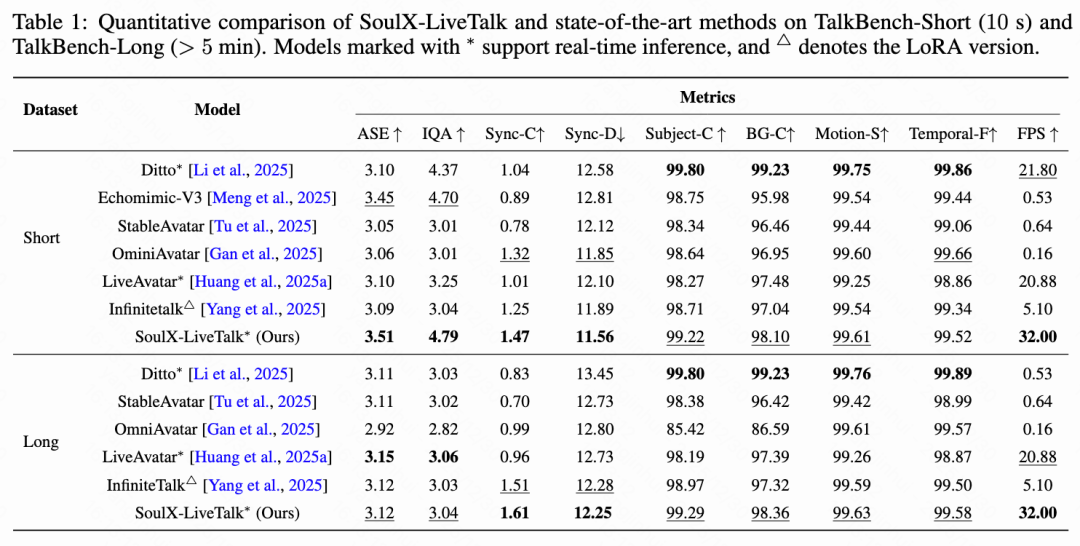
Regarding temporal consistency metrics, Ditto performs best in Subject-C and BG-C, but its generation paradigm limits full-body dynamics. SoulX-LiveTalk achieves a Subject-C of 99.22 while generating full-body motions, balancing motion expressiveness and temporal stability.
For long-cycle generation, SoulX-LiveTalk achieves a Sync-C of 1.61 and Sync-D of 12.25, outperforming InfiniteTalk and LiveAvatar while maintaining a throughput of 32 FPS. These results confirm that the bidirectional distillation strategy effectively reduces asynchrony and drift issues common in unidirectional streaming models.
Qualitative Analysis
This section qualitatively evaluates SoulX-LiveTalk's generation fidelity, long-term stability, and lip-sync accuracy.
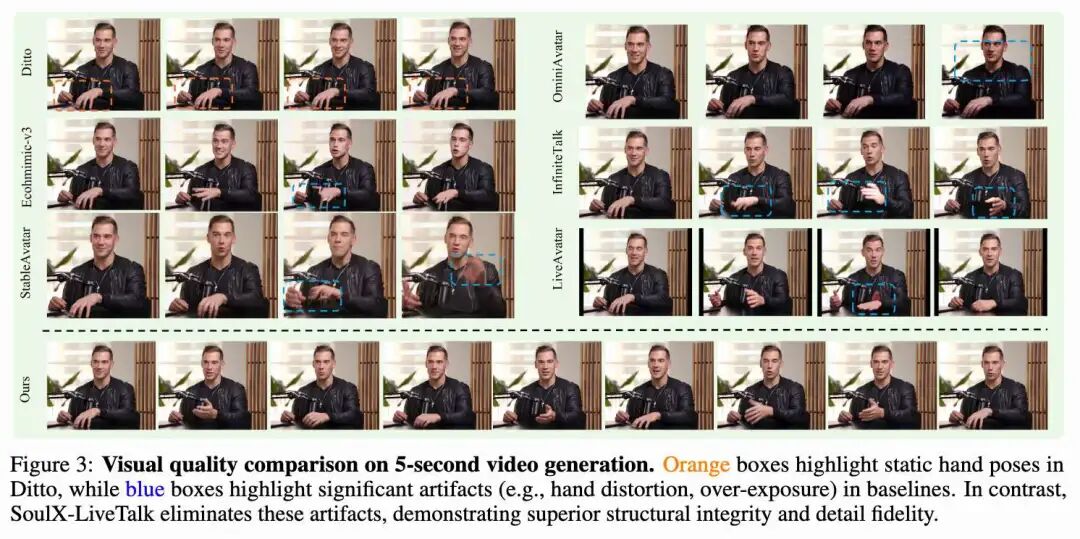
Visual Fidelity and Detail Preservation: As shown in Figure 3 below, during 5-second video generation, baseline models struggle with large limb movements. Ditto fails to synthesize meaningful hand motions (as indicated by the orange box), while EchoMimic-v3 and StableAvatar exhibit structural distortions and artifacts in hand regions (as indicated by the blue box). InfiniteTalk suffers from hand overexposure and motion blur during rapid gestures. In contrast, SoulX-LiveTalk eliminates these artifacts using its 14B DiT architecture and bidirectional attention mechanism, synthesizing clear, structurally intact, and sharply textured hand motions. It also outperforms LiveAvatar in background consistency and identity fidelity.
Stability in Infinite Generation: As shown in Figure 4 below, during continuous generation up to 1,000 seconds, baseline models (LiveAvatar, StableAvatar, InfiniteTalk) exhibit significant error accumulation, with severe texture blurring and detail loss in background regions (as indicated by the blue box). SoulX-LiveTalk mitigates error propagation through bidirectional streaming distillation and self-correction mechanisms (as indicated by the orange box), maintaining consistent facial geometry and clear background details even at the 1,000-second mark, validating its robustness in infinite streaming.

Fine-Grained Lip-Sync Accuracy: As shown in Figure 5 below, during specific Chinese pronunciations, baseline models exhibit structural misalignments on complex phonemes. For example, when pronouncing ' up ' ('shàng') and ' sudden ' ('tū'), their mouth openness and shape do not match ground truth (GT) values (as indicated by the yellow dashed box). In contrast, SoulX-LiveTalk captures these fine-grained phoneme dynamics, with generated lip geometries strictly aligned with GT, minimizing lip-sync drift and stiffness to ensure visual authenticity across different languages.

Impact of Distillation Ablation on Multi-Step Retrospective Self-Correction
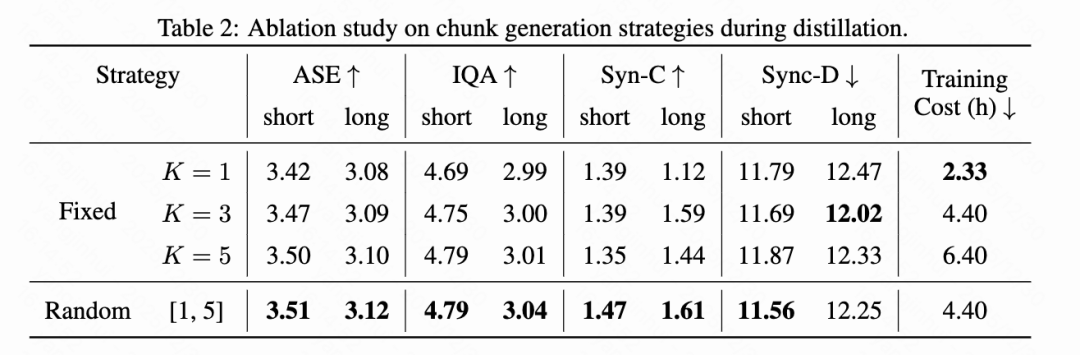
This section analyzes the impact of the number of generated blocks and scheduling strategies on long-term stability. Strategies with fixed at 1, 3, or 5 are compared with a random strategy where is randomly sampled between 1 and 5 during training.
As shown in Table 2 below, single-block training incurs the lowest training cost (2.33 hours) but fails to maintain long-term stability, achieving a Sync-C score of only 1.12 on long videos, confirming the error accumulation issue. Increasing to 3 significantly improves stability. However, further increasing to 5 raises training costs to 6.40 hours without corresponding improvements in synchronization performance. The random strategy achieves the best overall balance, attaining the highest long Sync-C score of 1.61 and the best visual quality metrics while keeping training costs moderate at 4.40 hours. This indicates that exposing the model to varying autoregressive lengths during distillation effectively enhances robustness to accumulated errors.
Impact of Motion Latent Variable Conditioning on DMD
This section examines the conditional settings of the Real Score network from three dimensions: motion latent variable source, noise injection, and loss computation. As shown in Table 3 below, using student-predicted motion latent variables yields better visual quality than using ground truth (GT) latent variables. Specifically, the noisy prediction strategy achieves an ASE of 3.51 and an IQA of 4.79, surpassing the GT configuration (3.48 and 4.77). This suggests that using predicted latent variables helps reduce discrepancies between training and inference.
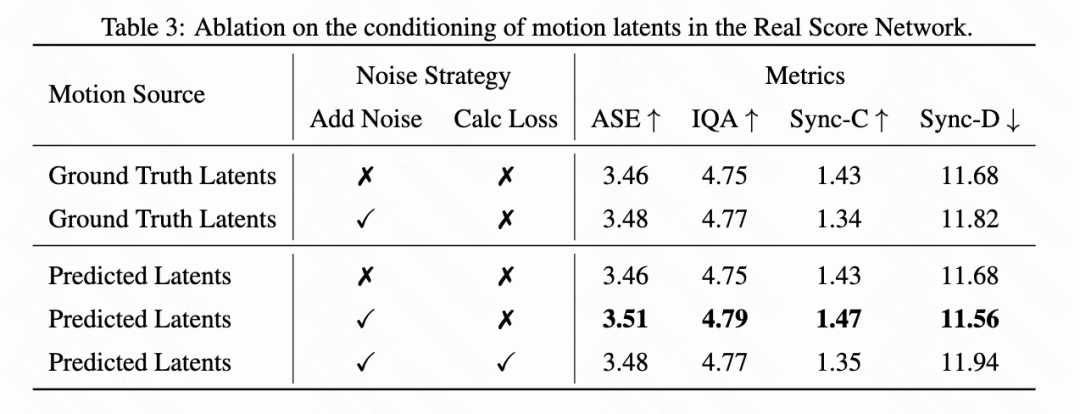
Regarding noise and loss, injecting noise into predicted latent variables improves performance, increasing ASE from 3.46 to 3.51. Conversely, including motion latent variables in loss computation reduces ASE to 3.48. This indicates that requiring the model to reconstruct conditioned frames diverts attention from the primary denoising task. Therefore, the predicted latent variable configuration with noise injection and no loss computation provides the best results.
Inference Latency Analysis
Component-level latency is analyzed on a single-node system with varying numbers of NVIDIA H800 GPUs. The experimental setup targets high-fidelity streaming at 720x416 resolution and 4-step denoising. Each clip contains 33 frames, including 28 generated frames and 5 motion frames. Under this configuration, the pipeline achieves a throughput of 32 FPS.
First, the latency of VAE and DiT is examined to highlight the necessity of multi-GPU parallelization, as shown in Table 4 below. On a single GPU, DiT inference alone incurs 1,070 ms of latency per step, while VAE inference requires 97 ms to encode motion frames and 988 ms to decode generated frames.
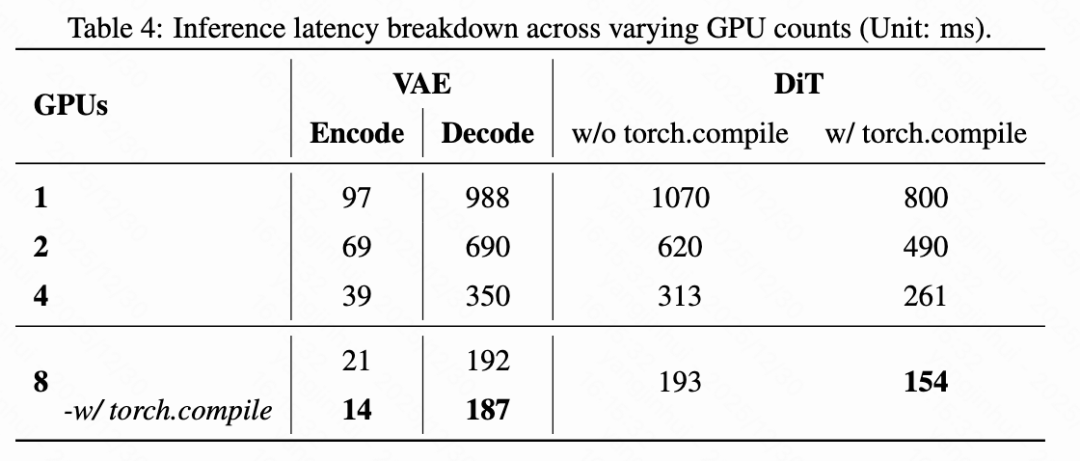
When scaled to 8 GPUs, DiT and VAE are parallelized using xDiT's hybrid sequence parallelism and LightX2V's slice-based parallel strategy, respectively. Due to inter-GPU communication overhead, acceleration is slightly sublinear, achieving a near 5x overall speedup. Specifically, DiT latency reduces from 1,070 ms to 193 ms, VAE encoding from 97 ms to 21 ms, and decoding from 988 ms to 192 ms. Additional latency reduction is achieved by enabling torch.compile.
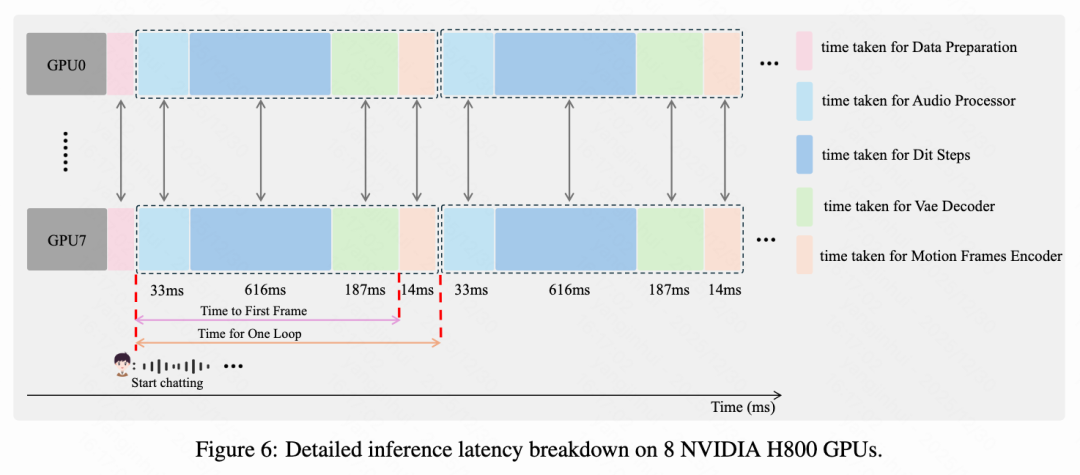
Building on core component optimization, this paper reports end-to-end pipeline latency on an 8-H800 GPU cluster, as shown in Figure 6 below. During steady-state generation cycles, the total latency per cycle is 876 ms, with audio processing taking 33 ms, core 4-step DiT denoising taking 616 ms, frame decoding taking 187 ms, and motion frame encoding taking 14 ms. The remaining latency is attributed to other overheads. By achieving sub-second end-to-end latency, the proposed pipeline meets the stringent throughput requirements of real-time streaming.
Conclusion and Future Work
SoulX-LiveTalk, a framework designed to meet real-time requirements while maintaining high-quality video synthesis. The framework combines bidirectional streaming distillation with a multi-step self-correction mechanism, enabling our 14B parameter DiT model to sustain stable, infinitely long streaming on an 8-H800 cluster. Our approach also simplifies training, demonstrating that distribution matching distillation following a brief SFT phase is sufficient to achieve state-of-the-art performance without requiring complex multi-stage pretraining.
Future work will prioritize model efficiency over system scaling. We plan to explore pruning, quantization, and optimized attention mechanisms. The goal is to deploy these models on consumer-grade hardware, eliminating reliance on expensive computing clusters.
References
[1] SoulX-LiveTalk Technical Report








