In-depth Analysis | Clawdbot Emerges as a New Favorite in the Global Agent Landscape, Elevating Expectations for Scalability This Year
![]() 02/06 2026
02/06 2026
![]() 371
371
Preface:
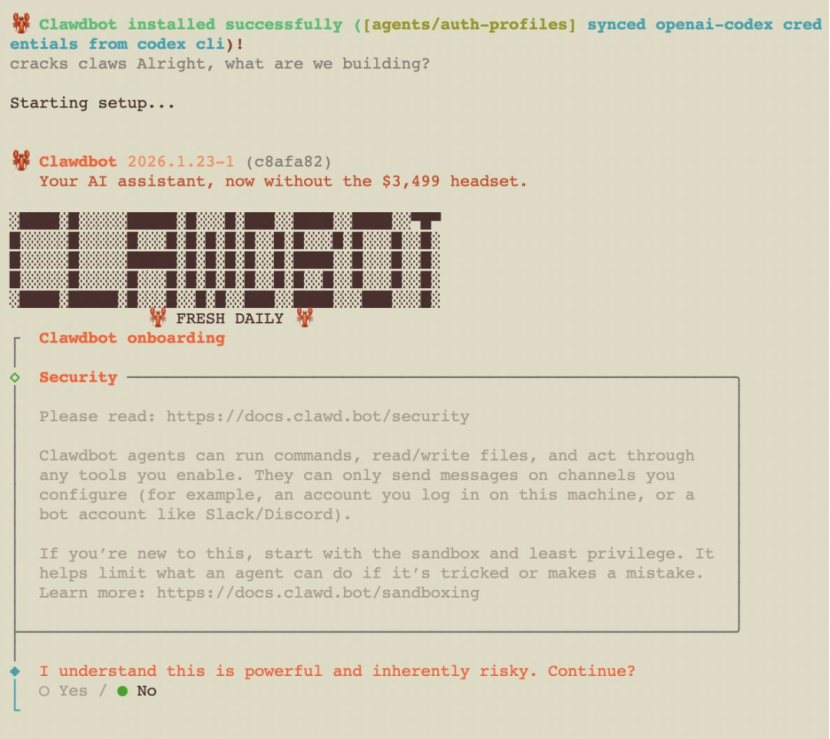
The tech world at the start of 2026 has been set ablaze by a [red lobster]. The open-source AI Agent project named Clawdbot has exploded across the global geek community in just a few days.
From being a [toy] for Silicon Valley geeks to a focal point of public discussion, and from [truly actionable AI] to a controversy over two forced renamings, Clawdbot's rise to fame is no accident.
Author | Fang Wensan
Image Source | Network

AI Agent Awaits a Catalyst for Takeoff
The Agent concept has been hyped for three years without achieving scalability. Over the past two years, the primary form of Agents has been [large models + tool invocation + task decomposition]. The issue lies in the fact that while this paradigm works well in laboratories, it nearly simultaneously hits three walls in the real world.
① Cost Impossibility: Multi-round reasoning, long contexts, and high-frequency tool invocations exponentially amplify the cost per task. Once concurrency increases, bills spiral out of control.
② Reliability Impossibility: Hallucinations in LLMs, uncertainties in tool return results, and state drift in multi-Agent collaborations make Agents [impressive] in PoC stages but [prone to failure] in production environments.
③ Engineering Uncontrollability: Prompt as logic, difficult state tracking, and extremely high Debug costs result in Agents that appear intelligent but cannot be managed like [software systems].
In 2025, the industry began to shift noticeably from focusing on intelligence levels to system stability, and from single-Agent performances to Agent factory-style production.
And it was in this context that Clawdbot rose to prominence.
However, on January 27th, Anthropic demanded a rename due to trademark infringement, leading Steinberg to rebrand Clawdbot as Moltbot (meaning [molting]), symbolizing [a lobster's growth through molting, with its mission unchanged]. Just two days later, the project was renamed again to OpenClaw, emphasizing its original commitment to [open source, openness, and community-driven development].
The Rise of a [Lobster]
[The AI that actually does things], the slogan on Clawdbot's official website, precisely captures its core difference from traditional AI.
Unlike [chat companion] AIs such as ChatGPT, which can only generate email drafts when you issue an instruction like [send the Excel sheet to the boss] and require you to manually complete subsequent operations, Clawdbot is a local AI agent capable of [getting things done].
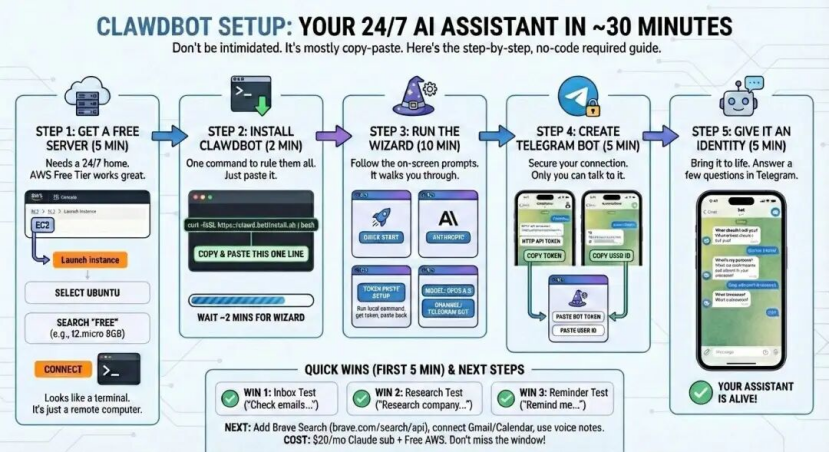
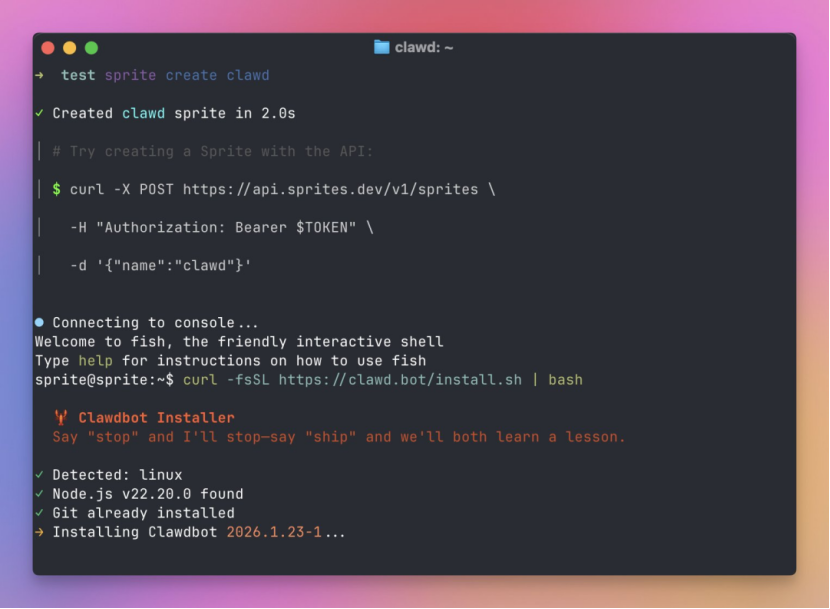
After users download the script for free from GitHub or the official website, they can deploy it via personal computers or cloud servers and connect it to mainstream communication tools like WhatsApp, Telegram, Discord, and WeChat Work. With just voice or text commands, it can complete a series of complex tasks.
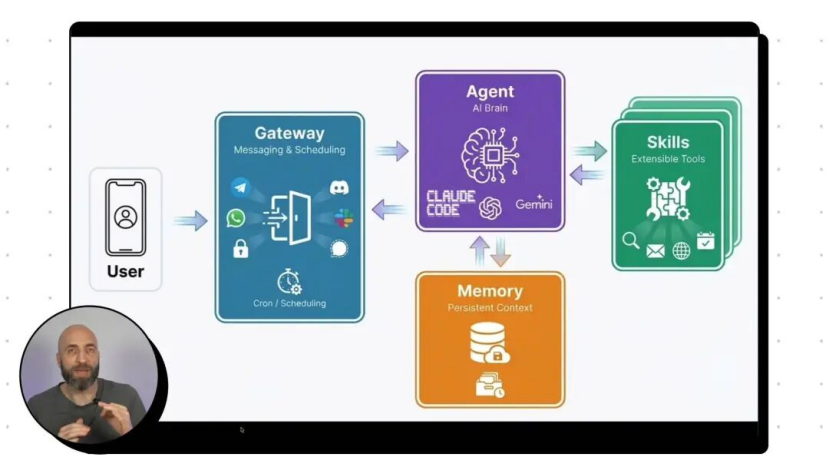
Supporting these powerful functions are four core components meticulously designed by Clawdbot:
① Gateway: The system's hub, responsible for connecting various chat platforms and coordinating information flow between AI and the external world, enabling users to remotely control devices through familiar chat windows.
② Agent: Driven by large models such as Claude, GPT, and DeepSeek, it handles context understanding, memory, and reasoning tasks, serving as the AI's [brain].
③ Skills: Extensible functional plugins covering web research, browser automation, file reading and writing, scheduled tasks, etc., equipping the AI with diverse [skills].
④ Memory: File-based persistent storage that saves conversation history, user preferences, and other data, enabling [long-term memory] and improving understanding of users over time.
More critically, Clawdbot achieves breakthroughs in cross-platform collaboration and proactive services.
It eliminates the need for users to open dedicated apps; the chat window serves as the interaction entry point. It can not only passively respond to instructions but also proactively trigger tasks.
Clawdbot is not about [making Agents smarter] but about [making Agents replicable, scalable, and controllable like industrial systems].
Traditional Agent design assumes that if the model is smart enough, it can handle everything.
Clawdbot, however, takes the opposite approach by intentionally [limiting intelligence] and strengthening execution.
① Strongly constrained task boundaries: Agents are no longer encouraged to [improvise] but operate around clear, structured objectives.
② Explicit state machine design: Every task stage is traceable, interruptible, and replayable.
③ Results-first, rather than reasoning-first: Reasoning is merely an intermediate process; what ultimately matters is delivering [deterministic results].
This makes Clawdbot more akin to an [automation execution engine] than a [thinking chatbot].
Chain Reactions Behind the Craze
The most direct impact has been felt in the hardware market. Since Clawdbot requires 24/7 operation and GUI support is limited to macOS, the compact, quiet, and low-power Mac mini has become the optimal choice.
A large number of users have placed orders specifically to deploy Clawdbot, leading to sellouts of the Mac mini in multiple regions worldwide and significant price increases in the secondhand market.
Some geeks have even stacked multiple Mac minis on their desks to create [private AI computing centers], forming a unique technological spectacle.
However, Steinberg quickly clarified: [Stop giving Apple your money; any device capable of running Node.js can deploy Clawdbot.].
In reality, a VPS cloud server costing $5 per month or an old idle computer at home can meet the operational requirements. The Mac mini buying frenzy is more a result of irrational consumption fueled by community enthusiasm.
Even so, this [endorsement effect] has unexpectedly benefited Apple and highlighted the potential of AI Agents to drive hardware demand.

The capital market reacted even more swiftly. On January 27, 2026, the first Hong Kong stock trading day after Clawdbot went viral, MiniMax, recommended by Steinberg as a Claude alternative, saw its stock price surge by 26.48%, with a market capitalization exceeding HK$150 billion, setting a new all-time high. [Global Large Model First Stock] Zhipu also rose by 7.56%.
In the U.S. stock market, network infrastructure stock Cloudflare saw a cumulative 18% increase over two days, while the cloud computing sector continued to climb. Concept stocks related to computing power, storage, and CPUs were generally favored.
Industry analysts believe that large-scale Agent deployment will shift computing power demand from training-intensive to inference-intensive. Demand for memory/storage with high random read-write capabilities and low latency will explode, while also driving server CPU demand.
Given the current CPU supply shortage and rising storage prices, Clawdbot's viral popularity may further exacerbate supply-demand imbalances and push up prices of related hardware.
Tech giants' follow-up moves confirm industry trends. Domestic cloud providers such as Tencent Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, and UCloud quickly launched one-click Clawdbot deployment services. UCloud even developed a WeChat Work channel overnight to address the pain point of domestic users being unable to use overseas communication tools.
The Future of AI Agents: Disruption or Integration
Clawdbot's viral success has brought profound insights to the AI industry. It marks the transition of AI product forms from scenario-level assistants to system-level Agent platforms, opening up new technological paradigms.
① Evolution of Product Forms: From Assistance to Execution
Clawdbot's core breakthrough lies in breaking down the [wall] between AI and real-world operations.
Traditional AI can only provide suggestions or generate content, whereas Clawdbot autonomously decomposes tasks, collaborates across systems, and executes specific operations, achieving a closed loop from [goals to results].
This [quasi-autonomous productivity] characteristic upgrades AI from a tool to an execution entity, significantly expanding its application boundaries.
Market attention is shifting from model parameter scale to [whether it can stably invoke external tools, decompose complex tasks, and complete real business processes].
② Restructuring of Industrial Structures: Dimensionality Reduction Attack on the Application Layer
Clawdbot's open-source nature enables individual developers to leverage large model capabilities and rapidly create multi-scenario Agent applications, posing a dimensionality reduction attack on traditional application-layer enterprises.
Steinberg admits that he no longer needs to open traditional browsers for most scenarios. As Agents become ubiquitous, the way humans interact with services will fundamentally change. Many single-function applications will be simplified into API interfaces, weakening the intermediary role of traditional application layers.
However, this does not mean traditional software will be replaced. A more likely trend is that Agents will become the [intelligent interaction and automation hub] of software, while traditional SaaS and software systems continue to handle underlying business logic and data infrastructure.
Agents act as [software value amplifiers], boosting overall efficiency through automated processes rather than completely disrupting the existing ecosystem.
③ Explosion of Individual Productivity: [Solo Combat] in the AI Era
Clawdbot's success validates the amplification effect of AI on individual productivity.
Steinberg, relying solely on himself and AI tools, completed project development in just 10 days, achieving efficiency comparable to a professional team.
This means that in the AI era, the ceiling for individual developers has been shattered. As long as one understands requirements and grasps model logic, it is possible to create products with industry influence.
In the future, there will be an increasing number of high-quality Agent applications developed by individuals or small teams to solve specific problems. The core competitiveness of large platforms will shift from application development to providing model foundations + security architectures and ecological support.
④ Breakthrough Direction for AI PCs: From Gimmicks to Intelligent Terminals
Currently, the AI features promoted by PC manufacturers are mostly gimmicks like knowledge base searches and meeting minutes. However, Clawdbot demonstrates the potential for deep integration of AI and PCs.
Transforming PCs into personal data centers that enable local data management, cross-platform collaboration, and automated task execution through Agents, truly making them intelligent terminals.
In the future, the core competitiveness of AI PCs will no longer lie in hardware parameters but in AI Agent ecological adaptability.
Can they provide a secure local operating environment, open skill expansion interfaces, and seamless cross-platform interaction experiences? Hardware products that refuse to open up AI access may be eliminated by industry trends.
Conclusion:
Clawdbot's rise to fame is propelling the entire Agent sector from the conceptual stage to the brink of scalability.
When Agents reach this point, scalability is no longer a vision but merely a matter of time. And 2026 stands right at the center of this timeline.
Partial References: AGI from TMTPost: "The Viral Clawdbot: Is It the Next ChatGPT?", Geek Park: "Clawdbot: The 'Greatest AI Application So Far' May Not Be for You", Tencent Tech: "Clawdbot Has No Commercial Value Yet, But It's Teaching 'Gimmicky' AI PCs a Lesson", APPSO: "The Clawdbot That Made Mac mini Orders Skyrocket Overnight Is What Apple's AI Siri Aspires to Be", AGI Interface: "Clawdbot Renamed to Moltbot: Why It Went Viral in Silicon Valley"]