Intel unleashes its power! Will Core Ultra 200S ignite the AI PC market?
![]() 10/11 2024
10/11 2024
![]() 539
539
Recently, Intel unveiled its latest generation of Core series processors. Unlike previous generations, these are not named after familiar digit-based generations but instead belong to the all-new Ultra series. As Intel's next-generation processor designed specifically for AI PCs, the Core Ultra 200S series differs significantly from traditional CPUs in terms of architecture and design.
LeiTech was invited to participate in Intel's relevant technical communication meeting on October 8th, giving us an early glimpse of this new processor. However, a detailed review will not be available until October 24th, at which time we will promptly publish our assessment.
Introducing Arrow Lake: Ushering in a New Era for Core Processors
If Alder Lake marked the beginning of the hybrid architecture era, Arrow Lake heralds a new era for hybrid architectures.

Source: Intel
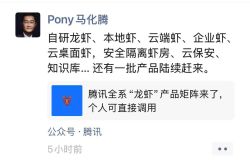
In Arrow Lake, Intel continues the modular design first experimented with in the Meteor Lake architecture. This approach involves splitting the various functions of the processor into independent modules: computation modules (P-Core and E-Core), an integrated graphics module (Xe-LPG), and an NPU specifically for AI acceleration, among others.
Source: Intel
The modular design not only facilitates targeted adjustments and optimizations for individual modules by engineers but also accelerates the entire chip design-to-production process. It also provides engineers with more room for creativity, enabling them to design processors tailored to different application scenarios.
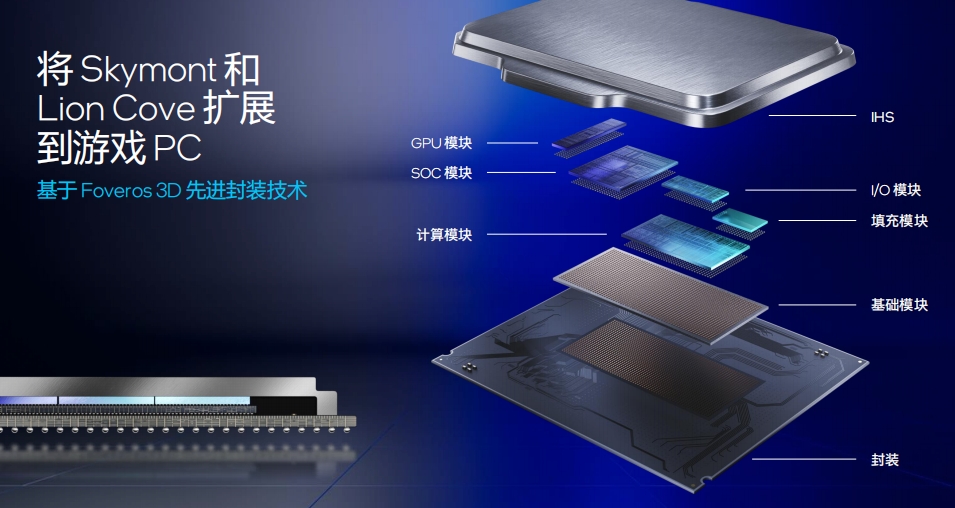
In other words, with the Arrow Lake architecture, we may see more customized models. However, Intel officially sells only three series: Ultra 9, Ultra 7, and Ultra 5. The specifications of the announced processor models are as follows:
Source: Intel
Long-time PC enthusiasts may notice an apparent question: why are the core and thread counts the same? That's right, one of the novel designs in the Arrow Lake architecture is the elimination of hyper-threading, adopting a single-core, single-thread design. Although there are still big and small cores, they differ primarily in parameters like clock speed, with the same thread count.
Additionally, apart from clock speed and other parameters, the AI computing power data of the NPU is also listed. Core Ultra 200S is Intel's first desktop processor equipped with an NPU, providing users with AI computing support without the need for a dedicated graphics card.

Source: Intel
Regarding clock speed, it's fair to say that compared to the 14th Gen Core, Arrow Lake is more conservative. Even the Ultra 9 285K has a maximum clock speed of only 5.7GHz, not much higher than the Ultra 7 265K. The primary difference lies in the core count, with the U9 boasting four additional E-cores for better performance in creative work.
In gaming, the performance gap between the two is likely to be minimal. However, the Ultra 9 285K offers higher overclocking potential, and the Core Ultra 200S series has been heavily optimized for overclocking, complete with a new generation of overclocking tools. Users can further tap into the processor's performance as needed.

Source: Intel
In terms of integrated graphics, Arrow Lake incorporates the Xe-LPG graphics module. Compared to its predecessor, while the number of graphics cores has been reduced, hardware acceleration for encoding and decoding has been further enhanced. Arrow Lake becomes the first desktop processor to support Sony's 8K XABC codec, empowering video creators and content producers with stronger tools even on PCs without dedicated graphics cards.
Moreover, Arrow Lake supports instruction extensions like AVX and VNNI, boasting up to 36 TOPS of AI computing power. This means that in addition to the AI computing capabilities of the NPU, the CPU can also effectively handle corresponding AI workloads, further expanding AI use cases and lowering the entry barrier for AI PCs.
What Significance Does the Soaring Energy Efficiency Ratio of Core Ultra 200S Hold?
The modular design combined with the all-new architecture significantly enhances the energy efficiency of Core Ultra 200S. At half the power consumption, Arrow Lake delivers comparable performance to the previous-generation Raptor Lake. While desktop PC users may not have paid much attention to CPU power consumption in the past, that's all changing now. As CPU power consumption rises, energy efficiency becomes a pressing concern for desktop PC enthusiasts.
Therefore, whether to enhance user experience or contribute to environmental protection, the improved energy efficiency ratio of Core Ultra 200S is worth celebrating. According to official data, the overall power consumption decreases by approximately 40% under equivalent watts-per-performance, meaning the same performance previously achievable at 100W can now be attained at just 60W.
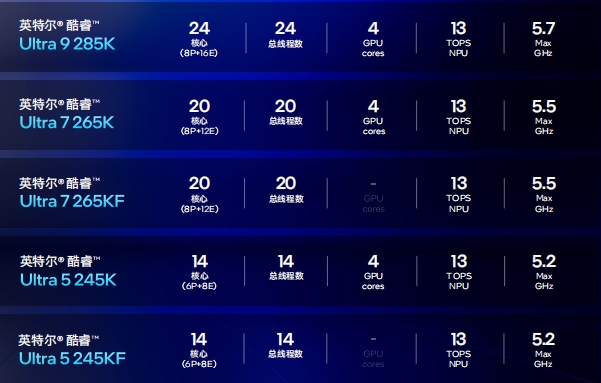
Based on Intel's actual test data, the Ultra 9 285K delivers gaming performance comparable to the i9-14900K while consuming 80W less system power. In multiple gaming benchmarks, the Ultra 9 285K achieves an average power savings of 73W and a maximum savings of 165W at the same framerate.
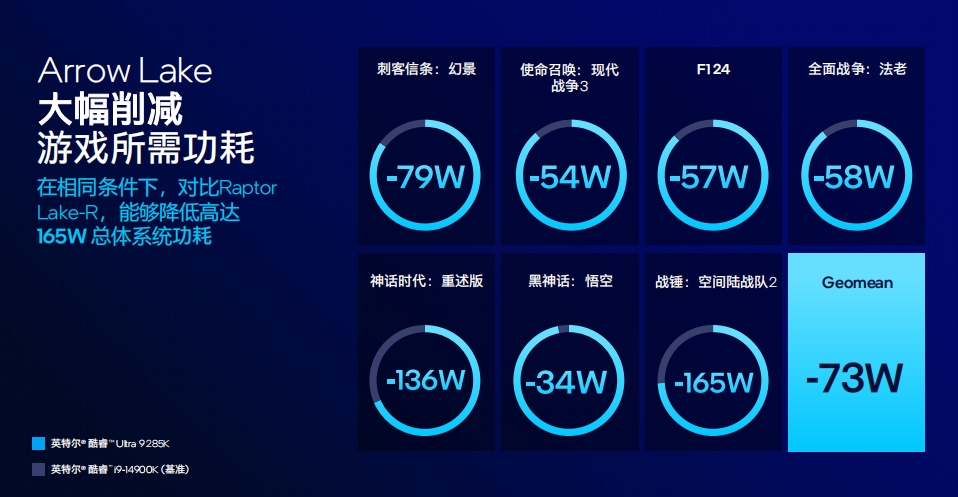
Source: Intel
If you find these test results extreme, consider the 1080P benchmarks. In mainstream games like Final Fantasy XIV, Assassin's Creed Mirage, and Call of Duty: Modern Warfare III, the Ultra 9 285K runs at least 10°C cooler than the i9-14900K, with peak temperatures generally below 60°C.

Source: Intel
Behind this 'coolness' lies a significant reduction in the cost of the cooling system. While top-tier 360mm water cooling was once necessary, now even a standard 360mm water cooler can tame the mighty Ultra 9 285K while delivering gaming performance on par with the i9-14900K.
Furthermore, this suggests that processors like the Ultra 9 285K have untapped potential, delivering more stable performance during extended rendering and modeling tasks. As the heart of any PC, CPU stability is crucial, explaining why Intel emphasizes energy efficiency as a key selling point. In subsequent tests, we will also overclock the Ultra 9 285K and other processors; stay tuned.
Can Intel's Power Move Reshape the PC Market Landscape?
With the release of Arrow Lake, Intel is driving the desktop processor market towards higher energy efficiency and smarter computing. The modular design and inclusion of AI accelerators allow chip manufacturers to flexibly meet the needs of diverse user groups, designing tailored processors for specific applications.

Source: Intel
For instance, high-performance gaming PCs can adopt configurations with more P-cores, while content creation PCs can enhance multi-core performance and maintain better energy efficiency by adding E-cores. Moreover, by modifying the integrated graphics and NPU, different types of desktop PCs, such as compact AI PCs and small form factor video decoding PCs, can be designed.
As AI applications gain popularity, the demand for compact AI PCs is soaring. Arrow Lake's improved energy efficiency and reduced temperatures will further propel the development of compact, high-performance desktops and all-in-ones.
Intel has planned to deliver 100 million CPUs with built-in AI capabilities by the end of 2025. By leveraging the Meteor Lake, Lunar Lake, and Arrow Lake series, Intel aims to become the most competitive AI PC supplier in the market.
Intel's Core Ultra 200S series processors, with their novel modular architecture and cutting-edge packaging technology, have achieved remarkable breakthroughs in energy efficiency, AI acceleration, and gaming performance. By efficiently combining P-cores and E-cores and leveraging the AI acceleration provided by the built-in NPU, Arrow Lake sets a new benchmark for desktop processors. For users seeking high performance and energy efficiency, Arrow Lake is an excellent choice.
With Intel's push into the desktop AI PC space, the curtain has risen on the next generation of desktop computing competition. Future PC processors will evolve beyond mere computing tools, transforming into intelligent, energy-efficient, and scalable AI-assisted devices.
Cover Image Source: Intel
Source: LeiTech