Amazon Web Services Launches a Comprehensive Array of Solutions to Empower Enterprises with One-Stop Agent Implementation
![]() 12/05 2025
12/05 2025
![]() 612
612

At the annual "Cloud Computing Gala"—the Amazon Web Services re:Invent 2025 conference—AI Agent stole the limelight, emerging as the undisputed star of the show.
From Amazon Web Services CEO Matt Garman to Swami Sivasubramanian, Vice President of Agentic AI at Amazon Web Services, extensive discussions were centered around AI Agent, highlighting its significance.
This clearly sends a strong message to the world: In the era of Agentic AI, AI Agent has shifted from being a mere option to a necessity.
"Agentic AI is at a pivotal juncture, transitioning from a 'technological marvel' to a 'practical value tool.' In the future, billions of Agents will permeate various industries, helping enterprises achieve a tenfold leap in efficiency!" Matt Garman proclaimed in his opening speech.

It's evident that an increasing number of AI technologies are making their way into the industrial sector. However, enterprises are grappling with the challenges of 'difficult setup, chaotic management, and costly implementation.' 'Why can't these outstanding Agents be deployed in production environments?' This is a common question among many business leaders.
The root cause of this issue lies in the fact that most experimental AI technology projects were not designed with 'production readiness' in mind from the outset. "We need to bridge this gap and truly break free from the PoC (Proof of Concept) cage of AI technology," Swami remarked.
So, how can Agents truly become productivity tools rather than just technological gimmicks?
As a global leader in cloud computing, Amazon Web Services provided answers at this conference.
At the Amazon Web Services re:Invent 2025 conference, Amazon Web Services showcased its full-stack capabilities in the Agentic AI domain, covering everything from underlying chip and computing network infrastructure to intermediate model training and development tools, and onto upper-layer Agent applications.
The emphasis was on providing a true 'out-of-the-box' toolkit for anyone looking to ride the AI wave.
"The future of AI Agent lies not in doing everything, but in doing everything reliably," Swami said. "And Amazon Web Services is the best platform for building and running AI Agents."
From 'Capable of Setup' to 'Effective Management': The Revolution of Enterprise Agent Implementation
An increasing number of enterprises are beginning to apply AI Agents to real-world business scenarios.
For instance, The Ocean Cleanup leverages AI technology to optimize plastic detection models, predict garbage movement trajectories, and maximize cleanup efficiency, ensuring operations in the most critical global regions. The Allen Institute develops neural network models to analyze single-cell multimodal brain cell data, hoping to unlock breakthrough therapies.
However, the reality is that constructing and deploying these outstanding Agent systems on a large scale poses greater challenges than the AI problems they aim to solve.
So, how can enterprises easily build reliable, precise, and scalable Agent systems?
Generally, an Agent consists of three core components:
First, the foundational model, which acts as the Agent's brain, responsible for reasoning, planning, and execution.
Second, the code, which defines the Agent's 'identity,' clarifies its capabilities, and guides the decision-making process.
Third, the tools, which are crucial for the Agent's 'practical effectiveness' and can be seen as the Agent's 'limbs.'
To truly unleash the potential of an Agent, these components must work together seamlessly. However, "integrating these AI components used to be an extremely cumbersome and fragile process," Swami said. "We hope that in the new world, building Agents will become a simpler task, where developers only need to define the three core components: model, code, and tools."
Based on this vision, Amazon Web Services developed and open-sourced the model-driven AI Agent framework, Amazon Strands Agents SDK, and introduced it to the TypeScript platform, enabling developers to build complete Agent stacks using Amazon SDK in TypeScript. Additionally, it added support for edge devices, allowing AI Agents to run on small devices and covering a wide range of application scenarios from automobiles and game consoles to robots.
In Swami's view, developers across various industries are attracted to the simplicity and scalability of this framework. "In just a few months, the download count for Amazon Strands Agents SDK has exceeded 5 million."
If Amazon Strands Agents SDK makes it easier and faster for developers to build Agents, then Amazon Bedrock AgentCore makes large-scale Agent deployment feasible.
Typically, many AI technologies at the PoC stage often have limited functionality and lack modularity, forcing developers to write custom logic to piece together these solutions, ultimately turning excellent models into maintenance nightmares.
Amazon Web Services' Amazon Bedrock AgentCore platform supports enterprises in building and deploying Agents securely in large-scale environments.
Although Agents possess the ability to reason and act autonomously, offering immense value, enterprises must establish robust control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized data access, inappropriate interactions, and system-level errors that could impact business operations. Even with carefully designed prompts, Agents may still make mistakes in practical applications, leading to severe consequences.

Therefore, among the latest updated features of Amazon Web Services' Amazon Bedrock AgentCore, the Policy function helps teams set clear boundaries for Agent tool usage, while the Evaluation function allows teams to understand Agent performance in real-world scenarios.
When used together, they can create enterprise-level Agents that possess autonomy while adhering to behavioral boundaries.
Furthermore, most current AI Agents still exhibit significant shortcomings in 'memory' capabilities. To make Agents more practical and overcome the threshold of performing complex tasks, a critical issue that must be addressed is long-term memory capacity.
AgentCore Memory fills this crucial capability gap, enabling Agents to form a coherent understanding of users over time. It introduces new contextual functions that help Agents learn from past experiences (context, reasoning, operations, and outcomes), allowing AI to gradually build a coherent understanding of users and deliver more intelligent decisions.
These Agent development platforms support enterprises in independently building Agents and rapidly achieving large-scale deployment and application. In addition to these platforms, Amazon Web Services also launched three standalone Agent products that can be directly applied in enterprise processes.
For example, Amazon Web Services' Kiro Autonomous Agent is designed specifically for software development and is defined by Swami as the 'AI colleague for developers.' The core breakthrough of Kiro Autonomous Agent lies in transitioning from 'passive execution' to 'proactive planning.' Through the 'specification-driven development' concept and persistent contextual memory capabilities, it can independently handle complex programming tasks for hours or even days after learning from humans.
"When enterprises deploy hundreds of Agents, security and failure risks grow exponentially," Swami warned in his speech.
Therefore, Amazon Web Services simultaneously introduced Amazon Security Agent and Amazon DevOps Agent, which serve as the 'virtual security engineer' and 'virtual operations expert,' respectively, upgrading traditional passive response modes to proactive management systems.
It's evident that Kiro Autonomous Agent, Amazon Security Agent, and Amazon DevOps Agent collectively usher in a new era of software development. These cutting-edge Agents not only enhance team efficiency but also fundamentally redefine what is possible when AI serves as an extended force within the team: automatically delivering partial outcomes throughout the software development lifecycle.
From simple, scalable platforms supporting large-scale, secure Agent deployments to Agent tools that can be directly integrated into enterprise business processes, Amazon Web Services has provided comprehensive service capabilities for the implementation of enterprise-grade Agents, developing practical 'limbs.'
Agent 'Brain': Choosing the Right Model and Enabling Customization
For enterprise-grade Agents, the 'limbs' are crucial for operation, while the 'brain' is vital for decision-making.
The 'brain' of an Agent derives from the capabilities of the foundational large model. To build a useful and efficient Agent, it's not enough to merely select a good foundational model; for enterprises, the ability to customize according to their business needs has become equally critical.
Unlike other cloud computing vendors that primarily promote a single foundational model, Amazon Web Services has always maintained an open approach, adhering to the principle that 'model selection trumps everything,' allowing global mainstream large models to run seamlessly.
As a result, Amazon Bedrock integrates the world's leading large model products, offering users a rich and diverse range of model choices, covering open-source models, general-purpose models, and specialized models.
This time, Amazon Bedrock also introduced several latest open-source models, including Google's Gemma, NVIDIA's Nemotron, and the latest models from Chinese large model vendors KIMI and Minimax.
Of course, in addition to external models, Amazon Web Services' self-developed large model product, the Amazon Nova family, has also received updates, launching four versions of the Amazon Nova 2 series.
Beyond model selection, more importantly, Amazon Bedrock provides enterprises with model fine-tuning services.
For instance, its latest updated Reinforcement Learning Fine-Tuning (RFT) can improve model accuracy by 66% compared to the foundational model, significantly lowering the barrier to model customization. Model Distillation, which focuses on specialized training for specific tasks, aims to create smaller and faster models, delivering a 10x speed increase while retaining 95%-98% of the performance.
However, Swami also admitted that although Amazon Bedrock provides enterprises with simple yet powerful model fine-tuning methods, many enterprises still need to customize models and hope to train large models using their own data to build competitive barriers.
After all, "no matter how good a general-purpose model is, it cannot replace an enterprise's proprietary data," Swami said.
This primarily involves two challenges: one is how to fine-tune the foundational model based on technology, and the other is how to fully and securely integrate proprietary data into the foundational model.
To address these two issues, Amazon Web Services launched two new products:
First is Amazon SageMaker, which provides enterprises with all the capabilities needed to 'build, train, and deploy exclusive AI models (proprietary AI models),' supporting large models of any scale.
According to reports, Amazon SageMaker AI supports all customization techniques, including 'model distillation, supervised fine-tuning, and direct preference optimization (DPO),' enabling 'full-weight training' or 'parameter-efficient fine-tuning' to meet the needs of any enterprise business scenario. With the comprehensive capabilities of SageMaker AI, enterprises can shorten the 'idea-to-production' cycle from 'months to days.'
Take the Indian company Dunn as an example: They required a large language model that 'deeply understands the complexities of the Indian financial market.' Using Mistral-7B as the foundational model, they built a proprietary model called 'Arthur M' (with 7 billion parameters). Throughout the process, they used Amazon SageMaker AI for model building and training, leveraging Bedrock for foundational model support.
"Ultimately, this customized model could run on a single GPU, outperforming existing top models in 88% of scenarios while operating at a fraction of the cost," Swami said.
Second is Amazon Nova Forge, which provides enterprises with access to full-stage training checkpoints of the Nova model, from pre-training to post-optimization. Enterprises can inject their proprietary data at any stage, mixing it with Amazon's curated datasets for hybrid training to create exclusive 'Novellas' (proprietary) models.
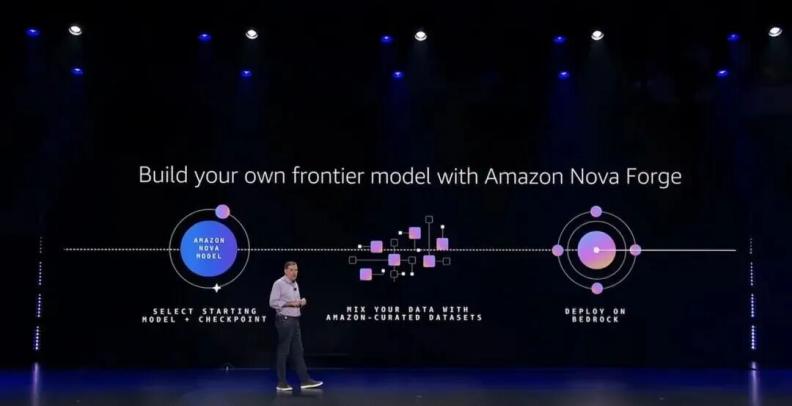
This is akin to building a house where enterprises can incorporate their own designs at any stage—whether laying the foundation, constructing the framework, or handling the interior decoration—rather than renovating an existing house.
In terms of functionality, Amazon Nova Forge offers three core capabilities:
First, custom reinforcement learning 'gym' (training environment). Enterprises can use their own business scenarios to construct reinforcement learning environments (i.e., 'gyms'), allowing models to continuously learn and optimize in highly realistic simulated scenarios.
Second, building smaller, faster, and cost-effective models. Customers can use synthetic data distillation methods to train smaller and more efficient models using examples generated by larger models, significantly reducing costs and latency while preserving intelligence levels as much as possible.
Third, a responsible AI toolkit. Nova Forge provides a suite of responsible AI tools to help customers implement safety controls during model training and application deployment, meeting compliance and governance requirements.
It is reported that currently, numerous enterprises or institutions, including Booking.com, Cosine AI, Nimbus Therapeutics, Nomura Research Institute, OpenBabylon, Reddit, and Sony, have already started leveraging Nova Forge to build exclusive models that better meet their specific needs.
Once enterprises have constructed their own cutting-edge models through Amazon Nova Forge, they can deploy them on Amazon Bedrock, enjoying enterprise-level security, scalability, and data privacy protection consistent with other Amazon Bedrock models.
Through this end - to - end solution—spanning from the in - house development of cutting - edge models to their deployment in production environments—enterprises can attain optimal AI performance that is precisely tailored to their specific business requirements. Moreover, they can securely host and exclusively own their model assets on Amazon Web Services (AWS).
"Our aim is to make models widely available,"
Swami highlighted that even enterprises lacking profound AI technical expertise can accomplish customization via Amazon Bedrock's low - code interface. This approach can significantly shorten training cycles from months to days and slash costs by 70%.
At present, as we step into the era of AI Agents, a growing number of enterprises are shifting their focus from "what to build" to "how to build it swiftly." In light of this trend, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is safeguarding the implementation of enterprise - level Agents through its full - stack, integrated capabilities.
If Agents represent the ultimate product form of AI applications and large models function as the "brain," then computing power serves as the "heart" that underpins everything.
As a frontrunner in global cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has already established a fundamental computing power infrastructure system that encompasses everything from chips to intelligent computing clusters. Now, AWS is breaking through the computing power bottlenecks hindering enterprise AI implementation through a dual - engine computing power system that combines "self - developed chips + ecological collaboration." This system achieves triple breakthroughs in performance, energy efficiency, and scalability, while simultaneously reinforcing its advantages in computing power infrastructure for the AI era.
On one hand, from the perspective of underlying chips, at the conference, Matt Garman announced the official launch of Amazon Trainium3 UltraServers, the first server from Amazon Web Services (AWS) equipped with a 3 - nanometer process AI chip.
Compared to Amazon Trainium2, it not only enhances computing power by 4.4 times and memory bandwidth by 3.9 times but also achieves a five - fold increase in the number of AI tokens processed per megawatt of computing power. The server's maximum configuration includes 144 chips, delivering an astonishing 362 Petaflops of FP8 computing capability. When running OpenAI's GPT - OSS - 120B model, it generates over five times the number of tokens per megawatt compared to Amazon Trainium2, achieving ultra - high energy efficiency.

In addition to Amazon Trainium3 UltraServers, Matt Garman also unveiled the Amazon Trainium4 chip for the first time. It promises to deliver six times the FP4 computing performance, four times the memory bandwidth, and twice the high - memory capacity compared to Amazon Trainium3, continuously solidifying Amazon Web Services' (AWS) long - term excellence in the AI chip field.
Currently, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has completed the large - scale deployment of over 1 million Amazon Trainium2 chips, providing core computing power support for most inference workloads in Amazon Bedrock, including the efficient operation of the latest generation of Claude models.
Apart from its self - developed chip products, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has been collaborating with NVIDIA for 15 years and was the industry's earliest provider of NVIDIA GPU services in the cloud. This deep - seated partnership enables enterprises to access mature computing power solutions that have been "validated by top - tier clients."
In a nutshell, a review of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) re:Invent 2025 conference reveals that, in the face of the era of AI Agents, its core competitiveness does not lie in a single product but in the dual advantages of "vertical integration + open ecosystem":
At the underlying level, it controls computing power pricing and delivery capabilities through self - developed chips (Trainium) and a global infrastructure.
At the middle level, with Bedrock as the hub, it caters to diverse needs through an open model ecosystem and deeply binds customers with customized tools (Nova Forge).
At the upper level, through AgentCore and industry - specific Agents, it bridges the "last mile" from models to applications.
This layout effectively addresses three major pain points in enterprise AI transformation: high computing power costs, difficulty in model adaptation, and significant implementation risks.
As cloud computing enters the "AI - native" era, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is demonstrating with its full - stack capabilities that a true AI leader must not only provide technology but also build an ecosystem that generates value from it.
From chips to models, from data to Agents—Amazon Web Services (AWS) is constructing a complete AI value closed loop, empowering enterprises to truly leverage intelligent transformation.
As indicated by the 20% growth rate behind Matt Garman's announcement of $132 billion in annual revenue, amid the wave of AI - driven industry restructuring, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is not just a participant but also a rule - maker.