Can vivo Vision, Weighing Just 398 Grams, Bridge the Divide Between the Digital and Physical Worlds?
![]() 08/24 2025
08/24 2025
![]() 642
642

Key Points:
1. Celebrating its 30th anniversary, vivo officially unveiled the vivo Vision mixed reality headset exploration edition. This headset signifies a significant milestone in machine vision capabilities and a pivotal step in vivo's mission to bridge the digital and physical worlds.
2. For vivo, mixed reality (MR) transcends a single hardware product. Its strategic vision envisions smartphones as personal brains, MR as digital avatars, and robots as physical surrogates, collaborating seamlessly over the next decade.
3. vivo views MR as the "brain + eyes" of home robots, focusing on the "cognition-decision" hub to overcome technical challenges.
4. vivo's launch of the Vision product is underpinned by strengths in strategic perseverance, tactical endurance, and industrial synergy.
Author: Chang Yuan
Editor: Key Points Master
From corded phones to feature phones, and from smartphones to the Internet of Everything, vivo has consistently been a key player in the mobile industry. Navigating numerous industry shifts, vivo has not only maintained stability but also secured top market share in China for several consecutive years.
Now, with the advent of the AI era, the evolution logic and limitations of smart hardware in the Moore's Law era have been disrupted, sparking a new revolution in consumer technology products such as smartphones, PCs, and tablets. vivo's every move has precisely addressed "what users need," and its explorations in the AI era offer valuable insights.
At the 2025 Boao Forum for Asia Annual Conference, vivo Executive Vice President Hu Baishan announced the establishment of a robot lab, positioning robots strategically alongside smartphones, fully deploying physical AI.
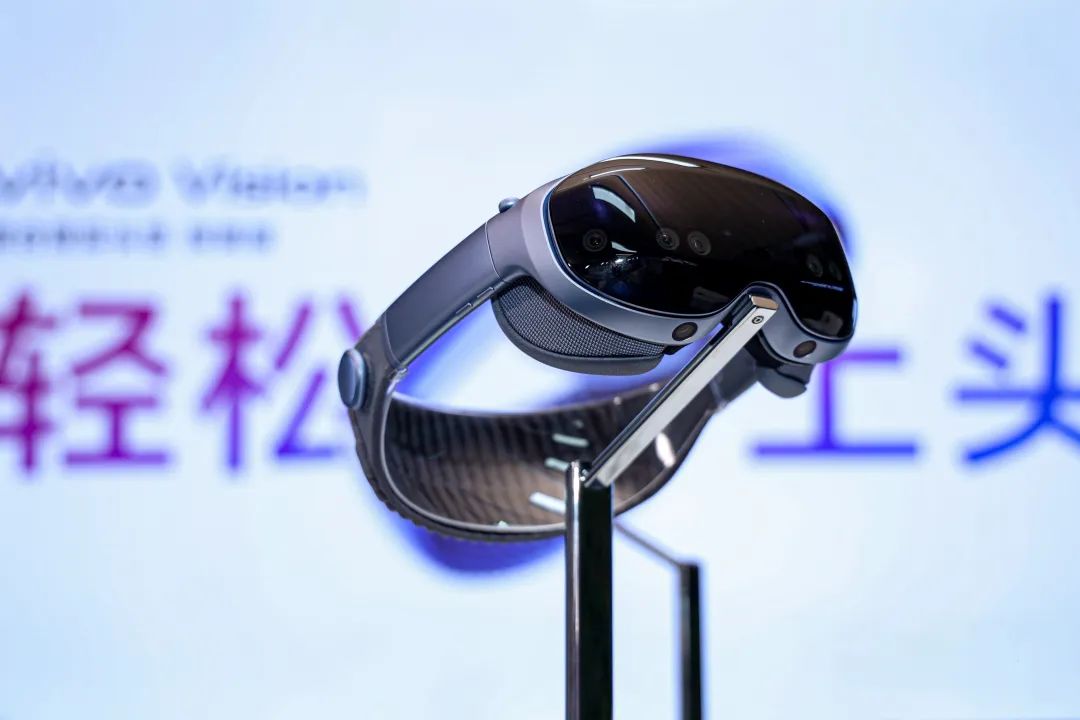
On August 21st, marking its 30th anniversary, vivo officially launched the vivo Vision mixed reality headset exploration edition, weighing a mere 398 grams with a latency of just 13ms. Instead of emphasizing specifications, this product prioritizes core experiences like lightweight design and localization, aiming to address current MR industry pain points like discomfort and lack of content.
Centered around human needs, with humans at the core, AI, imaging, and MR capabilities will initially meet users' demand for large-screen immersion. In the long term, they will serve as robots' eyes and brains, overcoming the "perception-decision" challenges in unstructured home environments. vivo is paving the way for home robots to enter thousands of households.
From vivo's technology strategy perspective, this headset represents a significant achievement in machine vision capabilities and a crucial attempt to bridge the digital and physical worlds.
01 The User Logic Behind 398 Grams

Over the past 30 years, screen media has undergone three significant iterations, from TVs to smartphones to MR headsets. MR satisfies users' quest for the ultimate experience, evolving and supplementing smartphone scenarios.
MR headsets are also bridging the physical and digital worlds, subtly transforming the technological landscape of future lifestyles. Designers from Ford and Volvo use MR headsets to sketch new car designs, placing virtual models directly in workshops. Surgeons from tertiary hospitals utilize MR devices to simulate surgical scenarios, accelerating medical advancements. Tour guides at the Forbidden City employ MR glasses to take tourists on a "time travel" experience, bringing the honor guard of the Hall of Supreme Harmony from a century ago to life.
Technologically, traditional VR headsets are evolving towards MR. According to incomplete statistics, half of the 17 VR/MR products released in 2024 are MR devices.
Market data reveals a compelling story: IDC predicts that global shipments of smart headsets will reach 12.8 million units by 2025, with the Chinese market growing even more dramatically, increasing by 107% to 2.75 million units. TrendForce estimates that global VR/MR shipments may exceed 37 million units by 2030.
Faced with this vast potential, global tech giants have made early moves. Apple uses Vision Pro to build a spatial computing ecosystem, aiming to replicate the iPhone's closed ecosystem in the MR field. Meta (formerly Facebook) dives into gaming and social media with the Quest series, continuing the metaverse narrative. ByteDance's Pico focuses on domestic short videos and live streaming, bringing mobile content to headsets.
However, a practical question lingers: Are these devices necessities or niche "geek toys"?
According to Boyan Consulting, MR applications currently account for over 47.5% in education and healthcare alone, with entertainment accounting for just 18.7%. This suggests that most MR headsets are used for online classes or medical demonstrations, with killer applications yet to emerge. Additionally, MR headsets generally weigh around 600 grams, causing discomfort like facial pressure, forward tilting, and stuffiness, as well as movement inconvenience.
The industry has overly focused on "showing off skills" while neglecting to solve users' real problems. Some products stack specifications, increasing resolution at the expense of weight. Others build closed ecosystems, compatible only with their own applications. Still, others bet on the metaverse, ignoring real-world vertigo issues.
Unlike most brands that prioritize "showing off skills," vivo Vision's starting point is always "what users really need." Each decision aims to solve practical problems rather than purely pursue technological demonstrations.
In content development, vivo Vision reconstructs the experience based on user scenarios. It offers immersive viewing experiences through 180-degree video, giant screen movie watching, and spatial photos/videos. It provides surreal entertainment through customized MR games, VR games without external devices, and giant screen projection of tabletop/mobile games. It enhances office efficiency with features like spatial multitasking, ultra-immersive environment themes, and VST see-through functionality.
While ensuring practical functionality, vivo Vision also emphasizes ease of use. Reducing headset weight is a crucial direction of its R&D. Leveraging 30 years of world-class supply chain integration, industrial design, and deconstruction/stacking optimization capabilities, vivo strategically places components like batteries and modules in an ultra-thin space, selecting materials like aviation-grade aluminum alloy and thinner Micro-LED screens, resulting in the world's ultra-lightweight headset weighing just 398 grams.
vivo Vision continuously improves wearing comfort. Its human factors laboratory, based on a vast database of Chinese head shapes, has designed 4 different face masks and 8 types of foam, providing customized wearing experiences for Chinese users.
For vivo, MR is more than just a hardware product; it's a key product that, alongside smartphones and robots, will enter thousands of households. vivo's strategic vision envisions smartphones as personal brains, MR as digital avatars, and robots as physical surrogates, collaborating seamlessly over the next decade.
02 Focusing on Home Robots, Bridging the Gap with MR Capabilities

If large AI models can understand user needs, possess thinking capabilities, and autonomously mobilize websites or apps to complete tasks, representing the digital world's future, then humanoid robots that understand spatial relationships and interactive behaviors in the physical world, achieving human-like precision and control, represent the physical world's future.
Among global tech giants, Samsung made an early move in robotics: in 2012, it showcased the humanoid robot Roboray at the Portuguese IROS exhibition. Apple has been involved in robotics technology since 2019, spanning indoor drones to household robots. After shelving its car-making plans, the strategic importance of home robots has been further elevated. Huawei's robotics exploration dates back to 2017, with a direction similar to the automotive field: instead of directly producing robots, it empowers enterprises through platforms for robot manufacturing, development, integration, and use, leveraging the capabilities of the Pangu large model to support the intelligent development of humanoid robots.
In China, startups have mushroomed, with robots from companies like Zhiyuan, Unitree, and Yinhe Universal emerging in abundance. At the 2025 World Artificial Intelligence Conference, robots became the "attention grabber" at the exhibition for the second consecutive year, with over 60 robots on display, 50% more than the number of large models exhibited during the same period.
However, for robots to truly possess environmental adaptability and task execution capabilities comparable to humans, continued efforts are needed in areas like dynamic balance and attitude control technology, low-latency environmental perception and decision-making systems, high-energy-efficiency battery life technology, multi-task generalization learning capabilities, and low-cost, high-reliability hardware solutions. This is why Huang Renxun prioritized "physical AI" at the 2025 NVIDIA GTC Conference.
In the global tech field, robots will be a long-term, world-class challenge, with home scenario robots being the "intelligent high ground."
vivo's choice to enter the home robot sector stems from a profound understanding of social status and family needs: on one hand, China will face severe aging issues in the future, with the population aged 60 and above expected to exceed 400 million by 2035; on the other hand, the average daily household labor time in Chinese households is close to 3 hours, with widespread demand for related services. To this end, vivo focuses on high-frequency user needs and household scenarios, striving to develop home robots and secure the "intelligent high ground" in robotics.
MR technology is crucial for bridging the digital and physical worlds. "In the future, home robots are something vivo aims to achieve, perhaps in five, ten, or even fifteen years. MR has found the direction for future robot integration," said Hu Baishan at a recent vivo event.
Without breakthroughs in MR technology, home robots' conquest of "unstructured scenarios" will remain a pipe dream. Mastering MR technology requires bridging three gaps: first, the environmental understanding gap, where continuous improvement in high-precision scanning and modeling capabilities helps robots establish millimeter-level spatial models in home environments; second, the natural interaction gap, where accurate recognition of human expressions, actions, and semantics helps robots better judge and understand human emotions; and third, the complex task gap, where multi-task processing and behavioral learning assist home robots in coping with complex environments, handling various tasks, and achieving generalization and migration of capabilities.
In the development of unstructured home robots, the "brain + eyes" constitute the robot's cognition-decision hub, while the "cerebellum + limbs" handle behavioral actions. The "eyes" scan the ever-changing environment in real-time, while the "brain" issues corresponding action instructions through cognitive strategies and thinking capabilities. vivo will focus on developing the "brain + eyes" to overcome the technical challenges of future home robots.
vivo is confident in its development in this field over the next decade, grounded in its profound technical accumulation in imaging and large AI models. By focusing on the "brain + eyes," vivo will create real-time environmental recognition and modeling capabilities, as well as fast and accurate action decision-making capabilities, for home robots, equipping them with a "super brain" and breaking through the technical barriers of unstructured scenarios.
03 It's Never Just Luck That Takes You Far

In areas like MR and robots that require long-term cultivation, a company's competitiveness often hinges not on short-term explosive power but on the endurance of sustained investment. vivo's ability to launch the Vision product is supported by robust strengths in three dimensions: strategic perseverance with a "ten-year view," tactical endurance in "long racetracks," and industrial synergy through "openness."
In terms of strategic perseverance, vivo always adheres to the principle of doing the right thing rather than the easy thing, not blindly chasing market trends but focusing on uncovering users' real needs. vivo's definition of the "right thing" is the demand point that frequently arises among users.
Reflecting on the past, 30 years ago, the need for reliable long-distance calls propelled vivo to prioritize telephone stability in the industry. A decade later, users' quest for superior smartphone camera effects drove vivo to delve deeply into technology, collaborating with Zeiss to develop a cutting-edge imaging system. Now, amidst the demand for wearable, user-friendly MR products that seamlessly integrate into daily life, vivo initiates its efforts by focusing on fundamental experiences, such as ensuring a lightweight design of just 398 grams.
This strategic commitment has shielded vivo from numerous industry pitfalls. In the realms of MR and robotics, this persistence is paramount: vivo aims for steady progress rather than sudden technological leaps, laying the groundwork by refining the MR user experience to garner consumer acceptance, subsequently applying MR technology to robots to imbue them with perception and interaction capabilities, and ultimately striving for widespread adoption.
"No industry can afford to rush; it must advance methodically. With a solid foundation in hardware expertise, the ecosystem will foster a virtuous cycle, propelling the industry forward," emphasized Hu Baishan.
vivo's imaging algorithms honed in the smartphone sector can be directly applied to robots' visual recognition, while the AI large model on smartphones enhances robots' ability to swiftly comprehend human instructions. This long-term investment exemplifies a commitment to long-termism, with current R&D endeavors aimed at reaping the "technological compound interest" a decade hence.
Whether in smartphones or MR, vivo consistently advocates for an ecosystem that fosters industry-wide prosperity.
At the hardware level, vivo concentrates on core technologies like MR algorithms and robot cognitive systems—the "brain" and "eyes"—while entrusting the "cerebellum + limbs" to seasoned partners within the supply chain for collaborative innovation. This division of labor allows vivo to concentrate on mastering core technologies while fostering mutually beneficial partnerships.
Concurrently, vivo embraces open standards to nurture the MR industry's ecosystem. Only with the participation of numerous developers can MR products truly transition from niche "geek toys" to mass-market consumer goods.
End
An exceptional technology product should blend seamlessly into daily life, becoming an extension of the user. vivo Vision transcends being merely a product; with its 398-gram weight, 13-millisecond latency, and direct integration into the Android ecosystem, it sets a new benchmark in the MR industry.
The advent of vivo Vision also heralds the realization of the "future life": MR is not the sterile, mechanical world depicted in science fiction films, but rather a harmonious convergence of mobile phones, MR devices, and robots working together like comrades.
Technology has continually evolved, yet 30 years on, vivo's mission to "create exceptional products for users" remains steadfast.