NIO Launches Nationwide Power-up Network Expansion Plan
![]() 09/02 2024
09/02 2024
![]() 567
567
In the new energy vehicle industry, NIO, known for its aggressive infrastructure buildout and battery swapping as a competitive differentiator, has made another major move.
On August 20, NIO officially unveiled its 'Power-up County-by-County' plan during the 'Power UP2024 NIO Charging Day', aiming to densify its charging and battery swapping network and extend services to every county-level administrative region in China, thereby reaching a wider audience of new energy vehicle owners.

In the automotive industry, NIO stands out for its 'user-centric' approach. 'Our initial motivation in energy infrastructure was simple: wherever users need charging stations, we build them, making charging as convenient as filling up a tank,' said Li Bin, Founder, Chairman, and CEO of NIO.
'Power-up' has always been a core obsession for NIO. From initial skepticism to achieving the 0-to-1 milestone and now entering a new phase of large-scale expansion, NIO's strategic energy layout has demonstrated foresight, leading new trends in the green energy era and attracting more like-minded partners.
Benefiting from favorable policies and relentless infrastructure investments, NIO's growing sales and user base have begun to yield economies of scale, with the company edging closer to profitability. Its battery swapping business model has also been validated. To accelerate nationwide county-level coverage, NIO launched the Power-up Partner Program, inviting partners nationwide through a 'hero's call' to collaborate through franchising, guaranteed income sharing, and other models for mutual success.
NIO aims to rally forces to expedite the weaving of a vast energy network, enabling more users to enjoy convenient and efficient charging experiences. In the long run, partnering with NIO's energy swapping stations promises significant economic benefits, presenting a win-win business opportunity.
Massive Demand Behind the Power-up County-by-County Plan
With the global push for sustainable development, heightened environmental awareness, and shifts in energy mix, governments worldwide are supporting the growth of new energy vehicles, ushering in unprecedented opportunities for the automotive industry.
The global automotive landscape is undergoing profound transformation, with a clear shift from gasoline to electric power. More eco-friendly new energy vehicles are gradually taking center stage. According to the China Automobile Dealers Association, domestic new energy vehicle sales reached 878,000 units in July 2024, with a market penetration rate of 51.1%, surpassing gasoline-powered vehicles for the first time.
As new energy vehicles gain popularity, the demand for charging and battery swapping infrastructure is soaring. Charging is considered the 'last mile' for electric vehicle adoption, and accelerating the construction of energy replenishment infrastructure is crucial for widespread EV adoption.
The 'battery swapping' model, offering faster refueling times, alleviates range anxiety to some extent and accelerates the transition from gasoline to electric power. This energy replenishment approach has garnered widespread industry attention and policy support.
As early as 2020, the 'Government Work Report' officially included battery swapping stations as part of China's new infrastructure projects. In January 2024, the National Development and Reform Commission and other departments jointly issued guidelines to accelerate the promotion of battery swapping, strengthen technological innovation and standardization in charging and swapping, optimize shared swapping services, and enhance safety, reliability, and economic viability.
Policy support has heightened market attention to charging and swapping infrastructure.
Among new energy vehicle makers, NIO was an early pioneer in energy replenishment infrastructure. Since 2018, NIO has been steadily building its charging and swapping facilities, currently leading the industry in terms of charging piles and power stations.
As of August 20, NIO had deployed 23,009 charging piles and 2,480 battery swapping stations nationwide, providing over 45.63 million charging sessions and 51 million swapping sessions to users.
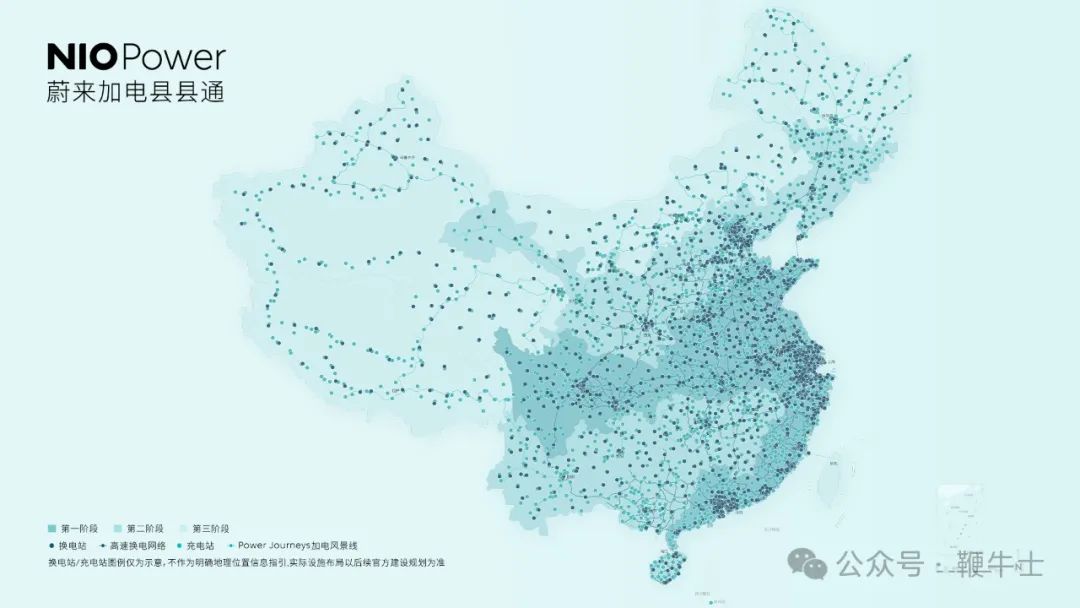
Through years of effort, NIO's energy replenishment network has expanded from key cities to highways and scenic routes. With the Power-up County-by-County plan, NIO will further densify its network. The company plans to add 1,000 new battery swapping stations in China in 2024.
As a pioneer in battery swapping, NIO's layout in energy replenishment infrastructure offers insights into industry trends. Its battery swapping network is accelerating beyond the initial stage, moving towards a denser network and targeting untapped markets.
Recently, NIO launched the Ledao brand, targeting the family market with a price range of around RMB 200,000. This more accessible positioning has paved the way for NIO to enter tier 3, 4, and lower markets. Within this price range, the key differentiator for NIO's sub-brand Ledao, amidst fierce competition, remains its battery swapping advantage. Li Bin previously revealed that a significant proportion of Ledao customers opted for the brand due to its battery swapping capability, even surpassing NIO's main brand in some cases.
While penetration rates in tier 1 and tier 2 cities are higher, the vast county and rural markets are experiencing substantial growth and consumption potential. According to statistics from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers' Charging and Swapping Branch, the penetration rate of electric vehicles in rural areas increased from 4% to 17% between 2022 and 2023, significantly outpacing urban markets.
Earlier, five ministries, including the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, jointly issued a notice to promote new energy vehicles in rural areas, further driving this trend.
In August 2024, the National Energy Administration announced plans to select 33 counties and 74 townships for charging infrastructure construction and promotion activities.
Guided by policies, NIO launched the Power-up County-by-County plan, aiming to cover 27 provincial-level and over 2,300 county-level administrative regions with battery swapping stations by the end of 2025.
NIO's Power-up County-by-County plan signals an acceleration in China's shift from gasoline to electric power in the automotive industry.
Partners 'Emerge,' Opening the Door to Win-Win Battery Swapping
As the Power-up County-by-County plan progresses, NIO's energy infrastructure will continue to expand, making charging and swapping services more accessible to new energy vehicle users.
Key steps in NIO's plan include:
For charging, NIO aims to achieve county-level coverage nationwide by June 30, 2025, except for Taiwan and Hong Kong, with battery swapping coverage in over 1,200 counties across 14 provincial-level administrative regions like Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangdong.
For battery swapping, NIO plans to cover an additional 13 provincial-level administrative regions, including Hunan, Hebei, and Shaanxi, by the end of 2025. From 2026 onwards, it will focus on building swapping stations in the remaining provincial regions.
This means that even users in county-level markets will conveniently access NIO's charging and swapping services, enabling true range freedom.
Notably, NIO's charging piles, open to the industry, serve non-NIO users for nearly 80% of their charging capacity. Essentially, NIO's energy replenishment system aims to enhance the public infrastructure of the entire new energy vehicle industry, addressing the strong demand for energy replenishment.
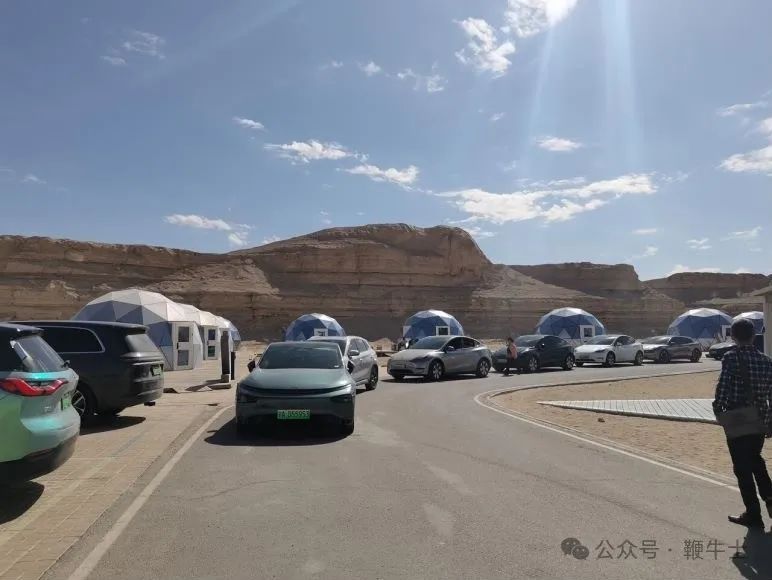

As of June 2024, China had 24.72 million new energy vehicles, according to Ministry of Public Security data. Concurrently, the total number of charging piles nationwide reached 10.244 million, with only 28.8% of these being private charging piles. This means over 70% of new energy vehicle owners lack home charging facilities, while public charging infrastructure remains insufficient and unevenly distributed, highlighting a significant gap in energy replenishment infrastructure.
Accelerating the construction of energy replenishment infrastructure is crucial for steady progress in new energy vehicles.
To achieve this mission, NIO alone is insufficient; cooperation is key to faster industry-wide transformation. Li Bin has emphasized, 'Cooperation is always the better option.' Under his leadership, over 3,000 enterprises have partnered with NIO Energy to build charging and swapping stations.
NIO has collaborated with energy giants like Sinopec, PetroChina, CNOOC, and Shell to establish 333 charging and swapping stations. In battery swapping, NIO has strategic partnerships with seven automakers, including FAW, Changan, GAC, Geely, Chery, JAC Motor, and Lotus Cars.
The capital market also recognizes NIO Energy's potential, with a strategic investment of RMB 1.5 billion from Wuhan in May 2024.
NIO Energy's reputation has attracted more like-minded partners. For these partners, NIO offers a vast and highly engaged user base, over 2,100 charging and swapping patents, six global energy manufacturing centers, rich experience in building charging and swapping facilities, and an efficient intelligent operation system. Its nationwide maintenance team provides robust support and a sense of security.
At the 2024 NIO Charging Day, NIO announced the Power-up Partner Program, offering three partnership models: charging station franchising, fixed income from charging and swapping stations, and guaranteed income plus revenue sharing from charging and swapping stations.
The charging station franchising model suits partners with sites and power resources, sharing service fee revenue. The fixed income model caters to partners seeking long-term, stable returns with low capital costs, offering a fixed service fee. The guaranteed income plus revenue sharing model targets partners aiming for potentially higher returns, combining fixed guaranteed income with service fee revenue sharing.
Industry insiders believe that opening cooperation channels for power-up network construction can reduce NIO's investment in energy replenishment while enhancing efficiency.
Previously, battery swapping infrastructure was often viewed as a money-losing venture due to high upfront costs and slow returns. However, as NIO's infrastructure expands, early investments in tier 1 and tier 2 cities are translating into sales. Data speaks for itself: as of July 2024, NIO delivered over 108,000 vehicles, a nearly 50% year-on-year increase, with monthly deliveries exceeding 20,000 for three consecutive months.
The battery swapping system has surpassed expectations, especially in untapped markets. By deploying swapping stations, NIO has increased user numbers and enhanced user loyalty. In some counties, NIO swapping stations are more recognizable than dealerships. Li Bin cited an example where nearly 1,000 NIO users in Xingfu Town, with a permanent population of only 80,000, attributed their choice to the local swapping station.
Beyond boosting sales, the commercial potential of battery swapping continues to unfold. As part of public infrastructure, swapping stations could offer additional services and generate revenue in the future.
As more 'partners' join, more users will recognize the commercial potential of NIO Energy.
The Value of the Battery Swapping Business Emerges
As NIO's core business model, the battery swapping service is gradually gaining market validation.
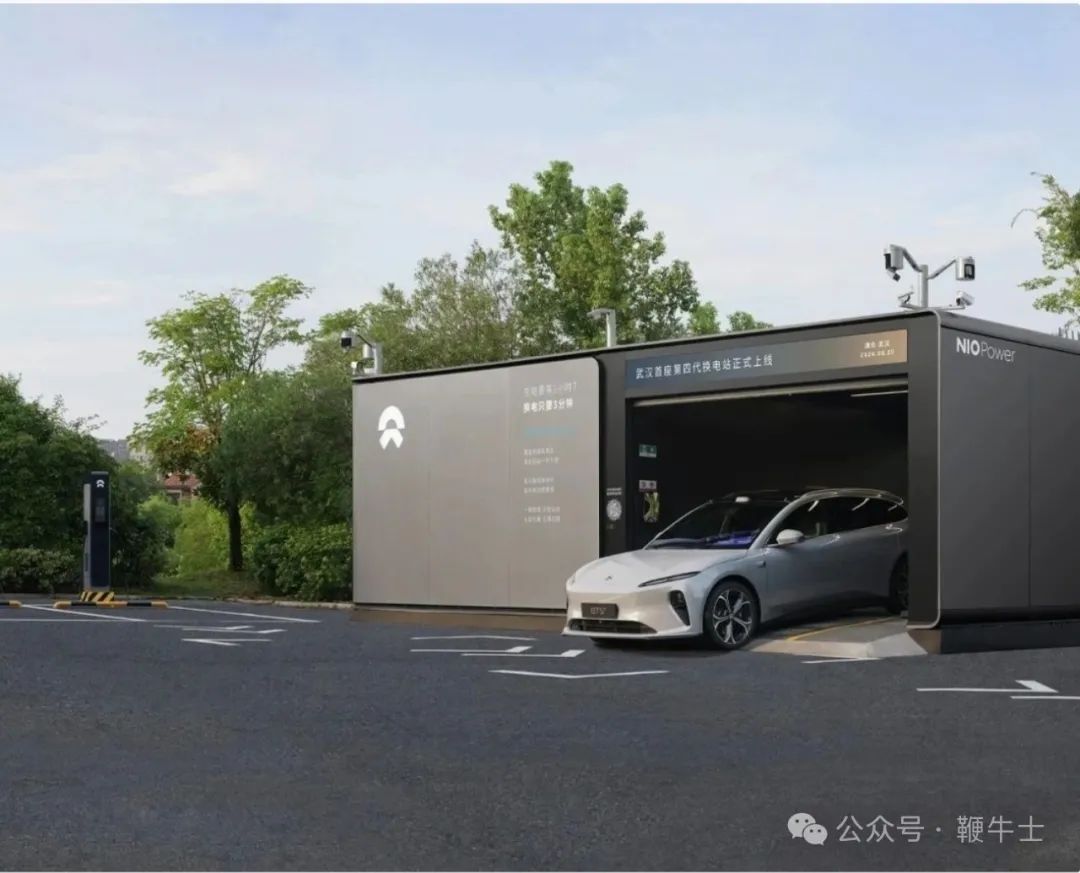

Forward-thinking players are significantly investing in charging and swapping stations, especially swapping stations, which are poised to replace gas stations as a new investment hotspot. A report by China International Capital Corporation Limited forecasts that in the battery swapping ecosystem, besides battery-swappable vehicles and power batteries, swapping station manufacturing, operation, and battery banking will become value-added points. By 2025, annual sales of battery-swappable vehicles are expected to reach 1.72 million, with 10,800 new swapping stations and a total of 23,100 stations. The entire swapping station market could exceed RMB 200 billion by 2025.
Amidst this multi-billion-yuan market, state-owned enterprises have made early moves. Since 2023, Sinopec and PetroChina have intensified investments and layouts in the charging and swapping markets. PetroChina and the Xinjiang Aletai State-owned Assets Investment and Management Group jointly established Xinjiang Youxing New Energy Co., Ltd., planning to build over 1,000 charging stations. Sinopec has announced three major layouts in the swapping sector, investing in Xi'an Lingchong Chuangxiang New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., forming a joint venture with charging station giant Wanbang Digital Energy, and deepening cooperation with international oil giant BP in new energy vehicle charging and related fields.
Vice Minister of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology Xin Guobin summarized seven advantages of the battery swapping model: separation of vehicle and battery significantly reduces vehicle purchase costs; enhances travel convenience; shortens refueling time compared to gasoline filling (as exemplified by NIO's battery swapping service); centralized battery monitoring, maintenance, and management by battery operators prolongs battery life and enhances safety; utilizes peak-to-valley electricity price differences to reduce charging costs; reduces vehicle weight and power consumption; addresses charging difficulties in older residential areas; and spurs new service industries. These advantages are evident in NIO's battery swapping model.
The battery swapping business thrives on user scale. While initial infrastructure investments are substantial, profitability emerges as user numbers grow. In the first seven months of 2024, NIO delivered 107,924 new vehicles, up 43.85% year-on-year, with stable monthly deliveries exceeding 20,000 for three consecutive months.
The tipping point has arrived. With the launch of NIO's sub-brand Ledao and battery swapping alliance models, utilization rates at NIO swapping stations will further increase. NIO Energy's charging services are approaching break-even, while its battery swapping business, though overall loss-making, has achieved break-even at 20% of its stations. Li Bin revealed that each swapping station needs to handle 60 swaps to reach break-even.
NIO has proven with concrete data and experience that battery swapping is a viable business. Today, NIO swapping stations' profitability model is becoming clearer, partly derived from service fees and electricity price differences through energy replenishment services.
In the long run, another major profit source lies in power system transactions, such as participating in vehicle-grid interaction and virtual power plant peak shaving and frequency regulation for additional revenue.
Currently, NIO has achieved large-scale vehicle-grid interaction. In March this year, NIO's first high-speed PV-ESS integrated battery swap station was established in Zhijiangxi Service Area of the G50 Shanghai-Chongqing Expressway in Hubei Province, realizing bidirectional interaction between the swap station and the power grid. Up to now, NIO has organized 1,767 battery swap stations and installed more than 27,000 charging piles, participating in the national power grid demand response and peak shaving auxiliary services, with a total peak shaving and valley filling capacity exceeding 300 million kWh.
Moreover, the most considerable revenue for NIO battery swap stations comes from earning electricity trading fees by connecting to virtual power plants.
A virtual power plant (VPP) is a highly intelligent energy management system. Based on the Internet of Things, it integrates distributed power sources, energy storage facilities, controllable loads, and other resources in the power grid for centralized dispatching and participates in the dispatch and operation of the power grid, providing flexibility services for the electricity market.
During the high temperature period this summer, more than 100 NIO battery swap stations in Shanghai have contributed to the peak shaving and frequency modulation of the Shanghai power grid, reducing the peak power load by more than 60,000 kWh. Using NIO's new 20kW V2G charging pile, users can also participate in the virtual power plant. The specific participation process is as follows: Assuming that the weather forecast predicts high temperatures for the next two days, and the virtual power plant expects a power gap, it will initiate an invitation to the user side to fill the power gap, thereby obtaining certain economic benefits, which is a win-win situation. According to NIO Vice President Shen Fei, users can earn up to 10,000 yuan a year from the virtual power plant.
The commercial potential of virtual power plants should not be underestimated. Earlier, the "Opinions on Accelerating the Comprehensive Green Transformation of Economic and Social Development" issued by the State Council mentioned that we should steadily promote the green and low-carbon transformation of energy, strengthen the clean and efficient utilization of fossil fuels, vigorously develop non-fossil fuels, and accelerate the construction of a new power system. In the process of transforming from fossil fuels to new energy sources, this segmented track has been listed as a key track in the entire industry chain of the new power system by industry analysts.
It can be seen that as the battery swapping and derivative energy storage models are widely recognized in the industry, the social value of NIO's charging system is evident. With the rapid expansion of its partner network, NIO's market potential will be further unleashed.