Li Auto Seeks Opportunities Amidst 2026 Crisis
![]() 12/03 2025
12/03 2025
![]() 603
603

Despite innumerable hardships, only gold stands the test of time.
——Liu Yuxi, "The Waves Wash Away the Sand", Tang Dynasty
The Turning Point: From 'Star Performer' to 'Survivor in Adversity'
Once hailed as a 'star performer' among China's new automotive forces, Li Auto made its mark by precisely targeting 'family users' and adopting a unique extended-range technology route. Launching with the Li ONE and rapidly gaining prominence with its L-series 'clone' models, the company set an industry benchmark with 11 consecutive quarters of profitability. However, the market is a realm where no myth lasts forever. Entering 2025, Li Auto faces its toughest challenge since inception.

The extended-range advantage that once fortified its moat is now under fierce homogenized competition due to its relatively low technological barriers. The highly anticipated pure electric transition, led by the MEGA model, stumbled amid controversies over its design. Ultimately, all issues came to a head in the third quarter 2025 financial report: revenue plummeted, the company incurred net profit losses, and its streak of consistent profitability was broken. This places Li Auto at a crossroads in its development, necessitating profound strategic adjustments. How will Li Auto break through and survive in this industry elimination race?
01
Performance Under Pressure: Key Data Reflects Operational Challenges
Numbers speak volumes. Li Auto's operational status in 2025 is first reflected in the 'transformation' of a series of key data points.
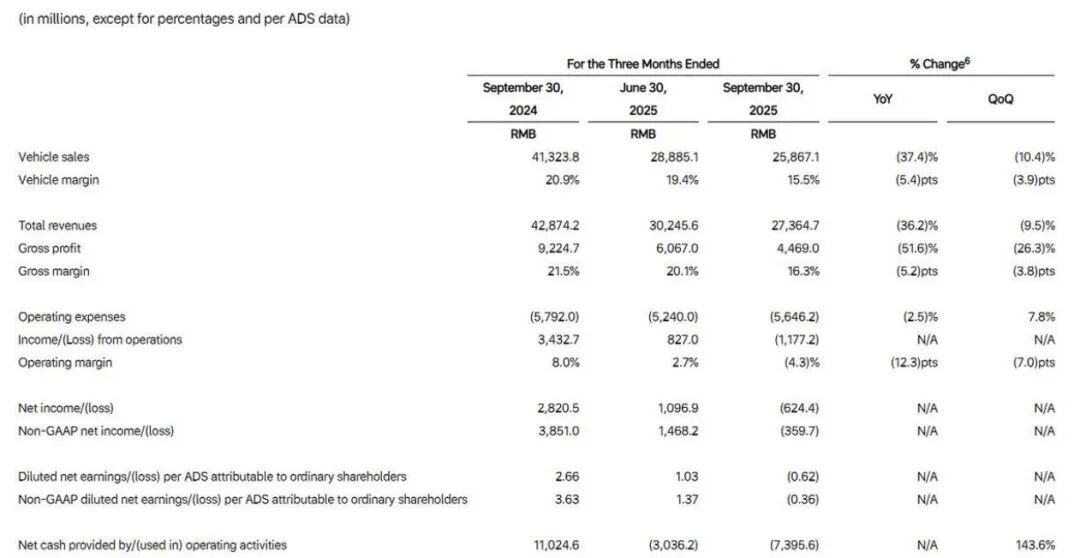
Financial performance raised red flags. According to Li Auto's third quarter 2025 financial report, the company's revenue for the period was RMB 27.4 billion, a significant year-on-year decrease of 36.2%. More notably, the company reported a net loss of RMB 624 million, ending its previous streak of 11 consecutive quarters of profitability and sparking widespread concerns among the market and investors.
As a key indicator measuring the core profitability of an automotive enterprise, vehicle gross margin declined from 20.9% to 15.5%. Li Auto's official explanation in the financial report attributed this primarily to the impact of recall events for certain models. Excluding this impact, the vehicle gross margin would be approximately 19.8%. Nevertheless, this figure still indicates significant pressure on profitability compared to its historical peak.
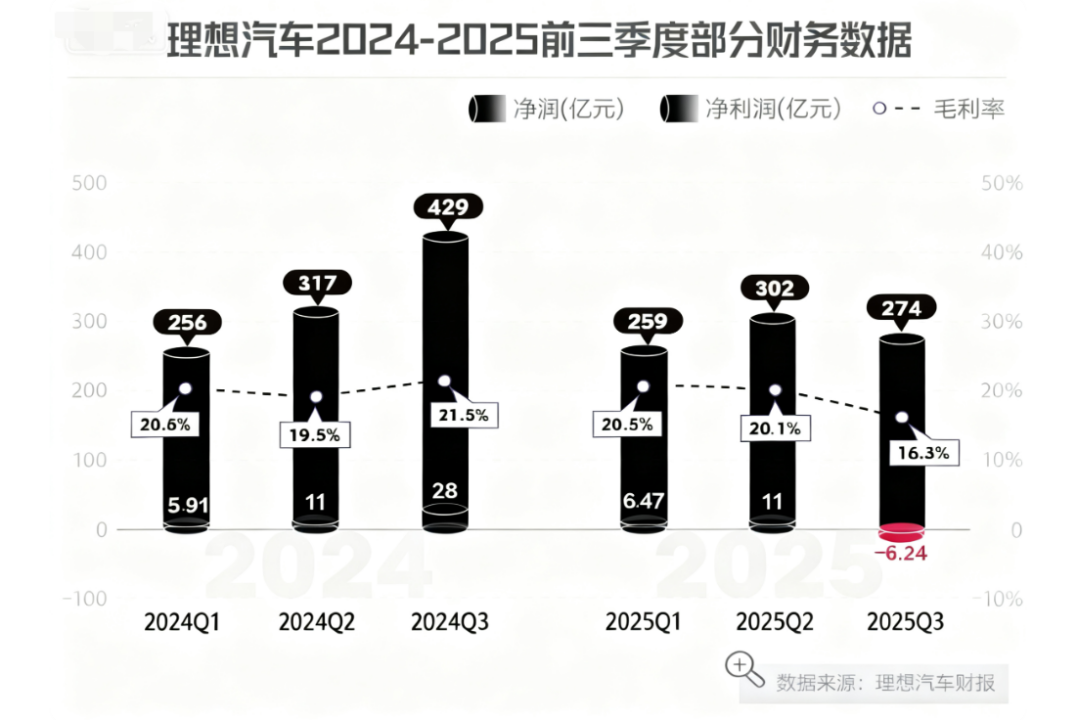
Sales growth abruptly stalled, with delivery volume being the lifeline for new automotive forces. Li Auto's Q3 2025 delivery data showed that only 93,200 new vehicles were delivered in the quarter, a staggering year-on-year drop of 39%. The precipitous decline in sales forced Li Auto to lower its annual sales target twice within the year. According to relevant reports from the Yangtze River Business Daily, its annual sales target has been gradually reduced from 700,000 units at the beginning of the year to 640,000 units. Notably, according to the 21st Century Business Herald, while the overall target was lowered, Li Auto's sales target for pure electric vehicles was increased from 50,000 units to 120,000 units against the trend. This subtly reflects an urgent adjustment in the company's internal business focus.
Market position faced challenges, with the once-dominant 'NIO, XPeng, Li Auto' landscape already shattered, and Li Auto's crown as the sales leader among new forces has been relinquished. This indicates that Li Auto is facing fierce encroachment in its traditional stronghold of extended-range vehicles from latecomers employing 'low-price, high-specification' strategies, rapidly eroding its market share.
02
Roots of the Crisis: Systemic Risks Amidst Internal and External Turmoil
Li Auto's current predicament did not arise overnight but is the result of the convergence of multiple internal and external factors.
External Competition: Moats Turned into Red Oceans, Surrounded by Strong Rivals
The starting point of Li Auto's success—extended-range technology—has swiftly become a focal point for numerous brands to catch up and even engage in homogenized competition due to its relatively low technological barriers. Brands such as Leapmotor, Arcfox, XPeng, and Xiaomi have executed a 'dimensionality reduction strike' against Li Auto with higher cost-effectiveness and more flexible configuration strategies. Meanwhile, in the pure electric vehicle sector where Li Auto is determined to transition, the landscape has long been solidified.
Tesla, leveraging its strong brand effect and self-developed technological ecosystem, firmly occupies the core position in the global new energy vehicle market, maintaining leading advantages in multiple key areas such as sales rankings, technological standards, and industrial ecosystems.
NIO has constructed extremely high competitive barriers through its unique battery swap system and user community.
XPeng has built its technological moat with 'full-stack self-developed intelligence + efficient energy replenishment ecosystem.' Additionally, XPeng's super extended-range X9 has been launched, directly encroaching upon Li Auto's territory.
Xiaomi Motors, relying on its user base of 600 million and AIoT ecological resources, as well as its accumulation in the consumer electronics sector, has forged a new competitive path through 'ecological reconstruction + cost control,' constructing a unique barrier of 'cross-border integration.' Furthermore, Xiaomi's extended-range SUV YU9 is expected to be launched in 2026.
As a 'latecomer' in the pure electric sector and a 'pioneer' in extended-range vehicles, Li Auto faces a tough battle on both fronts.
Moreover, in the first half of this year, the market share of extended-range vehicles in the domestic new energy vehicle market declined from 10.7% in 2024 to 9.8%. Since June, domestic terminal sales of extended-range vehicles have decreased year-on-year for five consecutive months.
Product Strategy: Transitional Gap and Internal Conflict
Currently, Li Auto has three pure electric models: MEGA, i8, and i6. The inaugural pure electric flagship model MEGA in 2025 sparked significant controversy in the market due to its avant-garde 'high-speed train-style' exterior design, failing to replicate its success in the extended-range market and encountering initial setbacks. Meanwhile, the delivery of the pure electric SUV i8, seen as crucial for volume, fell far short of expectations.
According to Autohome's sales statistics for October 2025, the average monthly delivery volume of the i8 in September and October was only approximately 5,700 units, performing rather mediocrely. Additionally, the long-criticized 'clone-style' family design has begun to cause aesthetic fatigue among consumers. More critically, the launch of the lower-priced pure electric sedan i6, which quickly became a hot seller with nearly 50,000 orders placed within 48 hours, exerted 'internal pressure' on the higher-positioned i8 and the original extended-range L-series, leading to internal competition within the product matrix and failing to form a synergistic effect.
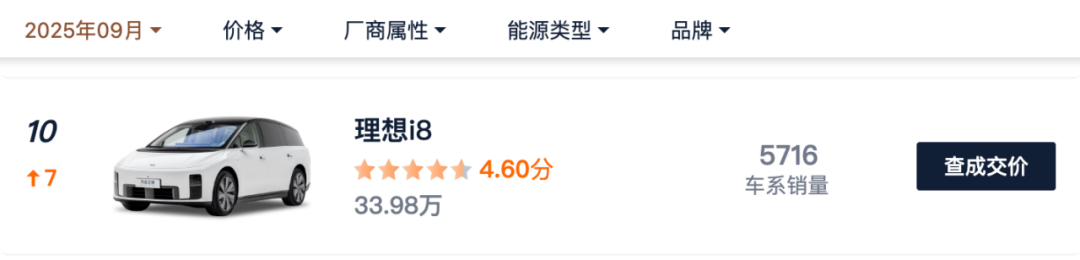
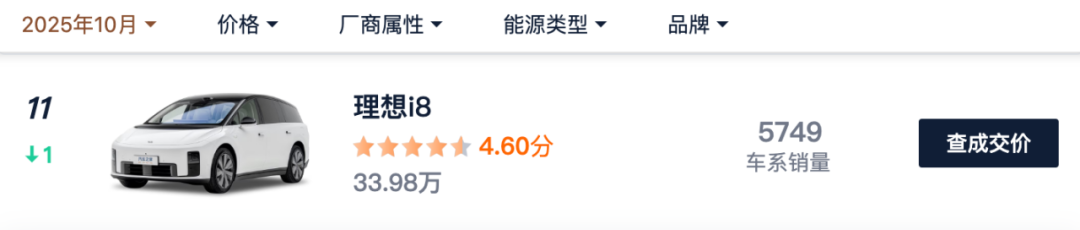
Internal Management: Big Company Syndrome and Supply Chain Dependency
As the company rapidly expanded, the 'professional manager' management model once adopted by Li Auto and the PBC (Personal Business Commitment) performance system sourced from Huawei were recently criticized for their inadequate compatibility with the company's original entrepreneurial culture, leading to prolonged decision-making chains and decreased efficiency.
At the recently held third quarter 2025 financial report conference, Li Xiang negated Li Auto's attempt to transition to a 'professional manager' governance system over the past three years. He believed that this model did not align with the current unstable market environment and Li Auto's actual situation, even bluntly stating that the performance over the past few years represented 'the worst version of ourselves.'
Therefore, Li Auto announced a comprehensive return to the entrepreneurial company model starting from the fourth quarter of this year.
At the supply chain level, over-reliance on a single supplier has also brought risks. The i6 model was affected by fluctuations in the supply of core components, impacting the production progress of some vehicles and causing it to miss out on some pure electric market opportunities.
03
The Outcome of Transformation Will Determine Survival
From the perspective of industry development patterns, the new energy vehicle market is shifting from high-speed growth to high-quality competition, and it is not uncommon for companies to experience periodic losses during technological iteration periods.
As Li Xiang stated during the financial report conference call, 'The third quarter of 2025 is the first quarter of Li Auto's second decade. We have faced multiple challenges such as product cycles, supply chains, and public sentiment, but these will all serve as stepping stones for our transformation.' In this transformation, which is crucial for success or failure, production capacity, cost control, and management models have become the most significant variables in Li Auto's strategic transformation.

Amidst pressure on the overall vehicle business, the only aspect in the financial report that showed counter-trend growth was R&D investment. According to Li Auto's third quarter financial report, the annual R&D expenditure is expected to be RMB 12 billion, with over RMB 6 billion invested in the field of artificial intelligence throughout the year. In other words, it is expected that over 50% of the R&D funds will be allocated to intelligent driving and AI large model domains.
Additionally, on December 2nd, according to Houchangcun News, Li Auto announced a strategic cooperation with Zeiss to launch a smart glasses product. Whether this technological investment can be transformed into commercial value, form explosive features that strongly resonate with users, and effectively drive sales remains uncertain. The current gross margin level of 16.3% is insufficient to support long-term R&D expenditures, and the capital market's patience for AI stories typically does not exceed two financial reporting cycles.
Moreover, in this fiercely competitive environment where 'big fish eat small fish, and small fish eat shrimp,' competitors will not remain idle during a company's critical transformation window. Tesla's price pressure, XPeng's cost-effectiveness offensive, and Huawei's technological encirclement will persist.
04
Conclusion:
2025 marks Li Auto's 'coming-of-age ceremony,' forcing it to bid farewell to its past comfort zone and enter a more complex and brutal arena. The core of its strategic transformation is to strive for a breakthrough in the pure electric vehicle sector while safeguarding its extended-range market, and to reconstruct its core competitiveness through organizational transformation, vertical integration of the supply chain, and technological leadership in AI. This is a race against time. Whether Li Auto can leverage this profound self-renewal to navigate through cycles and return to a growth trajectory depends not only on the firmness of its strategic execution but also on its adherence to and evolution of the brand's original aspiration to 'create a mobile home.' In the deep waters of transformation, only those with foresight, courage, and extreme efficiency can reach the other shore.
References:
"Li Auto Reports RMB 27.4 Billion in Revenue for the Third Quarter" - The Beijing News
"Disciples of Li Auto Overturn Li Auto" - Phoenix Finance
"Revenue and Profit Decline, Pure Electric Quality Control Faces Controversy: Li Auto's Three Musketeers Status at Risk?" - Lanjing News
"New Energy Vehicle Landscape Shifts: Leapmotor Leads, Second-Tier Players Accelerate Breakthroughs" - 21st Century Business Herald








