Lei Jun breathed a sigh of relief as Xiaomi Automobile entered the era of "Made by Xiaomi"
![]() 07/15 2024
07/15 2024
![]() 645
645
In March, Xiaomi SU7 was officially released and then deliveries began in April.
Since the release of Xiaomi SU7, it has set numerous new records, unprecedented ones at that. To date, Xiaomi Automobile has delivered over 25,000 vehicles, with over 10,000 delivered in June alone.
According to Xiaomi's plan, they aim to deliver over 100,000 vehicles in 2024, with an ambitious target of 120,000.

In fact, everyone is aware that for Xiaomi, the challenge is not sales but delivery.
As a new production capacity, automotive production cannot be easily scaled up, so Xiaomi's production capacity cannot keep up with demand. Currently, orders exceed 100,000 vehicles, but Xiaomi will take nearly a year to deliver them all. If production capacity were sufficient, delivering 50,000 or even 100,000 vehicles per month would not be an issue.
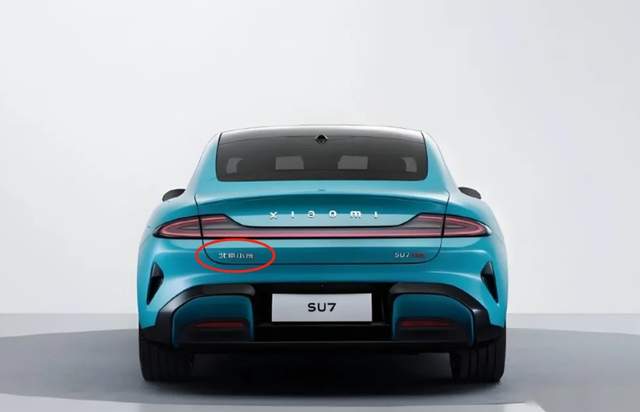
Behind this new production capacity, Xiaomi actually faces another issue: it previously lacked manufacturing qualifications and had to borrow Beijing Automotive Group Off-Road Vehicle Company's production qualifications. Therefore, the tail logo of Xiaomi SU7 reads "Beijing Xiaomi".

An automaker needs to obtain two licenses to independently manufacture and sell vehicles in the market: the production manufacturing license from the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and the product access license from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT).
Previously, Xiaomi lacked manufacturing qualifications and only had the access license, so it had to take a "detour" and let Beijing Automotive Group (BAIC) manufacture the vehicles. However, recently, Xiaomi officially obtained manufacturing qualifications.
This means that in the future, Xiaomi Automobile will be manufactured by Xiaomi itself, without the need to borrow BAIC's qualifications. The "Beijing Xiaomi" label will no longer appear on Xiaomi Automobiles, which can now be labeled simply as "Xiaomi".

Don't underestimate the significance of this achievement.
NIO delivered its first products in 2018 using JAC Motor's qualifications and did not obtain its own production license until the end of 2023. XPeng started delivering vehicles in 2018, using Haima's qualifications, and obtained its production license in 2020. Lixiang (LI Auto) delivered its first vehicles in 2019 using Lifan's qualifications and did not obtain its own manufacturing qualifications until 2023.
Clearly, compared to NIO, XPeng, and Lixiang, Xiaomi only took three months to obtain production qualifications after starting deliveries, demonstrating the support and recognition Xiaomi has received.

With these qualifications in hand, Xiaomi can breathe a sigh of relief as it now has complete control over its manufacturing process. It can autonomously manage production, flexibly adjust production plans, and quickly respond to market demands.
According to media reports, Xiaomi will soon launch an SUV model. With production qualifications in place, it is expected that production capacity will also increase rapidly.
So, while it's too early to declare Xiaomi Automobile a success, Lei Jun can certainly feel relieved now that qualifications and sales are no longer issues; it's just a matter of ramping up production capacity.