Will the Merger of Nissan, Honda, and Mitsubishi Usher in the World's Third Largest Automaker?
![]() 12/19 2024
12/19 2024
![]() 543
543
As the global automotive industry undergoes a once-in-a-century structural transformation, traditional automakers are intensifying their efforts to counter the challenges posed by emerging electric vehicle companies, particularly Tesla from the US and domestic Chinese brands.
In this fiercely competitive environment, Japan's two leading automakers, Honda and Nissan, appear poised to unite, leveraging their combined technical prowess and resources to vie for the title of the world's third-largest automotive group.

According to Car2C, Honda and Nissan are set to negotiate a business integration, including the establishment of a holding company to encapsulate both entities. Furthermore, given that Nissan is the largest shareholder in Mitsubishi, it is anticipated that Mitsubishi will also join their alliance in the future.
Honda and Nissan are expected to sign a memorandum of understanding soon, followed by the finalization of the holding company's shareholding ratio and other pertinent details.
The alliance between Honda and Nissan seems to have a discernible path. The two companies began exploring cooperation in March and launched comprehensive business collaboration in August, focusing on standardizing in-vehicle software and components.
From the areas of focus, it is evident that if Honda, Nissan, and Mitsubishi successfully integrate, they will amalgamate their technical capabilities and operational resources to compete with Tesla and emerging Chinese electric vehicle companies in the next phase of competition.
Moreover, post-merger, the combined annual global sales of these three automakers are projected to exceed 8 million vehicles, placing them among the top global automakers, trailing only Toyota Motor (11.23 million vehicles) and Volkswagen Group (9.23 million vehicles).
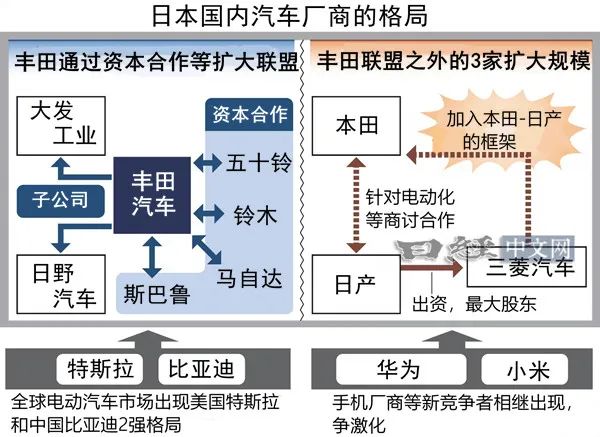
Notably, with Honda, Nissan, and Mitsubishi (at a scale of 8 million vehicles) joining forces with the Toyota alliance (at a scale of 16 million vehicles), the Japanese automotive market will consolidate into two major camps, marking the culmination of this round of restructuring in the Japanese automotive industry.
Why Ally?
Currently, Japanese automakers are facing increasing challenges in the Chinese and American markets.
Data indicates that from January to November 2024, Honda and Nissan experienced cumulative sales declines of 30.7% and 10.5%, respectively, in China, struggling amidst a tough market environment.
On one hand, robust Chinese government support for new energy vehicles has propelled local electric vehicle companies like BYD to swiftly fill market gaps. On the other hand, the escalating technological prowess and price competitiveness of Chinese automakers have put once-dominant Japanese automakers under unprecedented pressure.
Furthermore, Nissan's performance in the American market is also bleak.
Due to the slow development of new vehicles, particularly the failure to keep pace with market demand in the hybrid vehicle segment, Nissan's sales in the US have plummeted. To address this predicament, Nissan has not only announced a 20% reduction in global production capacity but also plans to lay off approximately 9,000 employees, striving to cut costs and bolster competitiveness through economies of scale.
However, the integration of Honda and Nissan is not solely a response to market pressures; it is also driven by the profound transformation underway in the global automotive industry—the accelerating shift from internal combustion engine vehicles to electric vehicles.
According to the International Energy Agency's forecast, by 2035, the market share of electric vehicles in global new vehicle sales will exceed 50%. Facing this trend, Japanese automakers must expedite their electrification process or risk being marginalized.
Nissan launched the world's first mass-produced electric vehicle, the "LEAF," in 2010, boasting relatively deep technical expertise in the field of electrification.
Simultaneously, Honda has amassed extensive experience in hybrid vehicles, ranking second only to Toyota in global hybrid vehicle market share due to its technological edge.
Moreover, Honda has invested heavily in battery production and aims to supply in-vehicle batteries to Nissan through collaboration.
Honda and Nissan's cooperation in the field of electrification will facilitate the rapid popularization and application of technology, enhancing their competitiveness in the global market.
Conclusion
The structural transformation of the global automotive industry is accelerating, and traditional automakers must navigate this challenge through mergers, collaborations, and technological innovation.
For Honda and Nissan, business integration represents not only a strategic adjustment for the two automakers but also a pivotal attempt by Japanese automakers to redefine their roles in global competition.
If the integration is successfully realized, Honda and Nissan will wield greater market influence and technological innovation capabilities, potentially emerging victorious in future global automotive competitions and reshaping the competitive landscape of the global automotive industry.
Image source: Reuters and Nikkei








