Technology Innovation | Enflame Technology Embarks on IPO Journey, Late but Determined, Finalizing the Capital Landscape for China's 'Four Little Dragons' in Domestic GPUs
![]() 01/27 2026
01/27 2026
![]() 557
557
Preface:
Recently, the Shanghai Stock Exchange Science and Technology Innovation Board has officially accepted the IPO application of Shanghai Enflame Technology Co., Ltd. As the first to be established but the last to go public among the 'Four Little Dragons,' Enflame Technology is making its debut with a substantial 6 billion yuan fundraising plan.
This milestone not only marks the inaugural IPO on the A-share market in 2026 but also signifies that all four members of China's 'Four Little Dragons' in domestic GPUs—Moore Threads, MetaX, Biren Technology, and Enflame Technology—have now entered the capital market, completing the assembly of the core domestic high-end chip group at the capital table.
Author | Fang Wensan
Image Source | Network

The Latecomer with a Differentiated Strategy: Enflame Technology's Path to Breakthrough
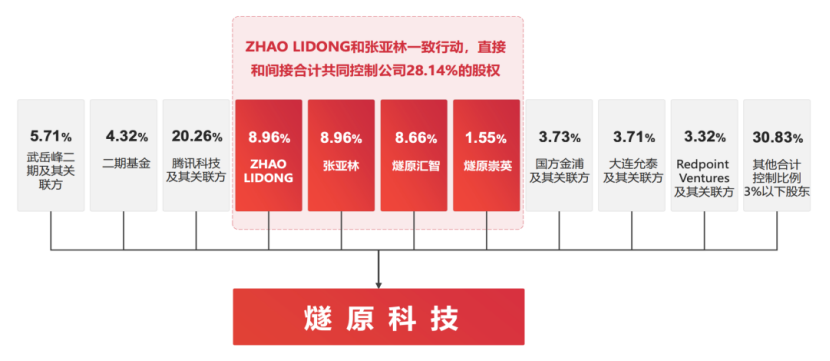
Among China's 'Four Little Dragons' in domestic GPUs, Enflame Technology stands out for its unconventional and resilient approach. Founded in March 2018 by two former AMD core executives, Zhao Lidong and Zhang Yalin, the company was established with a strategic focus on differentiated breakthroughs from the very beginning.
Zhao previously led AMD's CPU/APU product planning, while Zhang successfully developed heavyweight products such as the XBOX-ONE main chip. With over two decades of experience in the chip industry, the duo set a differentiated strategic tone for Enflame Technology from the outset.
While Moore Threads, MetaX, and Biren Technology opted to follow NVIDIA's GPGPU technology roadmap, Enflame Technology chose ASIC and domain-specific architectures from the start, concentrating on cloud-based AI chip training and inference tasks.
This choice is underpinned by a precise prediction of AI computing power trends: as large models transition from extensive training to inference deployment, computing power demands will shift from general-purpose computing to scenario-specific optimization. Non-GPGPU architectures will increasingly demonstrate advantages in energy efficiency, data throughput, and power consumption control.
This differentiated strategy boasts several key characteristics:
① Highly targeted: Dedicated chips offer superior energy efficiency and scalability for specific tasks compared to general-purpose chips.
② High coupling requirements between design and ecosystem: Deep collaborative development with customers and the establishment of corresponding software ecosystem support are essential.
③ Long iteration cycles: ASIC design and verification inherently involve high complexity, with stricter requirements for testing and market feedback.
Consequently, Enflame's pace is slower than general-purpose routes in terms of product maturity and market adaptation. However, its performance and energy efficiency advantages are gradually emerging in certain scenarios, particularly in large-scale cloud-based inference deployments.
At the hardware level, Enflame Technology has independently developed the GCU-CARE accelerated computing unit and GCU-LARE inter-chip high-speed interconnection technology, rivaling NVIDIA's TensorCore and NVLink systems. These innovations ensure high-performance parallel computing for AI large models while retaining flexible programming characteristics.
At the software level, facing NVIDIA's CUDA ecosystem monopoly, the company independently developed the full-stack AI computing and programming software platform 'TopsRider,' encompassing core modules such as drivers, compilers, and operator libraries. This effectively reduces migration and development costs for mainstream AI models.
This differentiated route is gaining market validation. Google's Gemini 3 large model, released in November 2025, was trained using its self-developed TPU (non-GPGPU architecture), breaking NVIDIA's absolute monopoly in large model training.
Goldman Sachs predicts that the shipment share of non-GPGPU chips in AI servers will rise from 36% in 2024 to 45% in 2027. Inference scenarios' reliance on the CUDA ecosystem continues to diminish, creating vast market opportunities for Enflame Technology.

Performance Review: Rapid Growth Amidst Prolonged Losses
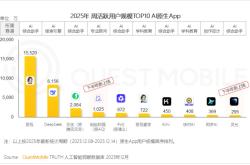
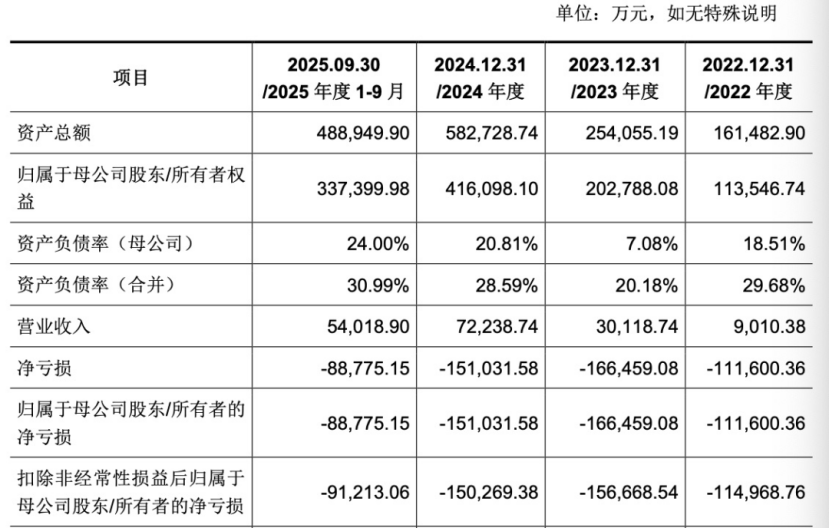
After nearly eight years of dedication, Enflame Technology has delivered a mixed performance review. Revenue has surged: from 90.1038 million yuan in 2022 to over 300 million yuan in 2023, and then to 722 million yuan in 2024, achieving a two-year compound annual growth rate of 183.15%.
Revenue reached 540 million yuan in the first three quarters of 2025, with AI accelerator cards and modules surpassing full-year 2024 levels, demonstrating significant commercialization progress.
This growth is supported by deep integration with Tencent. As Enflame's largest shareholder, Tencent has continuously invested since the Pre-A round and began business collaboration in 2019, progressing through single-scenario validation, multi-scenario scaled applications, and deep strategic cooperation.
In the first three quarters of 2025, sales revenue to Tencent accounted for 71.84% of Enflame's total, becoming the company's core income source.
This dual capital and business integration have enabled large-scale commercial use of Enflame's products in national-level applications like WeChat and Tencent Cloud, achieving a critical leap from technological to commercial closed loops.
However, behind the glossy growth lies the inherent pain points of the chip industry: high investment and long cycles. From 2022 to the first three quarters of 2025, Enflame's cumulative R&D investment reached 4.419 billion yuan, with R&D expense ratios consistently above 160%. Cumulative net losses exceeded 5 billion yuan during this period.
As of the end of September 2025, the company's accumulated undistributed losses reached 4.165 billion yuan, inventory book value increased to 958 million yuan, inventory write-downs reached 190 million yuan, and accounts receivable climbed to 385 million yuan, posing significant cash flow pressures.
In response, the company's management provided clear expectations in the prospectus: based on over 100,000 units in order reserves, mass production of the third-generation S60 inference accelerator card, and revenue contributions from the thousand-card-level intelligent computing center project, break-even is projected as early as 2026.
According to IDC data, China's total AI accelerator card shipments exceeded 2.7 million units in 2024, with NVIDIA holding a 70% market share (1.9 million units) and a 76% revenue share.
During the same period, Enflame's AI accelerator card and module sales reached 38,800 units, accounting for approximately 1.4% of the market. While ranking among the top domestic vendors, there remains a significant gap compared to industry leaders.
Nevertheless, this 1.4% market share represents a crucial breakthrough for domestic chips in key areas.
By the end of 2024, Enflame had built China's first 10,000-card domestic computing power inference cluster in Qingyang, Gansu Province, as part of the 'East Data, West Computing' initiative. Its third-generation S60 inference accelerator card achieved domestic leading performance levels, with cumulative shipments exceeding 100,000 units.
Under policy support and domestic substitution trends, such breakthroughs are continuously narrowing the gap with international vendors.
As of the end of September 2025, Enflame had obtained 262 domestic invention patents, undertaken over 10 national and local technology projects, participated in formulating 41 industry standards, and received authoritative recognition for its hard technology capabilities.
Gathering of the Four Little Dragons: Track Differentiation Amidst Capital Frenzy
The acceptance of Enflame's IPO marks the conclusion of the capital gathering for China's 'Four Little Dragons' in domestic GPUs.
In just over a month, three domestic GPU companies went public, followed by Enflame's entry, creating a rare capital boom.
Despite all belonging to the 'GPU Four Little Dragons,' the four companies have significantly different positioning and technology roadmaps, forming a diverse ecosystem in the domestic GPU industry.
Enflame focuses on inference scenarios, Moore Threads positions itself as a full-function GPU provider, and Biren Technology targets high-end large computing power. This deep cultivation of niche segments helps avoid direct competition with international giants while gradually accumulating market share.
Financially, none of the Four Little Dragons have achieved profitability yet. In 2024, Moore Threads reported revenue of 1.45-1.52 billion yuan with net losses of 950-1.06 billion yuan. MetaX reported revenue exceeding 700 million yuan with R&D investment ratios reaching 121%.
Biren Technology reported revenue of 337 million yuan with R&D investment ratios as high as 245%.
Enflame ranked second among the Four Little Dragons with 722 million yuan in revenue but still reported net losses of 1.51 billion yuan.
Goldman Sachs data shows that less than 5% of global AI chip companies will achieve break-even in 2026, with profitability remaining a challenge for all domestic GPU companies.
Technologically, AI large models are shifting from training to inference deployment. Global AI inference demand for accelerator cards will surpass training scenarios for the first time in 2026, and inference scenarios' lower reliance on the CUDA ecosystem provides opportunities for non-GPGPU architecture vendors to overtake competitors.
Google's TPU success further validates the competitiveness of dedicated architectures in specific scenarios.
Bernstein predicts that ByteDance, Alibaba, and Tencent will account for 50% of China's AI capital expenditures, with combined investments of 45 billion USD in 2025 and 85 billion USD in 2028.
Internet giants' adaptation needs for domestic chips provide scaled validation scenarios for companies like Enflame, while the 'East Data, West Computing' initiative directly drives intelligent computing centers' procurement of domestic GPUs.
Additionally, the accelerated listing processes of chip companies under internet giants like Baidu's Kunlun Core and Alibaba's T-Head complement the market-oriented approach of the Four Little Dragons, forming a collaborative development pattern between market players and internet giants.
Furthermore, Shanghai has become the core hub of this GPU entrepreneurial wave. Among the Four Little Dragons, Enflame, Biren Technology, and MetaX were all born in Zhangjiang, Shanghai. Alongside GPU companies like Vastai Semiconductor (Hantro Semiconductor) and Tiantian Zhixin (Tianshu Zhixin), Shanghai has formed the densest GPU industrial cluster in China.
This is attributed to Shanghai's complete integrated circuit industry chain, with an industrial scale exceeding 390 billion yuan in 2024 (accounting for 25% nationally), support from a 100 billion yuan industrial investment mother fund, and a capital ecosystem that 'invests early, in small amounts, and in hard technology,' providing full-cycle support from R&D to commercialization for enterprises.

Conclusion:
Despite facing challenges such as losses, weak ecosystems, and low market shares, domestic GPU manufacturers are rapidly improving their technological capabilities and commercialization under the combined push of policy support, market demand, and capital infusion.
With the Four Little Dragons' IPO fundraising, R&D investment will further increase, product iteration speeds will accelerate, and ecosystem construction will enter a fast lane.
The domestic computing power ecosystem is taking shape, and domestic GPUs are moving toward sustainable competition, with technological autonomy and industrial rise becoming a reality.
Partial references: Bu Huang Laboratory: 'Enflame Technology's Science and Technology Innovation Board IPO: The Offensive and Concerns of a Domestic AI Chip 'Alternative' Breakthrough Player,' TechWeb: 'AI Chip Company Enflame Technology's Science and Technology Innovation Board IPO Application Accepted, Tencent Holds Over 20% Stake,' Fourth Wave: 'Domestic GPUs: How Five 'Four Little Dragons' Compete in the Home Market,' Investment Circle: 'Shanghai is Making a Fortune Recently,' Science and Technology Innovation Board Daily: 'Four Little Dragons' Go Public +1! How Shanghai Forged a 'GPU City''