Huawei and ZTE Win the Bidding for China Mobile's Experimental Satellite Manufacturing Project! China's Satellite Industry Chain is in Action
![]() 06/17 2024
06/17 2024
![]() 709
709
IoT Intelligence Original
On June 7, China Mobile's Procurement and Bidding Website announced the results of the bidding for the "China Mobile Experimental Satellite Manufacturing Project".
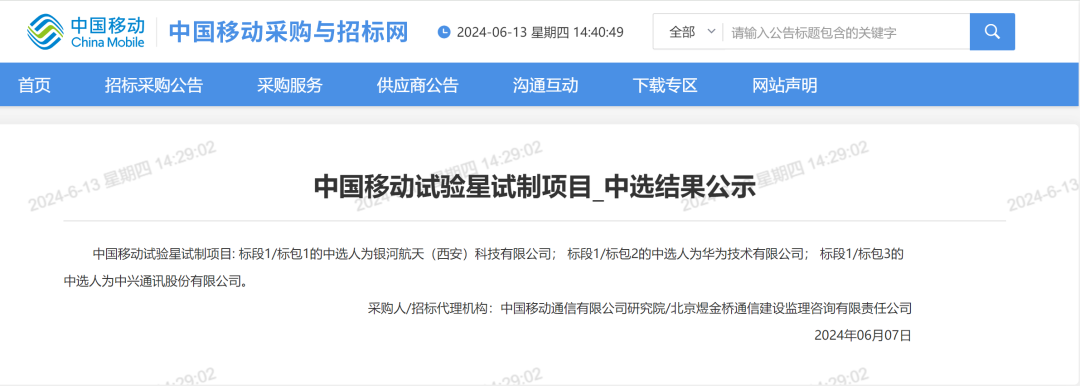
The results showed that the bidder for Lot 1/Package 1 was GalaxySpace (Xi'an) Technology Co., Ltd.; the bidder for Lot 1/Package 2 was Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.; and the bidder for Lot 1/Package 3 was ZTE Corporation.
Regarding the specific content of each package, according to previous bidding announcements, they are:
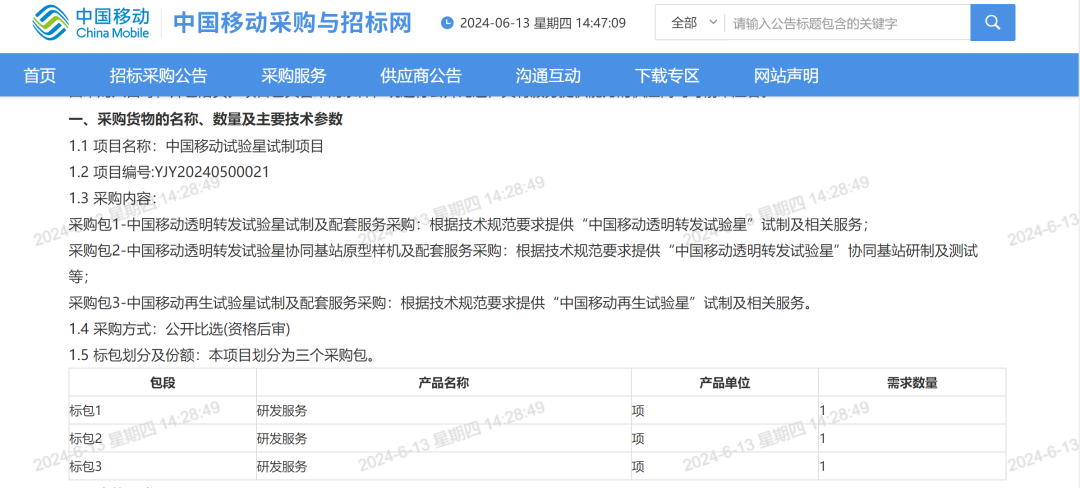
Package 1 - Procurement of China Mobile Transparent Forwarding Experimental Satellite Manufacturing and Ancillary Services: Provide manufacturing and related services for the "China Mobile Transparent Forwarding Experimental Satellite" in accordance with technical specifications.
Package 2 - Procurement of China Mobile Transparent Forwarding Experimental Satellite Collaborative Base Station Prototype and Ancillary Services: Provide development, testing, and other services for the "China Mobile Transparent Forwarding Experimental Satellite" collaborative base station in accordance with technical specifications.
Package 3 - Procurement of China Mobile Regenerative Experimental Satellite Manufacturing and Ancillary Services: Provide manufacturing and related services for the "China Mobile Regenerative Experimental Satellite" in accordance with technical specifications.
The results of this bidding have attracted widespread attention, partly because of the presence of Huawei and ZTE, two major giants in the list, and partly because it represents another significant breakthrough by China Mobile in the field of low-orbit satellites. With this, this article will briefly analyze the impact of this event on the industry.
The "Transparent Forwarding" Experimental Satellite and the "Regenerative" Experimental Satellite
Looking closely at the project content, Huawei won the bidding for the procurement of collaborative base station prototypes and ancillary services for the transparent forwarding experimental satellite; GalaxySpace won the bidding for the procurement of manufacturing and ancillary services for the transparent forwarding experimental satellite; ZTE won the bidding for the procurement of manufacturing and ancillary services for the "regenerative" experimental satellite. In other words, the project involves both the "Transparent Forwarding Experimental Satellite" and the "Regenerative Experimental Satellite".
What are [Transparent Forwarding] and [Regenerative] experimental satellites?
In the R14 standard research proposal, the 3GPP standards organization clearly proposed to integrate satellite communications into terrestrial communication networks. In the R15 phase, 3GPP began research on NTN (non-terrestrial network), forming technical research reports covering satellite access network protocols, architecture evaluation, channel models, application scenarios, and impacts on current NR protocols. In the R16 phase, 3GPP further conducted in-depth analysis and research on NTN in areas such as random access, uplink and downlink time-frequency synchronization, scheduling, mobility, interfaces, and architectures.
Entering the R17 phase, this stage can be considered an important milestone in 5G NTN standardization. 3GPP conducted comprehensive NTN standard research at this stage, focusing on technical standard formulation for wireless access networks, bearer networks, core networks, and terminals involved in NTN networks. The NTN project was also divided into two standard projects: IoT NTN (IoT terminal access based on non-terrestrial networks) and NR NTN (5G smart terminal access based on non-terrestrial networks).
IoT NTN focuses on supporting satellite IoT services for low-complexity eMTC and NB-IoT terminals, while NR NTN uses the 5G NR framework to enable "smartphone direct satellite connectivity" and provide data and voice services.
In the 3GPP NTN project, based on the satellite's on-board payload capacity, the network architecture can be divided into two typical modes: [Transparent Forwarding] and [On-board Regeneration].
Transparent Forwarding
This is the main network architecture studied in the 3GPP Rel-17/18 phases.
Under the transparent forwarding architecture, the base station is located on the ground, and the satellite functions as a transparent forwarding pipe between the UE (User Experience) and the base station without affecting the 5G transmission protocol and architecture. As shown in the figure below, the UE accesses the 5G network via the satellite and ground gateway based on the 5G NR wireless interface, and the data interaction between the UE and the ground core network is consistent with terrestrial mobile communication systems.
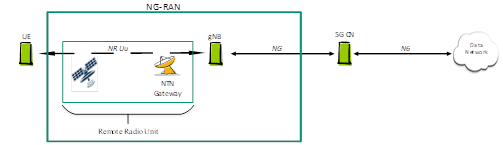
NTN Transparent Forwarding Network Architecture (Source: China Mobile Research Institute)
Since the transparent forwarding architecture has no on-board processing capability, network deployment can be based on existing satellites; the base station is located on the ground, making it relatively easy to implement and technically mature.
On-board Regeneration
This is an important technical direction in the 3GPP R19 NTN standard.
Under the on-board regeneration architecture, part or all of the base station functions are located on the satellite, as shown in the figure below. The base station F1 interface or the base station-core network NG interface is located on the wireless air interface between the satellite and the gateway.
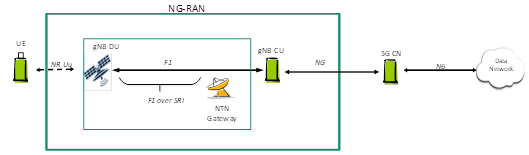
NTN On-board Regeneration Network Architecture - Partial Base Station Functionality On-board (Source: China Mobile Research Institute)
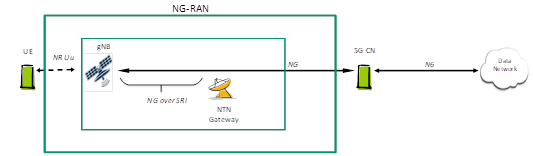
NTN On-board Regeneration Network Architecture - Full Base Station Functionality On-board (Source: China Mobile Research Institute)
The on-board regeneration architecture can achieve inter-satellite collaboration through inter-satellite links, thereby reducing the number of ground gateways required for actual deployment. However, this mode requires increased on-board processing capability and has higher requirements for satellite payload design.
Based on the above, it is easy to understand that the [Transparent Forwarding Experimental Satellite] refers to a satellite that uses transparent transponder technology. After receiving a signal from the ground, the transparent transponder performs only low-noise amplification, frequency conversion, and power amplification, without any further processing (such as demodulation or basic signal processing), and simply completes the forwarding task. In contrast, the [Regenerative Experimental Satellite] refers to a satellite that can process the received signal before forwarding it, rather than simply forwarding the original signal like traditional satellites.
Judging from the bidding results, China has taken significant steps in the most cutting-edge and frontier areas of satellite communications.
China's Satellite Communications Industry Chain is Strengthening Collaboration
As mentioned in previous articles, China is actively competing on the international satellite communications stage against the backdrop of the global trend of terrestrial-satellite network integration. Judging from the bidding results, under the leadership of operators, China's satellite communications industry chain, including equipment manufacturers, satellite solutions, and manufacturers, is actively strengthening collaboration to jointly promote the integration of terrestrial mobile communications and satellite internet.
Equipment Manufacturers Representatives: Huawei, ZTE
Consumers are familiar with Huawei's satellite communication capabilities on smartphones due to the slogan "reaching the sky." Behind this is Huawei's deep accumulation in the communications field.
In September 2023, Huawei officially announced that the Mate 60 Pro can establish satellite calls, allowing users to make and receive satellite phone calls in extreme environments without terrestrial network signals, enabling timely communication with the outside world. It is important to note that this feature is [satellite calling], not [satellite communication] - although the difference seems minor, the technical difficulty behind it is immense. While satellite direct communication previously only enabled "short messages," Huawei can now achieve satellite direct calling, indicating significant breakthroughs in antenna technology, power consumption control, and other aspects.
In April 2024, Huawei achieved another innovation breakthrough in satellite communications. Its Pura 70 series smartphones further upgraded the original dual-satellite communication capability to support sending Beidou satellite image messages. This means that in situations such as outdoor exploration and emergency rescue, even without signals or networks, users can send image messages through their phones to achieve two-way communication with the recipient.
In contrast, ZTE, while appearing more low-key, has also been advancing its work in satellite communications and achieved many outstanding results. In August 2022, ZTE completed the world's first operator 5G IoT NTN technology field test; in January 2023, it completed the world's first S-band 5G IoT NTN technology field test; in May 2023, it completed China's first 5G IoT NTN mobile phone direct satellite connection laboratory test; and in September 2023, it completed China's first maritime scenario 5G NTN verification.
Currently, ZTE has conducted a series of field tests in Zhoushan, Zhejiang, for scenarios such as marine and emergency communications, taking the lead in completing the industry's first 5G NTN field test in a maritime scenario, including applications such as marine water quality monitoring, ship supervision, environmental data monitoring, and emergency communications.
Operator Representative: China Mobile
As the main body of this experimental satellite manufacturing project procurement, China Mobile has achieved another significant breakthrough in the field of low-orbit satellites. This experimental satellite will be China Mobile's third low-orbit satellite after the "China Mobile 01 Star" and the "Xinghe" verification satellite.
On February 3 of this year, two space-terrestrial integrated low-orbit experimental satellites carrying China Mobile's satellite-borne base stations and core network equipment were successfully launched into orbit. Among them, the "China Mobile 01 Star" was jointly developed by China Mobile and Starlink, carrying a satellite-borne base station that supports 5G space-terrestrial integrated evolution technology. It is the world's first satellite-borne signal processing experimental satellite that can verify 5G space-terrestrial integrated evolution technology. The "Xinghe" verification satellite was jointly developed by China Mobile and the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Microsatellite Innovation Institute, carrying the industry's first satellite-borne core network system designed with 6G concepts and capable of on-orbit service capabilities, making it the world's first 6G architecture verification satellite.
It is worth mentioning that on April 20, China Space-Time Information Group Co., Ltd., with a registered capital of 4 billion yuan, was registered in Xiong'an New Area, with China Mobile as one of its three major shareholders. Through this, China Mobile can organically integrate its satellite network system with its terrestrial network to provide integrated space-terrestrial communication services.
Satellite Solutions and Manufacturer Representatives: GalaxySpace
GalaxySpace, which is also included in the bid winner list, is a star enterprise in the field of satellite communications. Founded in 2018 by Mr. Xu Ming, the co-founder and former president of Cheetah Mobile, which successfully listed on the NYSE, GalaxySpace is the first unicorn company in China's commercial aerospace field. The company is committed to the independent research and development and low-cost mass production of communication payloads, core single units, and satellite platforms. It has established internationally leading capabilities for the development of communication payloads, core single units, and solar wings in Xi'an, Chengdu, and Beijing, and has built a new generation of satellite intelligent manufacturing factories in Nantong, achieving mass production capabilities for hundreds of satellites.
On January 16, 2020, GalaxySpace successfully launched China's most powerful low-orbit broadband communication satellite, the GalaxySpace first satellite. In March 2022, GalaxySpace independently developed and successfully launched China's first batch of six low-orbit broadband communication satellites - the GalaxySpace 02 batch production satellites, verifying China's capabilities in low-cost satellite manufacturing, mass production, and networking operations necessary for building a giant satellite internet constellation.
In summary, space-terrestrial integration is a highly complex system engineering that requires cross-domain, cross-link, and deep collaboration and open innovation from all parties. It is clear that the upstream and downstream of the industry chain working together to build an integrated space-terrestrial digital information infrastructure has become the general trend.
In Conclusion
In the article "40 Billion! A New Giant Emerges in China's Satellite Internet Field, Competing in the International Space-Terrestrial 'Battlefield'," I mentioned that low-orbit satellites have advantages such as short distances, low transmission delays, low link losses, flexible launches, rich application scenarios, low overall manufacturing costs, and low terminal costs, enabling low-cost global interconnection services. Therefore, they have become a necessary battleground for major countries' space strategic competition and a development priority for the next-generation space information infrastructure.
Since space orbits and wireless spectrum are valuable non-renewable resources, it is crucial for China to compete on the international satellite communications stage and seize time opportunities. Now, judging from the actions of the upstream and downstream of the industry chain, China's satellite internet industry has already embarked on a fast track of accelerated development.
References:
China Mobile Procurement and Bidding Website, https://b2b.10086.cn/#/index
"Mobile Phone Direct Satellite Connection | The Rise of the Space-Terrestrial Integrated Industry: The Key Role and Impact of 3GPP NTN Technology," Communication World News
"Supported by Huawei and ZTE, China Mobile's Third Low-Orbit Satellite is About to Launch," Communication World News
"ZTE Hu Kaiwei: NTN Expands 5G-A Business Boundaries, Ushering in the 'Consumer-Grade' Satellite Communication Era," Securities Times Network
"Launch Success! 'China Mobile 01 Star' and 'Xinghe' Verification Star Successfully Entered Orbit," People's Posts and Telecommunications News