Empowering SMEs through 5G IoT: Ensuring 5G is Both Accessible and Affordable
![]() 12/16 2025
12/16 2025
![]() 495
495
Recently, at the 2026 China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT) In-Depth Observation Report Conference, 5G experts unveiled their research findings in a report titled "5G: Transitioning from Connectivity to Empowerment." Among the emerging trends in 5G applications, the author is particularly intrigued by the focus on "SME transformation and the creation of an empowerment ecosystem led by large enterprises to support smaller ones." In the author's opinion, the true indicator of 5G's widespread adoption across various industries is when a substantial number of SMEs can access and afford 5G technology. In this context, 5G "Internet of Things" (IoT) must play a central role. Only by continuously expanding the reach of 5G IoT across different sectors can we fulfill 5G's mission to drive digital transformation in each industry.
The penetration rate of 5G IoT will be a key metric for assessing 5G's impact across industries.
The In-Depth Observation Report Conference delved into the application of 5G in SMEs, highlighting that scenario-based, standardized, and cost-effective 5G solutions are crucial for widespread adoption by SMEs. On one hand, solutions developed by large enterprises can be refined into easy-to-deploy, cost-effective, and standardized offerings for SMEs to select based on their specific needs. On the other hand, large enterprises can take the lead by gradually extending 5G+ related applications to their upstream and downstream partners through industrial chain collaboration, fostering a "large enterprises leading small ones" development model.
The penetration of 5G IoT in SMEs, to a certain extent, reflects the effectiveness of 5G applications. Firstly, the number of connections is not only a core metric for gauging the large-scale deployment of mobile communications but also indicates the depth of application in specific vertical sectors. This is because the number of connections represents the user base. Over a decade ago, during the early stages of mobile internet development, the industry closely monitored the number of connections from mobile internet devices like smartphones. Once the number of connections from these mobile devices surpassed those from desktop PCs, the mobile internet experienced explosive growth. Currently, various mobile internet applications that have revolutionized our daily lives in terms of clothing, food, housing, and transportation are all built on a vast user base of mobile devices.
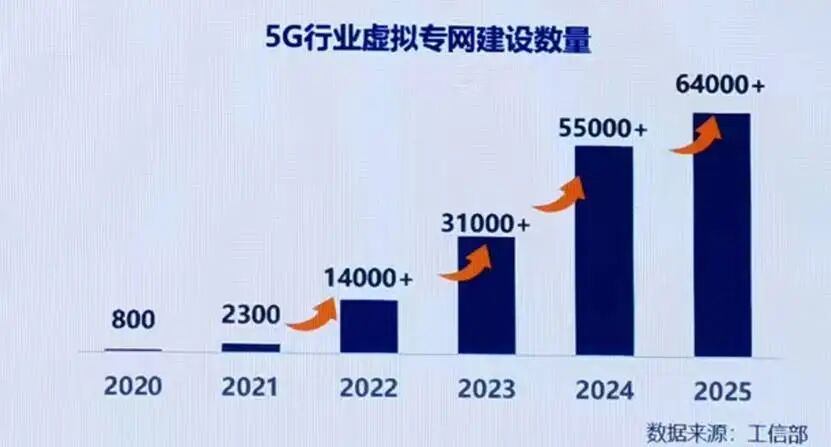
The evolution of 5G follows a similar pattern; the number of connections reflects the user base in specific sectors. Presently, the penetration rate of 5G smartphone users is relatively high, indicating a significant scale of individual users. However, for industry applications, although 5G has been integrated into 91 major categories of the national economy and there are over 64,000 5G virtual private networks, this does not necessarily equate to deep 5G applications within industries. We must examine how many device terminals in the industry are connected via 5G, i.e., achieving 5G "IoT."
It is now widely acknowledged that 5G achieves industry applications through IoT integration, a defining characteristic that sets 5G apart from previous generations of mobile communication technologies. To empower the core processes and the entire production and operation chain of various industries with 5G, leading to cost reduction, efficiency improvement, quality enhancement, and upgrading, it is essential to first enable all aspects and processes within enterprises to leverage 5G. These "carriers" are certainly not mobile phone terminals but physical terminals such as equipment and instruments used in enterprise R&D, production, warehousing, logistics, monitoring, management, and other scenarios. These physical terminals need to be equipped with sensing capabilities and 5G networks to form intelligent terminals. If these "carriers" are not connected or only a few are connected, then 5G empowerment of industry applications would be unattainable. Since most of these "carriers" are intelligentized in the form of IoT terminals, the scale of 5G IoT terminal connections largely determines whether 5G can be deeply integrated into industry applications.
Take the power sector as an example. Relevant entities have reported that 5G applications have expanded from unmanned inspections in the "transmission and distribution" stages to encompass all five major stages of "generation, transmission, transformation, distribution, and utilization." Clearly, 5G applications in these five stages require IoT connections for the physical entities such as major facilities, power lines, and assets in each stage. The power sector boasts a vast number of these physical entities, and in the future, it could even form hundreds of millions of 5G IoT connections. Currently, however, the penetration rate of 5G IoT connections in the power sector is negligible.
Similarly, various sectors of the national economy possess a massive number of devices and assets. Deep 5G applications in these industries necessitate connections to these devices and assets. Some industries have a far greater number of devices and assets than the population. However, presently, the average number of 5G IoT connections per major industry category is very low, representing only a tiny fraction. Therefore, the potential for 5G IoT is immense, and there is still a long road ahead to support deep 5G applications in industries.
Driving Effective 5G Utilization in Enterprises of All Sizes through IoT Empowerment During the 15th Five-Year Plan Period
Looking ahead to the 15th Five-Year Plan period, perhaps we need to first achieve a scenario where the number of IoT terminal connections surpasses that of human connections before truly forming deep and large-scale 5G applications in some industries.
Over the past few years of commercialization, with the industry's collective efforts, 5G has achieved a certain level of replication in key industries such as mining, power, and healthcare. 5G applications in the industrial sector have gradually penetrated from peripheral processes to core processes such as R&D, design, and manufacturing, exploring high-value application scenarios and solutions like 5G+AI quality inspection, and forming 5G application demonstrations. Simultaneously, the continuous R&D of 5G industrial gateways, inspection robots, wireless data terminals, vehicle-mounted terminals, and satellite mobile terminals has diversified the types of new 5G terminals. Next, "IoT" must play a pivotal role. Through deep penetration of IoT connections, 5G capabilities can be brought into various scenarios and processes of different sectors of the national economy, especially among SMEs, to truly achieve 5G empowerment of industries.
The author has repeatedly stressed that promoting the widespread adoption of 5G IoT can be achieved through multiple efforts:
1. Accelerate the R&D and promotion of 5G "native" IoT technologies to enable large-scale connections with native technologies.
The so-called 5G "native" IoT technologies refer to technologies proposed and standardized for IoT scenarios during the research and formulation of 5G standards, becoming an integral part of the 5G standards. These native technologies lay the groundwork for 5G to empower various industry applications and can also serve as the primary force for 5G connections, including:
- Firstly, promote the large-scale development of 5G RedCap. As a lightweight version of 5G technology, RedCap is specifically designed for medium-rate IoT scenarios and represents a typical area where 5G native and large-scale applications are evident. Considerable research has been conducted on RedCap. The author once pointed out in the article "What Will Be the Development Journey of 5G RedCap in the Next Decade or So?" that RedCap development has three stages, and during the 15th Five-Year Plan period, it will gradually gain an advantage over 4G IoT and achieve large-scale applications.
- Secondly, expedite the commercialization of passive IoT. As a technology supporting hundreds of billions of connections, passive IoT offers vast potential for the industry. If passive IoT based on 5G cellular networks can be implemented, then most assets in various industries can be equipped with extremely low-cost, maintenance-free communication modules, forming the largest IoT connection group under 5G networks and accelerating 5G applications in various industries.
- Thirdly, hasten the commercialization and ecosystem construction of satellite IoT. 3GPP initiated research on non-terrestrial networks (NTN) in the 5G standard R17 phase, covering standardization in aspects such as radio access networks, bearer networks, core networks, and terminals. IoT-NTN is a crucial direction within this. Currently, major global satellite communication players are focusing on 3GPP-compliant satellite IoT technologies to promote the implementation of IoT-NTN. On November 19, 2025, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the "Notice on Organizing Commercial Trials of Satellite IoT Services," marking the acceleration of satellite IoT commercialization and its future role as a vital component of 5G IoT.
2. Meet industry-specific needs and synergize 5G IoT with customization capabilities.
Deep 5G empowerment of industry applications also requires a thorough understanding of industry-specific needs and the provision of customized capabilities. The empowerment of 5G "IoT" should be deeply synergized with the provision of customized capabilities.
- Firstly, fully cooperate with the construction of 5G private networks and enrich IoT terminals in private network environments. Virtual private networks can be seen as diversified 5G network capabilities provided to industry users to meet their specific needs. Currently, the total number of 5G industry virtual private networks constructed in China exceeds 64,000. Next, consideration can be given to deploying some lightweight 5G private networks to serve SMEs. When SMEs use 5G private networks, the empowerment of 5G "IoT" can be enhanced. Virtual private networks provide an excellent infrastructure, and the construction of private networks simultaneously raises specific demands for the development of 5G IoT module terminals, requiring synchronous improvement of 5G IoT-related capabilities.
- Secondly, fully integrate into the "AI+" initiative. The proposal for the 15th Five-Year Plan suggests comprehensively implementing the "AI+" initiative and strengthening the integration of artificial intelligence with industrial development, cultural construction, livelihood protection, and social governance. IoT can deeply penetrate multiple levels of production and operation in various industries, providing application carriers and rich underlying trustworthy data for "AI+". Therefore, the development of 5G IoT applications should be fully integrated with the "AI+" initiative, leveraging IoT's differential advantages in sensing and transmission to provide AIoT technologies for SMEs and jointly promote industry transformation and upgrading.
Overall, 5G has laid the foundation for industry digitalization, providing a transformation basis for enterprises of all sizes. Data indicates that the number of SMEs in China has exceeded 60 million, accounting for approximately 99.8% of the total number of enterprises, representing the largest and most innovative group among enterprises. To empower diverse industries with 5G, efforts can be made through 5G IoT to empower a vast number of SMEs, providing them with suitable 5G solutions at a low cost, i.e., making 5G accessible and affordable for SMEs. This would truly signify 5G's empowerment across diverse industries.