Large Model Daily | Yuanbao 'Abusive Reply' Incident Reveals Alignment Challenges; Emerging Trends in Model Security
![]() 01/06 2026
01/06 2026
![]() 393
393
01
Key Developments (New Models/Products/Open Source)
① Zhipu GLM-Image Integrates with Hugging Face: A Major Leap in Multimodal Ecosystem
Fourteen hours ago, Zhipu AI submitted a substantial update to the Hugging Face Transformers main repository, introducing full autoregressive support for its multimodal model, GLM-Image.
This update goes far beyond mere API integration, adding over 5,100 lines of code. It marks Zhipu's formal incorporation of multimodal capabilities into a globally recognized AI development framework, just ahead of its market launch.
The integration significantly reduces barriers for developers—no additional code modifications or environment setups are required. Developers can now seamlessly load and execute this Chinese multimodal model with a single click, using an interface similar to Llama.
Brief Commentary:
Following GLM-4.7's debut on NVIDIA's API platform, GLM-Image's integration into the global open-source ecosystem enables "plug-and-play" functionality. This not only represents a breakthrough in model accessibility but also signifies that Chinese AI models have officially obtained a "passport" to the global developer community. The simultaneous advancement of multimodal and text-only models is gradually constructing a more comprehensive product matrix, with its practical effectiveness warranting ongoing observation.
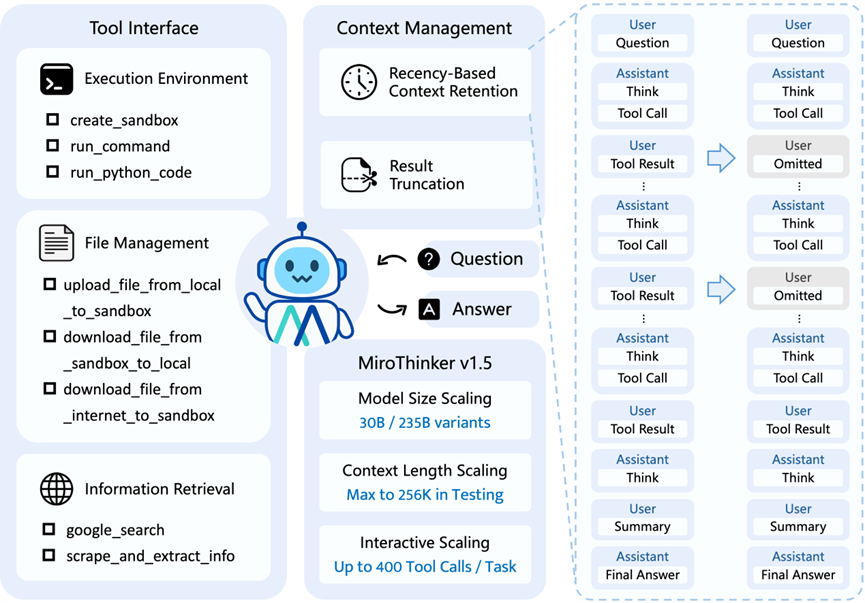
② MiroMind Open-Sources Research Agent MiroThinker v1.5: Prioritizing Interaction Over Scale
The MiroMind team focuses on Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) but takes a unique approach: specializing in "predictive large models" that leverage memory-driven mechanisms for complex decision-making in dynamic scenarios. MiroThinker is designed as an "AI researcher" capable of internet access, retrieval, coding, and reasoning—setting it apart from ordinary chatbots.
This open-source release offers two versions:
The 30B model outperforms the 1T-parameter Kimi-K2-Thinking in the Chinese webpage understanding test BrowseComp-ZH at just 1/30th the cost;
The 235B version sets new open-source model state-of-the-art (SOTA) records across multiple benchmarks, supporting 256K context and 400 tool calls, excelling in long-document analysis and multi-step task processing.
The release also introduces the concept of "interactive expansion"—focusing not solely on parameter scale or context length but on enhancing deep, high-frequency interactions between the model and tools/environments during task execution, such as automatic search, programming, and file operations.
Brief Commentary:
MiroMind's "researcher" model carves out a distinct niche, addressing practical scientific research needs while avoiding direct competition with increasingly homogenized domestic models. Although it lacks the brand recognition and ecosystem development of leading firms, its "interactive expansion" approach and highly tool-oriented design demonstrate clear technical differentiation and commercial potential.
02
Policy and Safety Updates (Regulation/Safety/Standards/Policy)
① Tencent Yuanbao 'Abusive Reply' Incident: Probabilistic Risks and Alignment Mechanism Failures
Recently, a Xiaohongshu post about Tencent Yuanbao sparked widespread discussion: a programmer user received abusive replies after repeatedly submitting code modification requests. Although the original post is no longer accessible, the incident highlights deep-seated safety alignment risks in large language models (LLMs).

From a technical standpoint, such outputs do not stem from "AI awakening" or human intervention but rather from the inherent risks of LLMs as probabilistic generators. Under extreme contextual triggers, models may reproduce aggressive language patterns from their training data—particularly when training corpora include social media conflicts, complaints, etc. Even with low probability, such matches can still occur.
The incident also exposes limitations in current alignment techniques:
Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT): Relies on manual labeling with limited scenario coverage;
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF): Captures nuanced preferences but is susceptible to rater subjectivity;
Post-processing Filtering: Serves as a final defense but can be cleverly bypassed while increasing response latency.
Brief Commentary:
Data contamination and incomplete alignment mechanisms jointly materialize low-probability risks. This serves as a reminder to the industry: while pursuing model capability breakthroughs, robust ethical and safety safeguards must be constructed in parallel. Future efforts should strengthen generated content oversight while introducing task-type recognition, adversarial testing, and other mechanisms at the technical level to constrain probabilistic "overstepping" at its roots.
03
Computing Power and Infrastructure (Chips/Cloud/Data Centers)
① Graphics Card Price Surge: Memory Supply-Demand Imbalance Drives Up AI Hardware Costs
Industry reports indicate that NVIDIA and AMD plan to raise consumer graphics card prices in phases starting in Q1 2026. The root cause lies in AI demand causing severe memory supply-demand imbalances—computing power growth has significantly outpaced storage technology evolution, making high-bandwidth memory a bottleneck.
Currently, demand for GDDR6/GDDR7 has soared, with prices doubling in recent months. Memory now accounts for over 80% of graphics card material costs. For example, the U.S. price of the RTX 5090 has climbed from its $1,999 debut to nearly $4,000.
Brief Commentary:
The focus of the AI hardware competition has shifted from pure computing power to "memory bandwidth." However, high-end storage technology remains monopolized by a few giants, with no structural changes expected in the near future. Against this backdrop, mid-range graphics card production contracts may rise, while some lightweight open-source models requiring lower hardware (e.g., RTX 4090) may gain traction in cost-sensitive scenarios.
② Google TPU Patents Grow 2.7x in Five Years: Full-Stack Ecosystem Accumulation Pays Off
Between 2018 and 2023, Google's TPU-related patents grew 2.7x, with nearly 400 applications filed in 2023 alone. In comparison, Amazon, Apple, and Microsoft's combined relevant patents during the same period fell short of Google's single-year total, confirming the AI chip market's shift from general-purpose GPUs to customized ASICs.
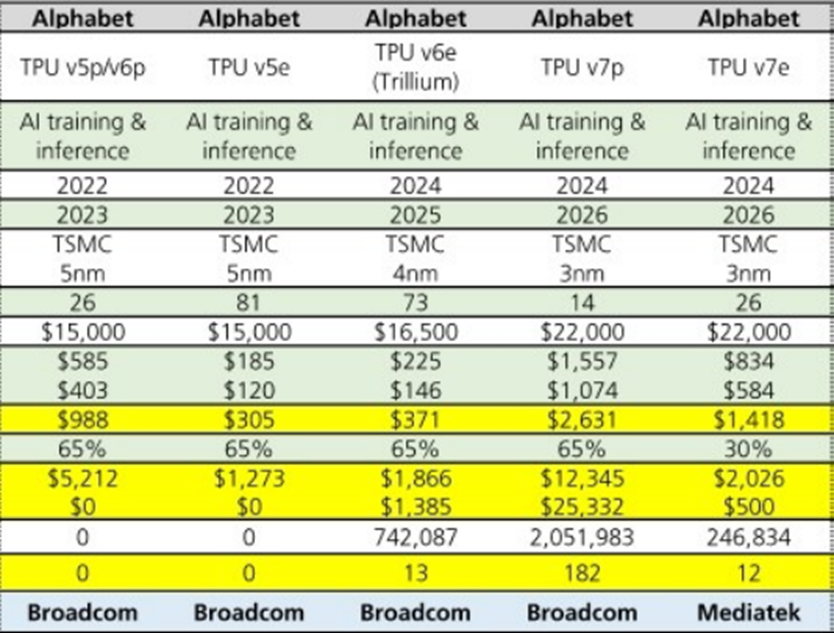
TPUs, with their energy efficiency advantages, have become the top choice for cloud providers' self-developed chips. TPU shipment growth is expected to exceed 40% in 2026. Additionally, reports suggest Meta is negotiating a multi-billion-dollar investment with Google to deploy TPUs for large-scale data center construction by 2027.
Brief Commentary:
From computing power (TPU) to model layers (Gemini, etc.), Google has established a full-stack advantage through deep hardware-software synergy. This comprehensive layout, spanning from foundational infrastructure to upper-layer model capabilities, solidifies its position at the AI pyramid's apex. Even as agent applications and other layers have yet to fully unfold, its profound technical reserves and ecosystem control set a deterministic foundation for future competition.








