BAIC and GAC Vie for L4-Level Autonomous Vehicle Commercialization with New Robotaxi Launches
![]() 01/28 2026
01/28 2026
![]() 349
349
As L4-level autonomous vehicles shift from test environments to urban roads, the collaboration between automakers and tech firms is sparking a transformation in intelligent transportation.
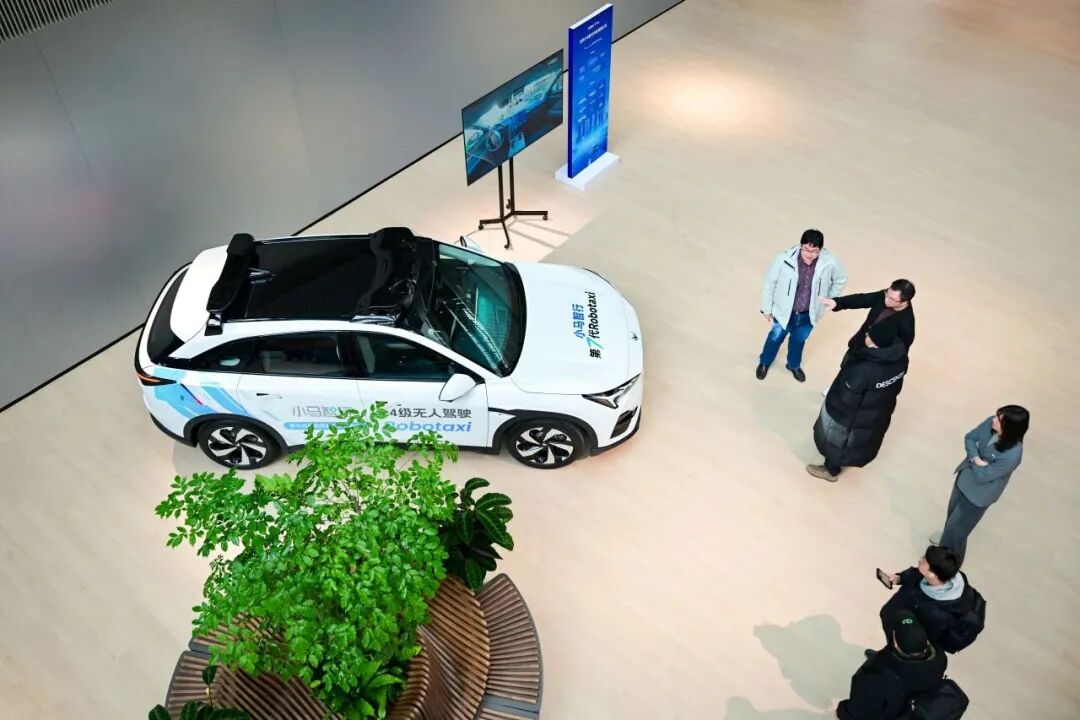

Recently, BAIC New Energy, in partnership with Pony.ai, and GAC Aion, collaborating with DiDi Autonomous Driving, have unveiled their latest Robotaxi models and ramped up their commercialization efforts. These alliances not only mark a new milestone in China's autonomous driving technology but also highlight two different business strategies and ecosystem approaches.
Technology vs. Redundancy Design: The Ultimate Clash
On January 10th, BAIC New Energy and Pony.ai announced at their Tech Day event that they had entered the 2.0 phase of their 'Five-in-One' strategic partnership, expanding their collaboration from a technical focus to encompass product development, market expansion, industry integration, ecosystem building, and capital alignment.
This advancement is built on the mass production of the ARCFOX Alpha T5 Robotaxi. Since establishing their technical partnership in November 2024, the two entities have delivered and deployed over 600 mass-produced vehicles, setting a new standard for Robotaxi cooperation.
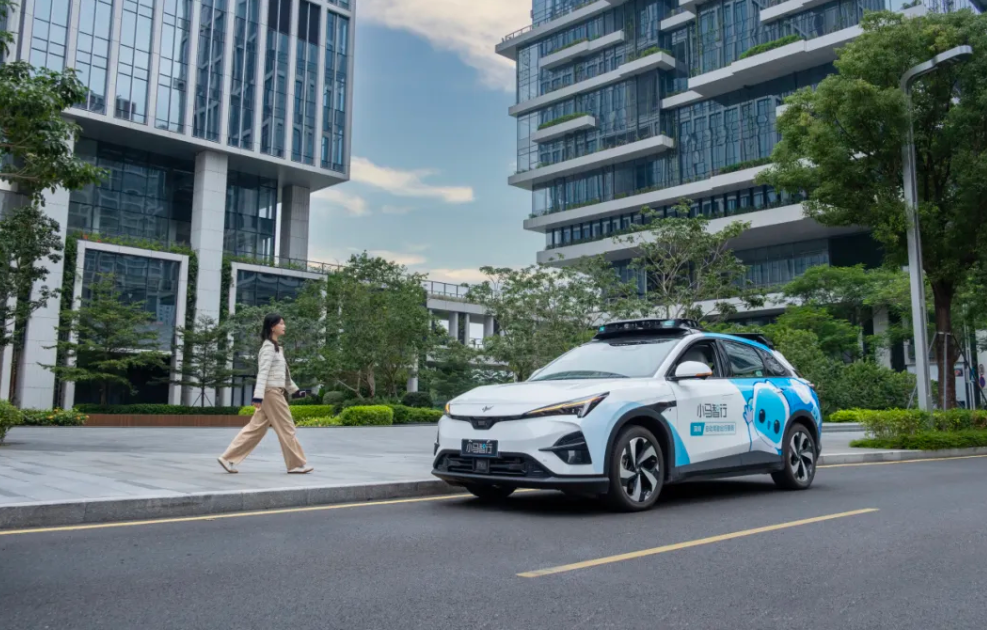

Just two weeks later, on January 23rd, the joint venture between GAC Aion and DiDi Autonomous Driving reached a key milestone. The new-generation Robotaxi, the R2 model, co-developed by the two, was officially launched at the GAC Aion factory, marking the first Robotaxi project in China to be driven by a joint venture between an automaker and an autonomous driving company.
The arrival of these two models signals that China's Robotaxi industry has reached a pivotal moment, transitioning from 'technical validation' to 'large-scale commercial deployment'.
A comparison of the technical features of the two Robotaxi models reveals both distinct differences and notable similarities in their design philosophies. The ARCFOX Alpha T5 Robotaxi is equipped with Pony.ai's seventh-generation automotive-grade autonomous driving system, featuring 9 LiDAR sensors, 14 cameras, and 4 millimeter-wave radars, enabling 360-degree, blind-spot-free perception.
The vehicle's standout feature is its redundancy design: 7 types of software redundancies, 7 types of hardware suite redundancies, 5 types of vehicle platform redundancies, and 3 types of service interaction redundancies, totaling over 20 layers of safety redundancies, complemented by more than 1,000 real-time monitoring points.
'We're not just adding hardware components; we're building a comprehensive, multi-layered safety net,' stated Zhang Ning, Vice President of Pony.ai and Head of Robotaxi Business, in an interview.
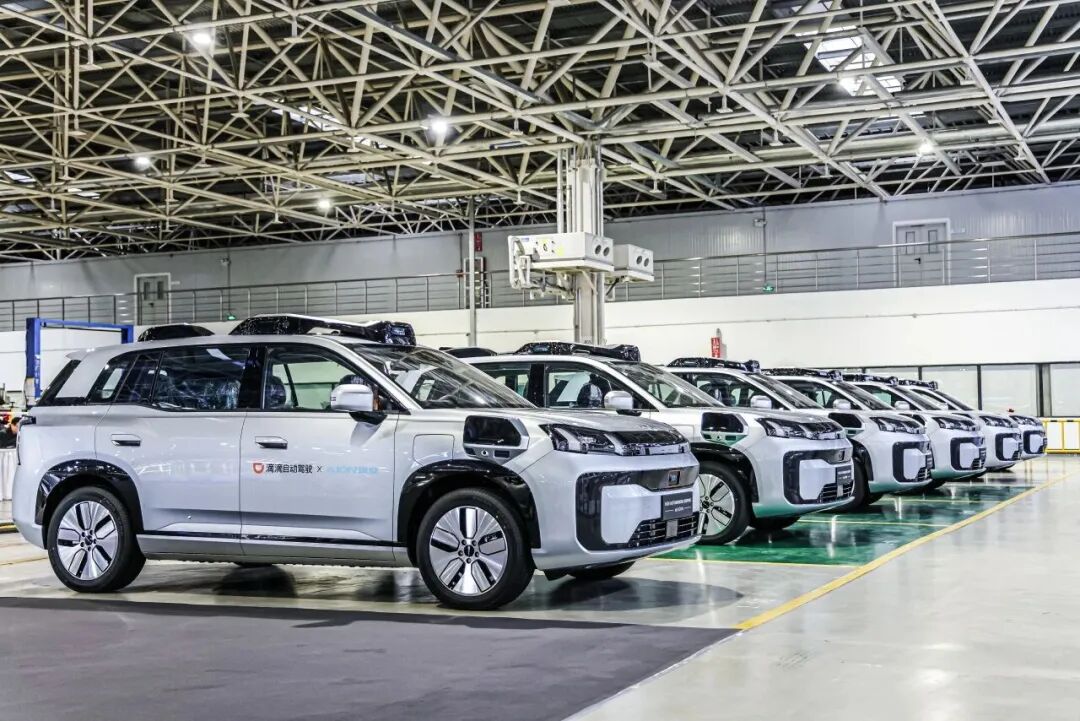

In contrast, the GAC Aion R2 follows a different technical approach, equipped with 33 high-precision sensors and the industry's first mass-produced three-domain integrated computing brain, boasting a computing power exceeding 2,000 TOPS. The vehicle also adheres to dual five-star safety standards for China and Europe, establishing a comprehensive safety redundancy system.
Notably, while significantly boosting performance, the R2 has achieved a 74% cost reduction, reflecting the partners' focus on cost efficiency for commercial operations. Balancing safety and cost has become a critical factor for the widespread adoption of Robotaxis.
Both vehicles are built on the mature electric platforms of their respective automakers: the ARCFOX T5 utilizes BAIC New Energy's fully redundant chassis architecture, while the R2 is based on GAC's GEP 3.0 platform and Xingling electronic and electrical architecture.
Ecosystem Collaboration vs. Joint Venture Innovation: Two Business Models
Beyond technical differences, the two collaboration projects also showcase distinct business models.
BAIC New Energy and Pony.ai have adopted a model of strategic deep integration. Starting with product collaboration, they have expanded into joint market development, shared industrial chains, ecosystem co-construction, and integrated capital, aiming to create a complete business ecosystem.
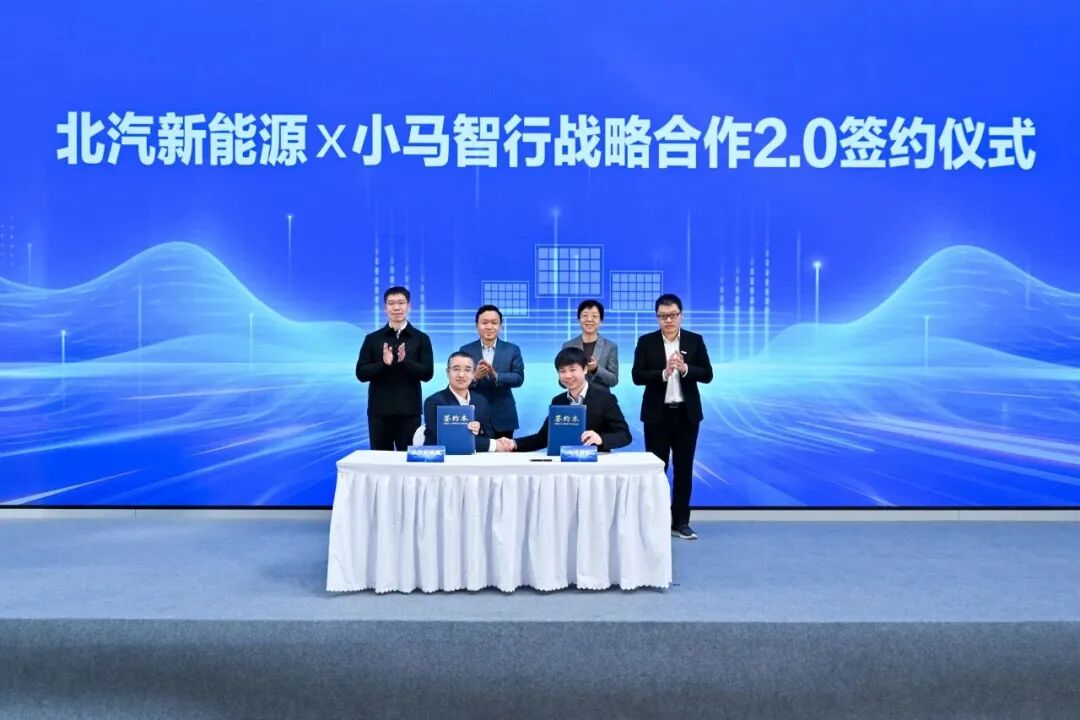

'This isn't just about producing a few hundred more vehicles; it's about building a complete ecosystem from technological R&D to commercial operations,' emphasized Zhang Guofu, Deputy General Manager of BAIC Group and Chairman of BAIC New Energy, at the Tech Day event.
In contrast, GAC Aion and DiDi Autonomous Driving have chosen a joint venture model, marking the first Robotaxi project in China to be driven by a joint venture between an automaker and an autonomous driving company. This model aligns the interests of both parties, enabling more efficient resource integration.
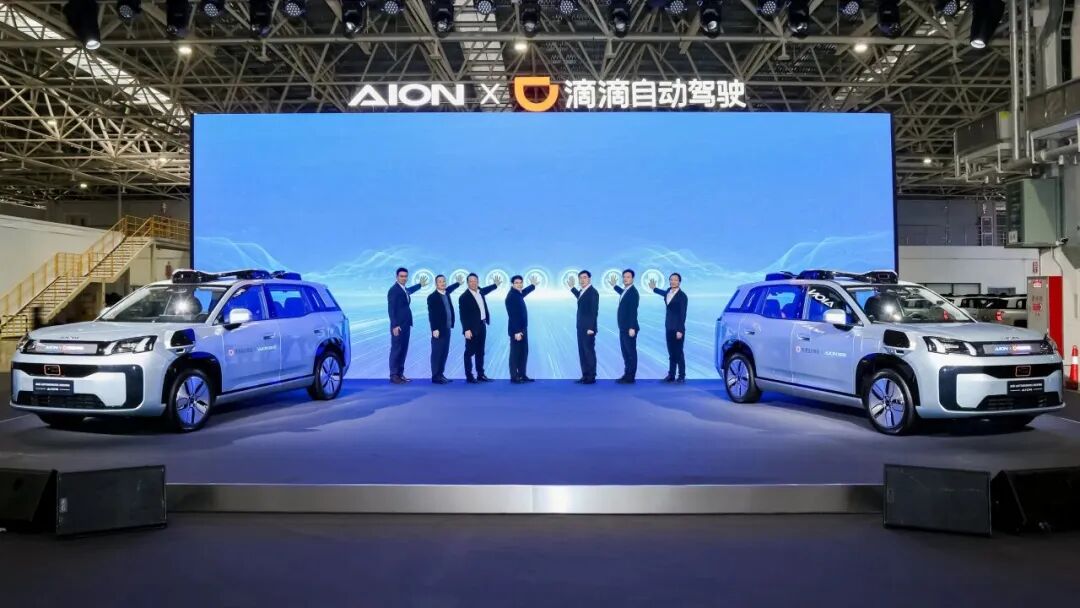

The R2 is designed to seamlessly integrate into DiDi's vast mobility network, achieving a full-link ecosystem from 'technological R&D to intelligent manufacturing to commercial operations.' DiDi's real-time mobility demand and scheduling capabilities are its greatest strengths.
Feng Xingya, Chairman of GAC Group, stated at the R2 launch ceremony, 'Both parties will fully leverage their complementary strengths in vehicle manufacturing, autonomous driving technology R&D, mobility ecosystems, and scenario operations.'
The two models have distinct focuses: the former emphasizes an open ecosystem and gradual expansion, while the latter pursues deep integration and efficient decision-making. This reflects the industry's diverse explorations for the optimal Robotaxi business model.
Core Competencies in the Robotaxi Sector
The progress of commercial operations is a key indicator of Robotaxi project maturity. In this regard, the BAIC-Pony.ai collaboration appears to be taking the lead.
Since November 2025, the ARCFOX Alpha T5 Robotaxi has been fully operational in core areas such as Yizhuang in Beijing and Nanshan and Bao'an districts in Shenzhen, covering airports, high-speed rail stations, commercial districts, and peak commuting hours. The large-scale deployment of over 600 vehicles provides a solid foundation for data accumulation and system iteration.
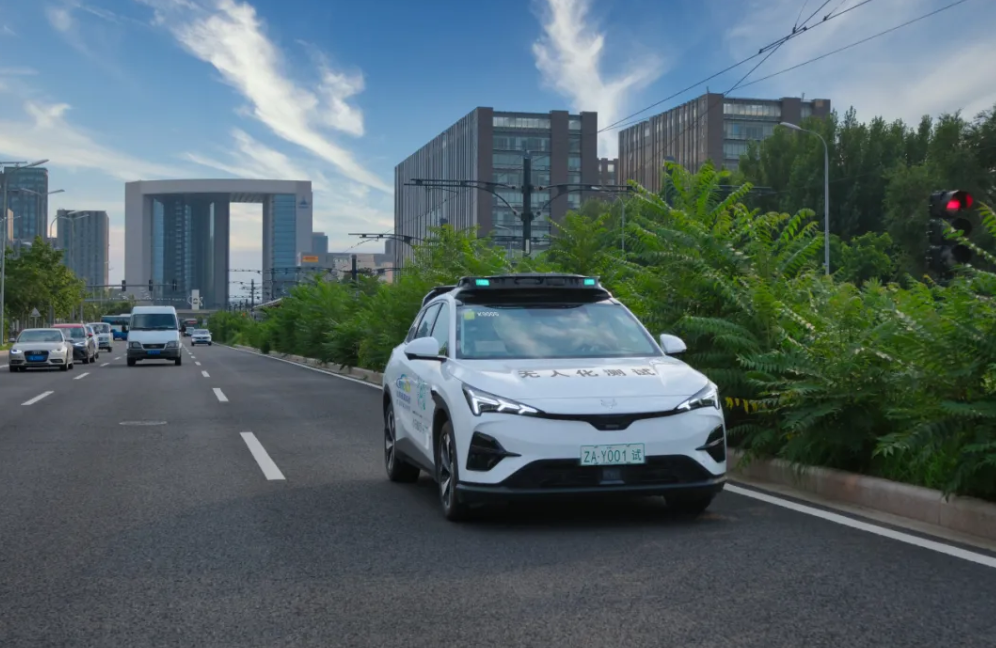

The R2 from GAC and DiDi has just obtained the road testing license for intelligent connected vehicles in Guangzhou and is currently in the road testing phase. However, according to their plans, by 2026, the R2 will be deployed in a phased and orderly manner for demonstration applications in cities such as Guangzhou and Beijing.
Both projects emphasize the importance of commercial operations but adopt different timelines. From these two collaborations, we can identify several core competencies in the Robotaxi field: technological maturity, cost control capabilities, commercial operation experience, and ecosystem construction.
The technological highlight of the ARCFOX Alpha T5 Robotaxi lies in its fully redundant design and over 20 layers of safety systems, reflecting an ultimate commitment to safety. Zhang Ning, Vice President of Pony.ai, stated, 'Safety is our top priority in all decisions.'
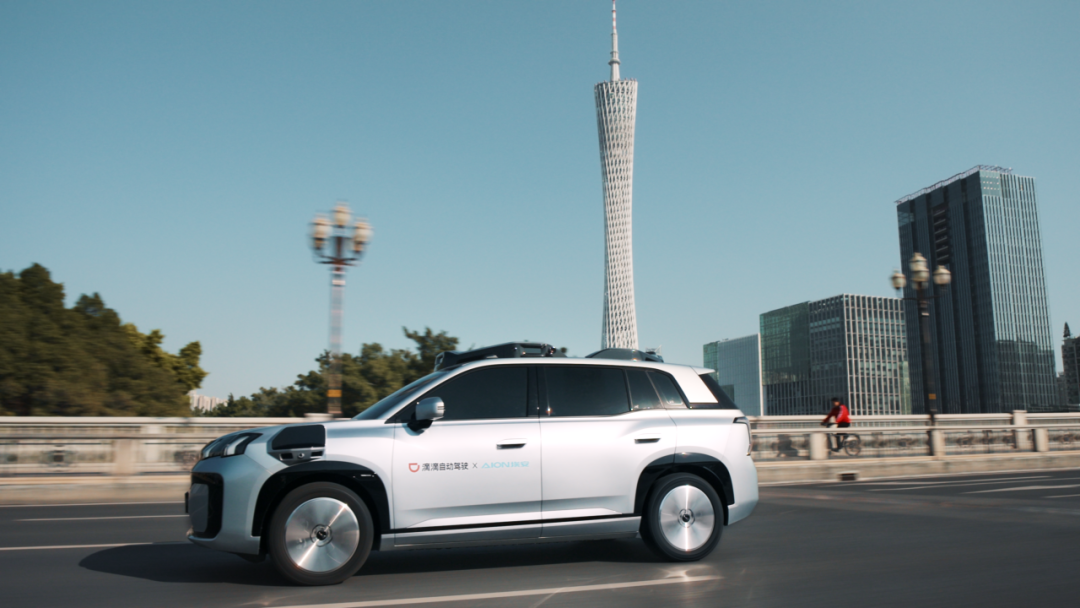

In contrast, the GAC Aion R2 demonstrates innovation in balancing cost control and performance. The 74% cost reduction breakthrough makes large-scale commercial deployment feasible. Additionally, the optimized rear passenger space and UV disinfection system, tailored for ride-sharing scenarios, reflect a deep understanding of shared mobility needs.
Industry analysts point out that the current competition in the Robotaxi sector has shifted from a pure technological race to a comprehensive competition encompassing technology, cost, operations, and ecosystem.
'The future winners will not only need advanced technology but also a sustainable business model and ecosystem,' said a representative from an autonomous driving research institution.
Meanwhile, both projects also focus on industrial ecosystem construction. BAIC New Energy has proposed a special initiative to 'supplement, build, stabilize, and upgrade' the industrial chain, aiming to cultivate a local cluster of intelligent mobility supply chains. In contrast, GAC and DiDi are exploring full vehicle lifecycle management, scenario expansion, and model iteration and upgrading. These initiatives indicate that leading companies have begun to strategize industrial ecosystems, enhancing their long-term competitiveness by constructing complete value chains.

In China's Robotaxi landscape, there is also an unavoidable player—Baidu's 'Apollo Go.' It is setting the pace and scale of autonomous driving commercialization through another model.
From Baidu Apollo Go's early lead to the alliances formed by BAIC-Pony.ai and GAC-DiDi in pursuit, the competition in China's Robotaxi sector is no longer centered around a single technological route but has evolved into a multi-dimensional competition of business models based on diverse strengths and resources. Consequently, automakers are also adopting a 'multi-pronged' strategy. For instance, Pony.ai has also collaborated with GAC Aion and Toyota to launch seventh-generation Robotaxi models based on vehicles from these two brands.
As more cities open up demonstration operations for autonomous driving in 2026, this mobility revolution jointly driven by automakers and tech firms will shape the future of intelligent transportation in China and beyond.