Break Free from Japanese Dominance! With 80% Market Share Monopolized by Sony, Can China's AIAR Smart Glasses Break Through the Japanese Supply Chain Barrier?
![]() 11/21 2025
11/21 2025
![]() 566
566
Smart glasses are heralded as the next pivotal human-machine interaction interface, drawing widespread attention from the global tech sector. Their application scenarios are continuously expanding, encompassing augmented reality, information prompts, medical assistance, and industrial uses.
Supporting this cutting-edge product is a complex, highly technical global supply chain. Notably, Japanese companies play pivotal roles in multiple key segments. While this deep dependency offers technological assurances, it also poses considerable industrial risks in today's complex and volatile landscape.
Today, let's delve into some significant Japanese enterprises operating in the upstream and downstream sectors of the smart glasses supply chain, aiming to provide insights and references.
Technical Core of the Visual System: Display and Optical Solutions
For smart glasses to seamlessly integrate digital information with the real world, their display systems and optical solutions represent the most technically demanding components. In this realm, certain companies have established significant technological advantages through long-term accumulation.
In the microdisplay sector, silicon-based OLED (Micro-OLED) is widely regarded as the most suitable display technology for high-end smart glasses. This technology enables high-resolution, high-contrast displays in extremely compact sizes while meeting stringent low-power requirements for devices.
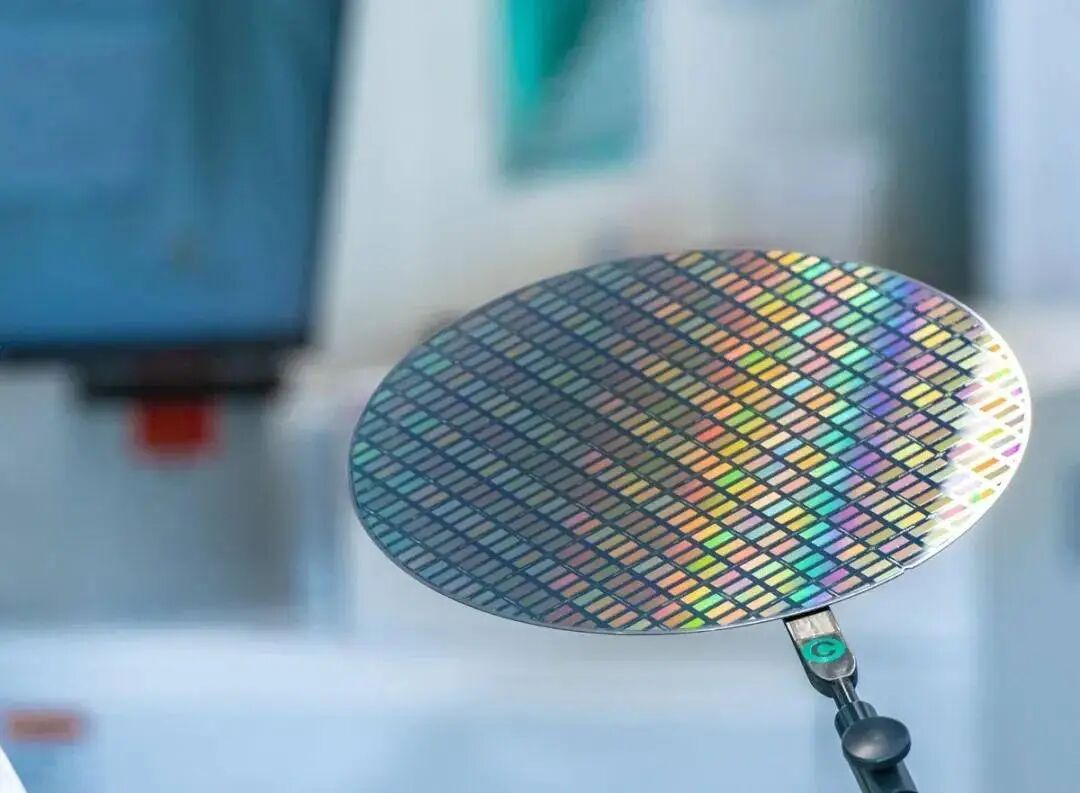

Sony has consistently led in this field, with its Micro-OLED displays widely adopted in smart glasses products due to their superior performance metrics. Leading domestic enterprises such as Rokid, Thunderbird Innovation, XREAL, and even Sony itself utilize Sony's Micro-OLED screens.
From the microdisplay industry chain perspective, Sony is undeniably the dominant force. By 2022, it accounted for over 60% of the global market share in shipments, with an even higher 80% share in VR/AR applications.
Optical solutions are equally critical—waveguide technology, as the current mainstream approach, enables large field-of-view displays with relatively thin lens forms. In recent years, Japanese AR display company Cellid has made significant breakthroughs in waveguides, emerging as a leader in the industry.
In November of the previous year, Cellid unveiled a verification model of AR glasses, showcasing their design philosophy and latest waveguide technology. Previously, they also launched several display modules, such as the 'Cellid Waveguide 60' featuring an ultra-compact Micro LED projector and an optical module with a 60-degree field of view. In terms of corporate development, Cellid's financing has progressed smoothly, providing greater support for sustained investment in core technology R&D.

In the lens segment, Mitsui Chemicals' resin lenses for AR glasses waveguides have garnered significant supply chain attention, capable of meeting the demands of multi-sized AR device modules.
Additionally, HOYA boasts deep technical accumulation in diffractive waveguide technology, with its optical components adopted by multiple smart glasses manufacturers. Ricoh Group focuses on R&D in surface relief waveguide technology, offering diverse solutions for varying product needs. Notably, Canon and Panasonic, leveraging their technical reserves in traditional optics, continue to invest in optical solutions like free-form curved surface prisms, providing more options for smart glasses' optical design.
Key Components of the Perception System: Sensors
For smart glasses to perceive environments and user states, various precision sensors are indispensable. In this field, certain Japanese companies play irreplaceable roles.
Sony's CMOS image sensors dominate the global market, widely used in smart glasses' camera modules. These sensors are crucial not only for traditional photography and videography but also for core augmented reality functions like gesture recognition, spatial positioning, and environmental understanding.

The Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is another critical component. With the further integration of AI and edge computing, IMUs, as core sensors, are undergoing technological innovation. Globally, TDK, STMicroelectronics, and Murata have each introduced high-performance new products.
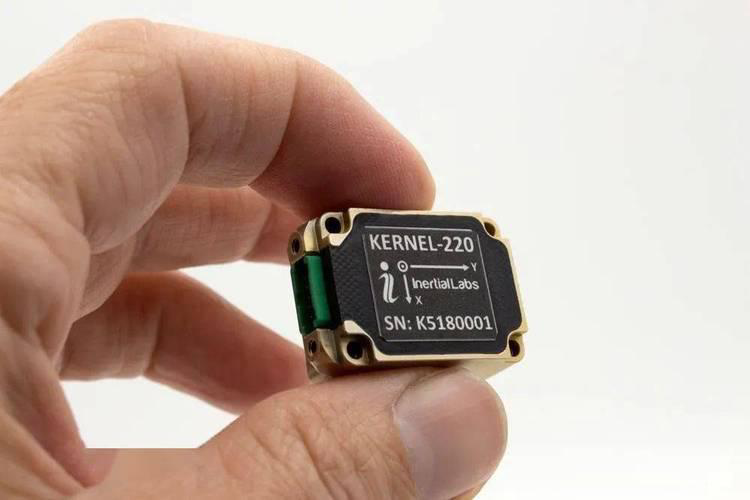

Among them, Murata Manufacturing and TDK's IMU modules integrate gyroscopes and accelerometers, enabling precise tracking of minute head movements. This is vital for maintaining stable virtual content display and preventing user dizziness.
At a more fundamental electronic component level, passive components like multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), inductors, and filters produced by Murata, TDK, and Taiyo Yuden, though seemingly insignificant, form the basis for stable device operation. These components are used in large quantities in smart glasses with high requirements, directly impacting the reliability and lifespan of the entire device.
Support System Assurance: From Batteries to Physical Structural Components
Beyond core display and perception systems, smart glasses' battery life, acoustic experience, and physical structure equally influence the final product experience.
Battery technology is one of the key factors restricting smart glasses' development. As a major global lithium battery supplier, Panasonic's high-energy-density, high-safety-standard pouch batteries provide basic assurance for smart glasses' battery life. As early as 2016, Panasonic developed small lithium-ion batteries specifically for smart glasses, which can be integrated into temple arms.

Achieving longer battery life within limited internal space requires balancing energy density and safety—exactly where Panasonic excels.
In acoustic systems, while original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) may handle overall assembly, Japanese companies like Foster Electric maintain technological advantages in micro-speakers.
Breaking Deep Dependency: The Rise of China's Supply Chain and Technological Fortifications
Despite foreign companies' significant positions in multiple key segments of smart glasses, China's supply chain is rapidly rising, forming an industrial landscape of competition and complementarity.
In the core display field, BOE has accumulated years of experience in OLED microdisplay technology, with its silicon-based OLED microdisplays achieving mass production and validation in multiple AR/VR devices. Sight Display Technologies also shows strong momentum in silicon-based OLED, continuously improving key indicators like brightness and power consumption in its products.

Shanghai MicroLED Display (JBD)'s MicroLED microdisplay technology holds a significant position in optical module fields, addressing bottlenecks in AR glasses mass production and becoming a key supply chain enterprise for domestic AR glasses. Lipin Optics is also a leading supplier of AR glasses waveguide modules, possessing core patents in geometric waveguides and exclusive molecular bonding processes, enabling it to supply top AR device brands and form strategic partnerships with multiple enterprises.

In optics, LetinAR has achieved breakthroughs in array waveguide technology, achieving mass production and application in multiple AR glasses models. HuiNiu Technology, as a first-tier supplier of domestic AR/VR optical solutions, provides new technological paths with breakthroughs in coaxial air-guided (CA) and Pancake technologies. Currently, it serves as Huawei's exclusive optical solution supplier for AR glasses and has deep collaborations with iQiyi, Deepoon, and other enterprises.
The rapid development of these companies is reshaping the original market landscape.
From a supply chain security perspective, this diversified landscape benefits device manufacturers. On one hand, continuous innovation by key foreign supply chains in critical technological areas provides crucial support for industry development. On the other hand, China's supply chain growth offers more options, helping to mitigate supply chain risks.
Meanwhile, China's supply chain possesses unique developmental advantages. A well-established electronic industry ecosystem, strong mass production capabilities, and rapid market responsiveness are all competitive strengths. With sustained increases in R&D investment by domestic companies, the technological gap with foreign giants is gradually narrowing.
Looking ahead, the development of the smart glasses industry chain will emphasize greater collaboration among companies. The technological advantages of foreign companies in basic materials and core components complement China's capabilities in mass manufacturing and system integration. This complementary pattern promotes technological advancement and cost optimization across the industry.
Conclusion
Currently, as the entire smart glasses market explodes, its industry chain is undergoing rapid development and transformation. While foreign companies maintain leading positions in certain key technological areas, China's supply chain progress is reshaping the original market landscape. This diversified supply chain system lays a more solid foundation for the sustainable development of the smart glasses industry.
Looking forward, with continuous technological advancements and market expansion, competition and cooperation among domestic and foreign companies in the smart glasses industry chain will intensify.
Constructing a secure, diversified, and efficient supply chain system is crucial for the steady development of the smart glasses industry. Only through global industry chain collaboration and innovation can this emerging tech product truly unleash its potential to transform human-machine interaction.
Written by / Qingyueling
All images in the text are sourced from the internet






