Qingdao introduces Internet giants, backed by the strongest "national team"
![]() 10/09 2024
10/09 2024
![]() 807
807
After the bubble burst, current Internet giants are seeking new growth points on brand-new tracks.
According to data from VG Insights, a foreign data analysis company, "Black Myth: Wukong" has sold 21 million copies on the Steam platform, with total revenue exceeding $1 billion.
Behind the popularity of "Black Myth: Wukong" lies a metaphor for the momentous changes in China's Internet industry:
The traditional Internet battleground represented by BAT is evolving into competitive fields with a more international perspective, such as gaming and cross-border e-commerce, which are more closely integrated with cultural soft power, overseas expansion of manufacturing, AI, virtual reality, and other emerging industries.
This is precisely where Qingdao, which has long lacked Internet companies, sees an opportunity.
For example, the current popular AI large-model generative video technology can deeply integrate with Qingdao's already established industrial film strengths on the one hand, and on the other hand, as AI real-time 3A game generation technology matures, it is expected to lead a revolution in 3A game production.
Taking this as a breakthrough, Qingdao can intensify efforts to attract more companies in the generative video production chain to gather in Qingdao. At the same time, these content production companies can not only continuously improve production standards for industrial films and 3A games but also interact with hardware and software fields such as virtual reality, integrated circuits, new displays, and AI, helping Qingdao's emerging industries gain momentum quickly.
At a time of tremendous change in the Internet industry, Qingdao's introduction of Internet giants in gaming and cross-border e-commerce has brought the strongest support.
In September this year, the Qingdao International Telecommunications Gateway (abbreviated as "Qingdao International Gateway") was launched. An international telecommunications gateway refers to an interconnection node between the communication networks of domestic telecom operators and those of foreign, Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan operators, mainly used to enable interconnectivity and data exchange between the two sides. In 1994, China established nine international telecommunications gateways in Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou for the first time.
Two months ago, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology organized a workshop on international telecommunications gateways and issued licenses to China Telecom, China Mobile, and China Unicom, approving the establishment of six international telecommunications gateways in Nanning, Guangxi; Qingdao, Shandong; Kunming, Yunnan; and Haikou, Hainan.
Among them, the Qingdao International Telecommunications Gateway is established by China Unicom.
Against the backdrop of intensifying global digital economic revolution and economic and trade cooperation entering a new stage, Qingdao's approval to establish an international telecommunications gateway is of great significance.
On the one hand, as the first new international telecommunications gateway established in the north in 30 years, the Qingdao International Gateway is largely intended to divert China Unicom's communication traffic to Japan, South Korea, and the Americas. Therefore, its establishment will further boost Qingdao, Shandong, and even the northern region in accelerating their integration into the new opening-up paradigm and strengthening cooperation with Japan, South Korea, and the Americas.
On the other hand, the Qingdao International Gateway enables Qingdao enterprises and users to directly connect to the international network without having to pass through other cities, significantly improving Qingdao's international telecommunications service quality. This, in turn, will attract large Internet companies and global companies to settle in Qingdao and surrounding areas, effectively promoting digital economy innovation and economic development.
It can be said that the establishment of the Qingdao International Gateway will bring new opportunities for the development of Qingdao's Internet and technology industries. Taking advantage of this to intensify efforts to attract Internet giants and actively develop new Internet formats such as gaming and cross-border e-commerce is a key focus for Qingdao.
1
Judging from the development of Internet giants in recent years, gaming and cross-border e-commerce are becoming new profit growth points.
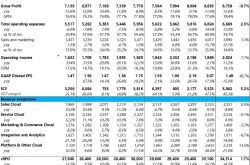
According to the first-half 2024 financial reports of various giants, Tencent, whose gaming business is virtually dominant, achieved a net profit of RMB 89.519 billion with a growth rate of 72.15% thanks to its high-margin value-added services (consisting of gaming and social networking businesses) with a gross margin of up to 57%.
Pinduoduo, one of the three major e-commerce players, has shown a remarkable growth momentum fueled by its cross-border e-commerce platform Temu. Its revenue reached RMB 183.9 billion, a year-on-year increase of 104.9%, and its operating profit reached RMB 58.338 billion, a year-on-year increase of 198.3%.
Specifically, Temu's sales in the first half of the year surged to US$20 billion, surpassing last year's full-year performance of US$18 billion. According to plans, Temu aims to achieve US$60 billion in sales this year, expected to account for 43% of Pinduoduo's total revenue.
As the strategic focus of giants shifts, traditional Internet powerhouses such as Hangzhou and Chengdu have also begun to change course. A new round of competition among cities for Internet giants has quietly begun.
For example, Chengdu, where the gaming and esports industry has developed rapidly in recent years, has gathered over 7,000 network gaming-related companies such as Tencent, Xishanju, Ubisoft, and Perfect World. The gaming industry and related sectors have generated revenue of RMB 60 billion, accounting for one-eighth of China's gaming industry revenue.
In Chengdu's gaming industry development, the popularity of "Honor of Kings" and its deep ties with Tencent are two landmark events.
In 2017, "Honor of Kings," produced by Tencent's Timi L1 Studio in Chengdu, swept the gaming market, propelling Chengdu to the status of the country's "fourth gaming city" and "mobile gaming capital."
Since then, Chengdu and Tencent have embarked on a series of close collaborations.
In January 2019, Tencent's cultural and creative brand TGC (Tencent Games Carnival) landed in Chengdu, and Tencent signed a strategic cooperation agreement with Chengdu High-tech Zone to jointly build a model area for digital cultural and creative cities.
In 2020, Tencent's first functional headquarters in China – Tencent NeoCulture Headquarters – was established in Chengdu, continuously promoting the layout of systematic "culture + technology" content such as animation, esports, and gaming in the city.
In 2022, Tencent's Future Center project was established in Chengdu, focusing on key areas such as cultural and technological innovation to jointly explore the construction of future technologies and scenarios such as the Metaverse.

Chengdu Denglinggu Digital Cultural and Creative Industry Base
Currently, Chengdu is actively deploying a new track for gaming exports.
At the 2024 Chengdu-Dubai Investment Cooperation Promotion Conference held on July 1, Chengdu enterprises such as Wofei Aerospace and AG Esports Group gathered in Dubai to promote cooperation and expand markets. AG Esports Group signed a strategic cooperation agreement with STE Esports Club. On August 19, at the Sino-German Game and Animation Industry Promotion and Exchange Meeting, Chengdu once again organized key enterprises in the gaming and animation sector to visit Frankfurt and signed a series of cooperation memorandums with German enterprises.
Another example is Hangzhou, the stronghold of NetEase Games, which has given birth to games such as "Identity V," "Jianghu," "Party Animals," "Naraka: Bladepoint," and "New Ghost Story Butterfly Lovers."
Apart from "NetEase-series" games, the recent phenomenally popular game "Black Myth: Wukong" was also born in Hangzhou and produced by Game Science, a company that arrived in Hangzhou six years ago.
Information shows that Game Science was established in Shenzhen earlier, with its main creative team all coming from Tencent. In 2018, the company decided to venture into single-player game development and began its "second startup" in Hangzhou.
Game Science's relocation to Hangzhou is inseparable from the city's superior development ecosystem for the gaming and animation industry.
It is understood that since 2005, Hangzhou has introduced six rounds of support policies for the animation industry. In the sixth round of support policies introduced in November 2022, Hangzhou aims to build an international animation capital and esports city and allocates RMB 100 million in special funds annually to support the deep integration and mutual promotion of the animation gaming and esports industries with related industries.

Yichuang Town, Xihu District, Hangzhou
Supported by "real money," Hangzhou's gaming industry has entered a fast lane. By the end of 2023, Hangzhou's animation and gaming output value had exceeded RMB 50 billion, forming two national animation industry bases in Hangzhou High-tech Zone's National Animation Industry Base and Hangzhou Digital Entertainment Industrial Park. The city has gathered 274 animation and gaming companies, including NetEase Games, Game Science, Dianhun Networks, and Bianfeng Networks.
Apart from Hangzhou and Chengdu, another city, Guangzhou, has set its sights on cross-border e-commerce.
As a traditional foreign trade powerhouse, Guangzhou has seized the opportunity of global foreign trade industry transformation and vigorously developed cross-border e-commerce based on the complete industrial chain in the Pearl River Delta. With a flexible supply chain system and continuous policy support, Guangzhou has developed into China's leading city in cross-border e-commerce.
In 2023, Guangzhou's cross-border e-commerce import and export volume reached RMB 200.465 billion, a 93-fold increase over eight years, with import scale ranking first nationwide for nine consecutive years.
Currently, among the four leading domestic cross-border e-commerce players, the headquarters of SHEIN and Temu are both located in Guangzhou. AliExpress's first cross-border e-commerce industrial park in southern China is also located in Jupai International Industrial Park, Panyu District, Guangzhou. Guangzhou's cross-border e-commerce industry demonstrates strong "magnetic attraction."
2
Turning to Qingdao, it also has advantages in developing new Internet formats such as cross-border e-commerce and gaming.
In terms of cross-border e-commerce, Qingdao, like Guangzhou, is a foreign trade powerhouse. On the one hand, its port logistics advantages are prominent, helping enterprises achieve "global sales." On the other hand, Qingdao boasts a solid manufacturing base, such as the eyelash industry in Pingdu, the hat industry in Jiaozhou, the garment industry in Jimo, and the Hanfu industry in Caoxian Province, which are well-suited for cross-border trade and have vigorous export demand.
Just as SHEIN helped 34,000 garment enterprises in Guangzhou's Panyu District achieve high-quality exports through its "on-demand production and quick response to small orders" digital flexible supply chain model, Qingdao's advantageous industries have also undergone transformation through cross-border e-commerce.
Among them, Pingdu, as the world's largest production base for beauty eyelashes, accounts for 70% of global production.
To promote the development of the eyelash industry's cross-border e-commerce business, Pingdu accelerates the interconnection between upstream raw material production, midstream processing and manufacturing, and downstream e-commerce sales, driving industrial upgrading. Currently, Pingdu can design and produce over 3,000 different styles of eyelashes, with thousands of boxes of "Made in Pingdu" eyelashes shipped across the globe every day.
The hat industry in Jiaozhou and the garment industry in Jimo have attracted the attention and cooperation of SHEIN and TikTok.
Not long ago, SHEIN and TikTok held matchmaking meetings in Qingdao, with SHEIN holding a matchmaking meeting for the baseball cap industry belt in Jiaozhou and TikTok holding one for the women's wear industry belt in Jimo, joining hands with high-quality enterprises to explore overseas markets.
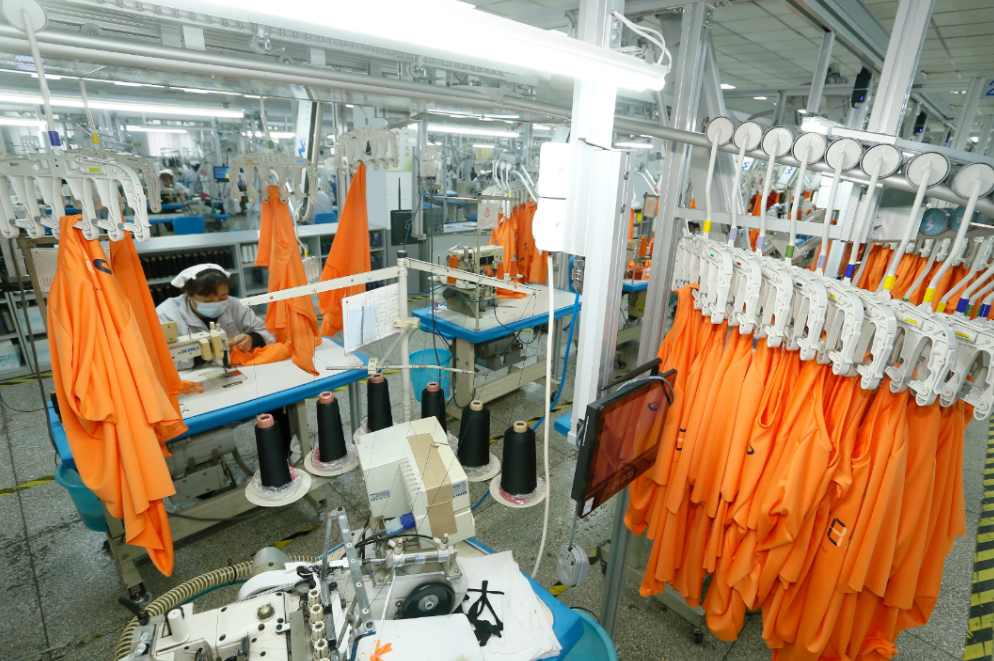

Jifa Group workers rush to produce products for export
In terms of the gaming industry, Qingdao is vigorously developing the virtual reality industry and cultural film industry, which are upstream and downstream sectors of the gaming industry, demonstrating prominent industrial linkage effects.
For example, the integration of the gaming industry and Qingdao's film and cultural industry can help gaming companies reduce R&D and production costs and accelerate industrial agglomeration, promoting the development of Qingdao's entire digital cultural and creative sector.
Furthermore, the combination of gaming and intelligent hardware such as VR devices will further strengthen Qingdao's virtual reality industry.
Currently, relying on Goertek's layout, Shandong accounts for over 80% of global shipments of mid-to-high-end VR headsets. With the successive commissioning of major projects such as the first phase of the Qingdao Microelectronics Industrial Park and Qingdao's virtual reality complete machines and optical modules, Shandong's advantages in virtual reality intelligent hardware manufacturing will be further consolidated.
As the most common content application for VR devices, the demand for game product R&D and production will continue to grow, offering ample opportunities for Qingdao to develop its gaming industry.
It is worth mentioning that Goertek has already collaborated with gaming companies.
In 2022, Goertek teamed up with two major gaming companies, miHoYo and 37 Interactive Entertainment, to establish a RMB 556 million venture capital fund in Qingdao, hailed as a "powerful alliance between intelligent hardware manufacturing and game content production."

With a superior industrial base, the establishment of the Qingdao International Telecommunications Gateway will give wings to Qingdao's cross-border e-commerce and gaming industries.
In particular, Qingdao's network latency will be significantly reduced, which is a significant boon for the development of esports, cross-border e-commerce, and even the digital transformation of the entire industry.
According to estimates, after the establishment of the Qingdao International Gateway, the communication transmission distance between Qingdao and Japan and South Korea will be reduced by about 1,600 kilometers, and network latency will be reduced by about 20 milliseconds.
What does this mean?
Taking the popular esports events of recent years as an example, it is estimated that the requirement for network latency in esports events is within 5-20 milliseconds.
In other words, the 20-millisecond reduction in network latency between Qingdao and Japan and South Korea means that Qingdao will have stable network support for hosting international esports events in the future.
Furthermore, reduced network latency in cross-border e-commerce operations will further enhance operational efficiency, facilitate trade with countries worldwide, and optimize user experience.
3
For Qingdao to truly strengthen its cross-border e-commerce and gaming industries, it must pay particular attention to the cultivation and introduction of relevant talent, in addition to relying on its industrial base and national strategic support.
Take Chengdu as an example. It boasts universities such as the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Southwest Jiaotong University, and Chengdu Dongruan College, which are closely integrated with its gaming industry, providing a steady stream of talent resources for industrial development.
A powerful piece of evidence is that the main members of Chengdu Timi L1 Studio, which developed "Honor of Kings," come from universities in Chengdu, such as Sichuan University, the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, and Southwest Jiaotong University.
Currently, Chengdu is also attracting talent through the hosting of esports events.
At the Chengdu 2023-2024 World Esports Event Launch Conference held in November last year, Chengdu announced five major events, including the 2023 Arena of Valor World Cup and the 2023 CrossFire World Finals (CFS), and announced their landing in Chengdu.

According to the planning of Chengdu High-tech Zone, it will promote the construction of a world-class esports industry base with high-end and intensive events, the gathering of leading enterprises, leading technological equipment, a rich industrial ecosystem, and a pool of professional talent by hosting world-class esports events, nurturing leading esports enterprises, planning and building landmark esports venues, and supporting the healthy development of esports talent.
As the Internet enters its second half, integration with manufacturing has become the key direction for future Internet industry development. In addition to focusing on new formats such as cross-border e-commerce and gaming, Qingdao must also introduce relevant upstream and downstream Internet companies to support key development industries such as smart home appliances, new energy vehicles, virtual reality, integrated circuits, and film and culture.
For example, as Internet giants like Huawei and Xiaomi have entered the automotive industry, the new energy vehicle industry is accelerating its iteration from electrification to intelligence.
For Qingdao, which is eager to make new breakthroughs in the new energy vehicle industry, it is also necessary to introduce companies related to smart cockpits, intelligent networking, and autonomous driving and cultivate new growth in the new energy vehicle sector.
From a longer-term perspective, the introduction of these hard technology enterprises will also force Qingdao to strive for more high-end models and key industrial chain resources to land, thereby increasing the added value of the new energy vehicle industry and promoting the optimization and strengthening of the industry.